Recombinant Human CDC37 protein(Met1-Val378), GST-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CDC37-3072H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CDC37 (NP_008996.1) (Met 1-Val 378) was expressed in Insect Cells, fused with the GST tag at the C-terminus. |
| Availability | April 20, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Insect Cells |
| Tag : | GST |
| Protein Length : | Met1-Val378 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 0.5mM GSH, 0.5mM PMSF, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human CDC37/GST chimera consists of 603 amino acids and has a predicted a molecular mass of 70.7 kDa as estimated in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | CDC37 cell division cycle 37 homolog (S. cerevisiae) [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CDC37 |
| Synonyms | CDC37; cell division cycle 37 homolog (S. cerevisiae); CDC37 (cell division cycle 37, S. cerevisiae, homolog) , CDC37 cell division cycle 37 homolog (S. cerevisiae); hsp90 co-chaperone Cdc37; CDC37 (cell division cycle 37; S. cerevisiae; homolog); CDC37 cell division cycle 37 homolog; Hsp90 co chaperone Cdc37; P50CDC37; hsp90 chaperone protein kinase-targeting subunit; CDC37 (cell division cycle 37, S. cerevisiae, homolog); |
| Gene ID | 11140 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_007065 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_008996 |
| MIM | 605065 |
| UniProt ID | Q16543 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CDC37-555H | Recombinant Human CDC37 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CDC37-3124H | Recombinant Human CDC37 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CDC37-2013HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human CDC37 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CDC37-1275R | Recombinant Rat CDC37 Protein | +Inquiry |
| CDC37-6260C | Recombinant Chicken CDC37 | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CDC37-001MCL | Recombinant Mouse CDC37 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| CDC37-648HCL | Recombinant Human CDC37 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Li K, et al. Andrology. 2021
Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is involved in protein changes during sperm capacitation, but the details aren't well understood. This study looked into how Hsp90 interacts with its partner protein, Cdc37, in human sperm. It was found that Hsp90 pairs up with Cdc37. During sperm capacitation, inhibitors like H-89 and Go6983 reduced Hsp90’s phosphorylation on certain amino acids. Additionally, using 17-AAG lowered the phosphorylation at a key Src protein site and decreased threonine phosphorylation levels with both 17-AAG and geldanamycin. This suggests a complex role of Hsp90 in human sperm capacitation.
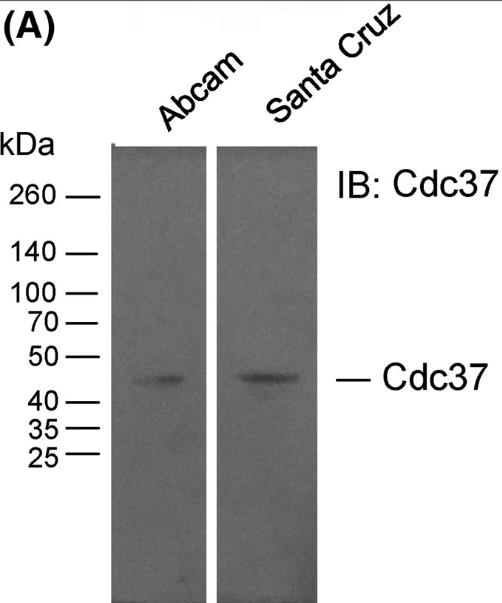
Fig1. Immunoblot analysis of the Cdc37 protein in human spermatozoa.
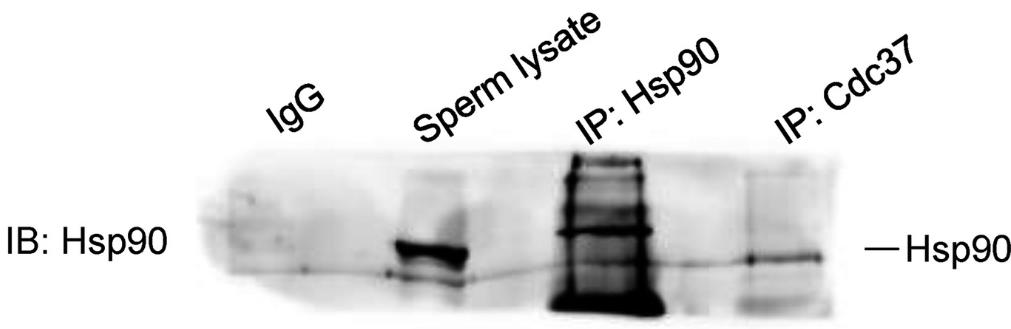
Fig2. Hsp90 detection in sperm lysate by immunoblotting (IB) and immunoprecipitation (IP) of 350 µg total protein with antibodies against Hsp90 and Cdc37.
