Recombinant Human CCR3 Protein
| Cat.No. : | CCR3-0690H |
| Product Overview : | Human CCR3 full-length ORF (NP_001828.1) recombinant protein without tag. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Wheat Germ |
| Tag : | Non |
| Description : | The protein encoded by this gene is a receptor for C-C type chemokines. It belongs to family 1 of the G protein-coupled receptors. This receptor binds and responds to a variety of chemokines, including eotaxin (CCL11), eotaxin-3 (CCL26), MCP-3 (CCL7), MCP-4 (CCL13), and RANTES (CCL5). It is highly expressed in eosinophils and basophils, and is also detected in TH1 and TH2 cells, as well as in airway epithelial cells. This receptor may contribute to the accumulation and activation of eosinophils and other inflammatory cells in the allergic airway. It is also known to be an entry co-receptor for HIV-1. This gene and seven other chemokine receptor genes form a chemokine receptor gene cluster on the chromosomal region 3p21. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009] |
| Form : | Liquid |
| Molecular Mass : | 41 kDa |
| AA Sequence : | MTTSLDTVETFGTTSYYDDVGLLCEKADTRALMAQFVPPLYSLVFTVGLLGNVVVVMILIKYRRLRIMTNIYLLNLAISDLLFLVTLPFWIHYVRGHNWVFGHGMCKLLSGFYHTGLYSEIFFIILLTIDRYLAIVHAVFALRARTVTFGVITSIVTWGLAVLAALPEFIFYETEELFEETLCSALYPEDTVYSWRHFHTLRMTIFCLVLPLLVMAICYTGIIKTLLRCPSKKKYKAIRLIFVIMAVFFIFWTPYNVAILLSSYQSILFGNDCERSKHLDLVMLVTEVIAYSHCCMNPVIYAFVGERFRKYLRHFFHRHLLMHLGRYIPFLPSEKLERTSSVSPSTAEPELSIVF |
| Applications : | Antibody Production Functional Study Compound Screening |
| Usage : | Heating may cause protein aggregation. Please do not heat this product before electrophoresis. |
| Storage : | Store at -80 centigrade. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Storage Buffer : | 25 mM Tris-HCl of pH8.0 containing 2% glycerol. |
| Gene Name | CCR3 chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 3 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CCR3 |
| Synonyms | CCR3; chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 3; CMKBR3; C-C chemokine receptor type 3; CC CKR 3; CD193; CKR3; CCR-3; C-C CKR-3; b-chemokine receptor; CC chemokine receptor 3; eosinophil eotaxin receptor; eosinophil CC chemokine receptor 3; CC-CKR-3; MGC102841; |
| Gene ID | 1232 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001164680 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001158152 |
| MIM | 601268 |
| UniProt ID | P51677 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| RFL16676CF | Recombinant Full Length Dog C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 3(Ccr3) Protein, His-Tagged | +Inquiry |
| CCR3-0691H | Recombinant Human CCR3 Protein, GST-Tagged | +Inquiry |
| CCR3-3015M | Recombinant Mouse CCR3 Protein | +Inquiry |
| CCR3-0690H | Recombinant Human CCR3 Protein | +Inquiry |
| RFL9135MF | Recombinant Full Length Macaca Fascicularis C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 3(Ccr3) Protein, His-Tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CCR3-7694HCL | Recombinant Human CCR3 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Liu X, et al. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2017
Fibroblast-like synoviocyte (FLS) invasion in synovium appears one of the features of OA, but expression and function of CCR3 on FLS remain uninvestigated. This study explored it. Enzymatically dispersed synovial tissue cells were analyzed by flowcytometry. Primary cultured FLS isolated from OA synovium were challenged and the expression of CCR3, eotaxin-1 and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 was determined by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) and ELISA. Approximately 4.5% dispersed OA synovial tissue cells are CCR3+ cells. Eotaxin-1 induced up to 5.8 and 7.2-fold increases in the expression of MMP-9 mRNA and protein, respectively following 12h incubation with FLS, which was inhibited by antagonist of CCR3 SB328437 and an inhibitor of ERK U0126, indicating that action of eotaxin-1 on FLS seemed via CCR3 and ERK signaling pathway.
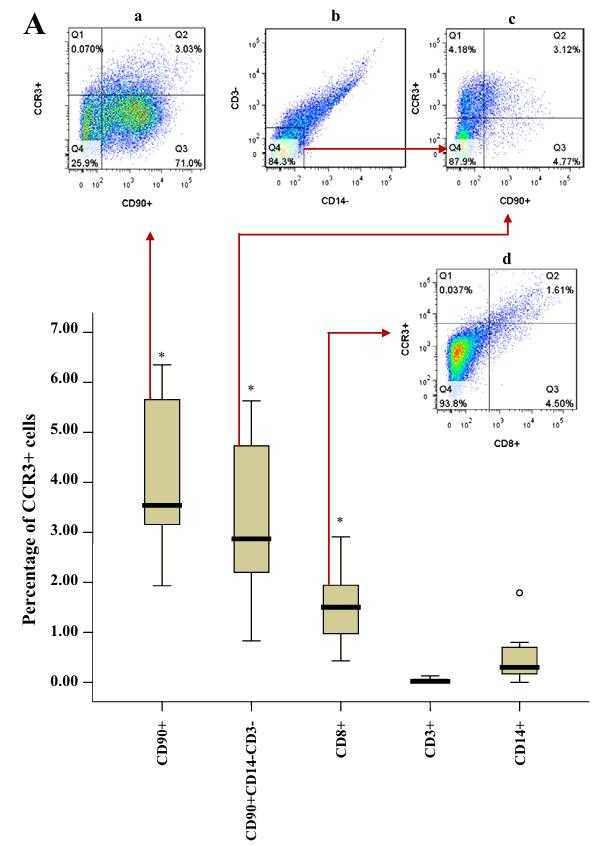
Fig1. Percentage of CCR3+ cell populations from total dispersed synovial tissue cells.