Case 2: Liu W, et al. Biochemistry. 2015
Protein kinases need chaperones to fold properly, and in higher organisms, CDC37 helps guide them to HSP90. This process involves CDC37’s unstructured N-terminal domain, which undergoes a change when phosphorylated at Ser13 by CK2, shifting CDC37 into a more compact form. This change is not due to the phosphate group itself but happens because Ser13 loses its original traits. The N-terminal tail seems to act as an internal chaperone for CDC37, helping it switch states and influencing how it binds clients and interacts with HSP90.
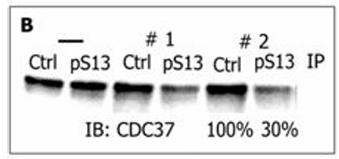
Fig1. Estimate of phosphorylation efficiency of endogenous CDC37 in MCF7 cells.
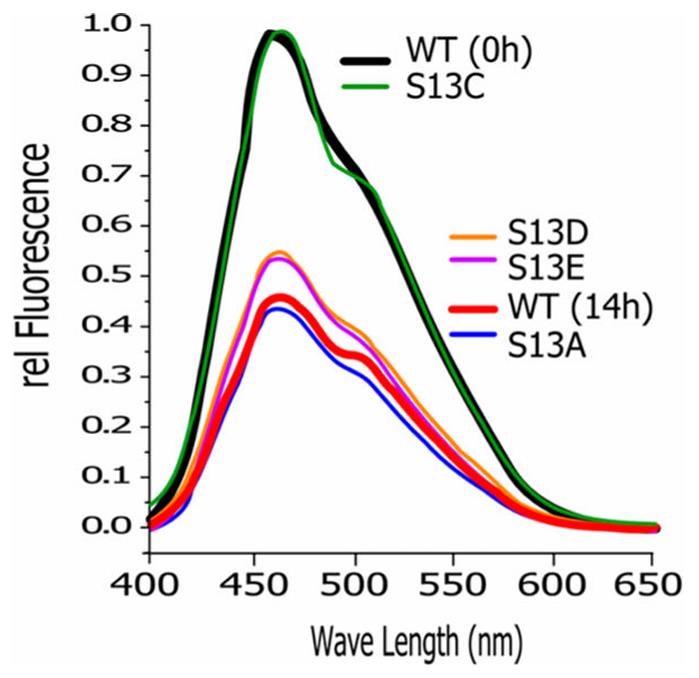
Fig2. Increase in compactness requires the removal of Ser-like properties.
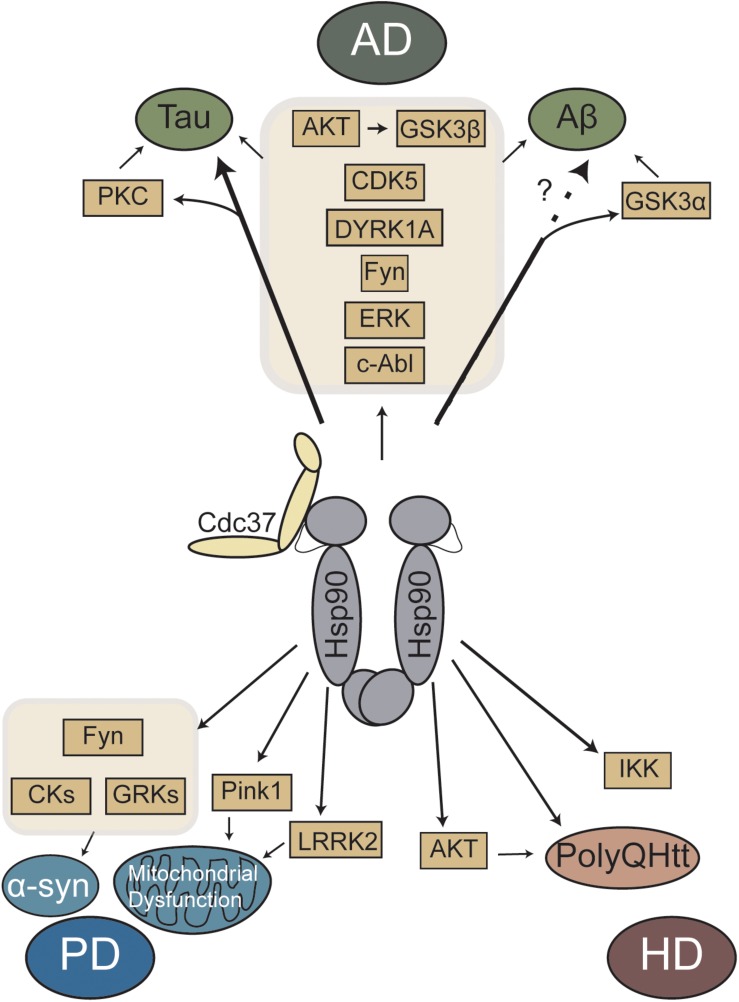
Fig1. Schematic representation of Hsp90/Cdc37 regulated major kinases and proteins linked to neurodegenerative diseases. (Liam Gracia, 2019)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CDC37 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CDC37 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