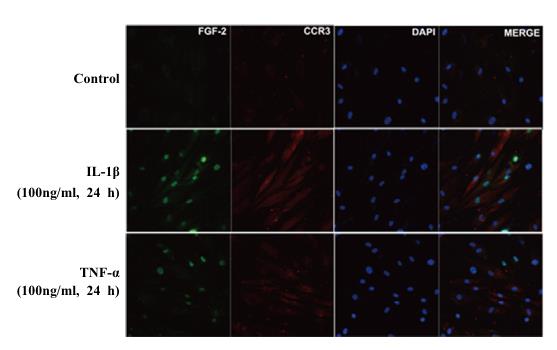
Fig2. Expression of CCR3 in human FLS.
Case 2: Khanolkar A, et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2013
Recent reports have provided conflicting evidence on the stability of CCR3 expression on the surface of basophils. This study aimed to independently evaluate the diagnostic usefulness of CCR3 as a surrogate marker of basophil activation and function. Researchers examined the correlative relationship between CCR3 expression on the surface of donor basophils and histamine release after donor basophils were treated with agonistic antibodies directed against the high-affinity IgE-Fc receptor and serum samples from 80 individuals displaying symptoms of chronic urticaria (CU). The results showed that CCR3 was significantly downregulated on donor basophils treated with the agonistic antibody. CCR3 downregulation was also observed on donor basophils incubated with more than 40% of CU-patient serum samples with HRA scores less than or equal to 10.
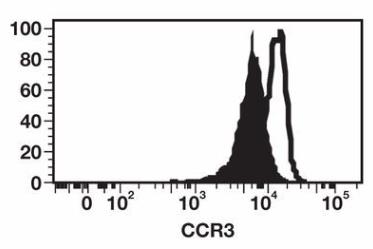
Fig1. Representative histograms depict CCR3 expression patterns on the surface of basophils.
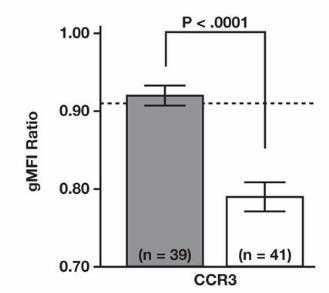
Fig2. Bar graphs depict the fold change in MFI (gMFI ratio) for CCR3 on donor basophils.
Recombinant Human CCR3 Protein refers to the laboratory-produced version of the CCR3 receptor, a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) found on the surface of various immune cells, including eosinophils, basophils, and some T cells and monocytes. CCR3 is involved in immune cell signaling and plays a significant role in allergic diseases, asthma, and potentially in neurodegenerative conditions.
The CCR3 receptor binds to multiple chemokines, including eotaxin (CCL11), RANTES (CCL5), and MCP-4 (CCL13), which are crucial in the recruitment of immune cells to sites of inflammation. In the context of medical research, recombinant CCR3 is used to study the interaction between these chemokines and the receptor, which can lead to a better understanding of immune cell trafficking and the development of new therapeutic strategies for diseases involving immune dysregulation.
In terms of practical applications, recombinant CCR3 protein is valuable for drug discovery, particularly in the development of small molecule antagonists or monoclonal antibodies that can modulate its activity. By targeting CCR3, it may be possible to reduce eosinophilic inflammation, which is a feature of allergic rhinitis and asthma. In fact, studies have shown that inhibiting CCR3 can reduce nasal symptoms and pathological changes in animal models of allergic rhinitis. Furthermore, CCR3 has been implicated in age-related cognitive changes and T-cell infiltration into the brain, suggesting potential therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative diseases as well.
In summary, recombinant Human CCR3 Protein is a key tool in immune system research and drug development, with implications for treating a range of conditions from allergic diseases to potential neurological applications.
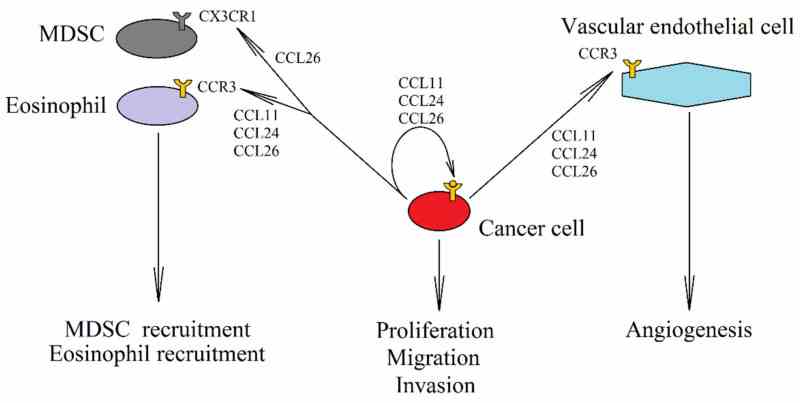
Fig1. The role of eotaxins in cancer. (Jan Korbecki, 2020)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CCR3 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CCR3 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


