Recombinant Human CCL13 protein(Gln24-Thr98), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CCL13-241H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CCL13 (NP_005399.1) (Gln24-Thr98) was expressed in Yeast with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Yeast |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | Gln24-Thr98 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human CCL13 consists of 85 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 10 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 14 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Purity : | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | CCL13 chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 13 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CCL13 |
| Synonyms | CCL13; chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 13; SCYA13, small inducible cytokine subfamily A (Cys Cys), member 13; C-C motif chemokine 13; CKb10; MCP 4; MGC17134; NCC 1; SCYL1; CK-beta-10; new CC chemokine 1; small-inducible cytokine A13; monocyte chemotactic protein 4; monocyte chemoattractant protein 4; small inducible cytokine subfamily A (Cys-Cys), member 13; NCC1; MCP-4; NCC-1; SCYA13; |
| Gene ID | 6357 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_005408 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_005399 |
| MIM | 601391 |
| UniProt ID | Q99616 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CCL13-277H | Active Recombinant Human Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 13, HIgG1 Fc-tagged, mutant | +Inquiry |
| CCL13-241H | Recombinant Human CCL13 protein(Gln24-Thr98), His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CCL13-09H | Recombinant Human CCL13 Protein | +Inquiry |
| CCL13-73H | Recombinant Human CCL13 Protein | +Inquiry |
| CCL13-151H | Recombinant Human CCL13 Protein, DYKDDDDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CCL13-7734HCL | Recombinant Human CCL13 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Fang C, et al. Can Respir J. 2023
This study explored how MCP-4 and eotaxin-3 are involved in COPD. We found these proteins were higher in patients, especially during acute exacerbations. They effectively distinguished between different stages of COPD and healthy controls. Their levels also rose when cells were exposed to LPS, a COPD risk factor. These findings suggest MCP-4 and eotaxin-3 could be key markers for better diagnosing and treating COPD, especially by targeting specific receptors involved in the disease.
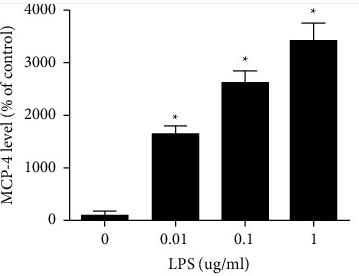
Fig1. Expression of MCP-4 in culture medium of HBEs was increased after the treatment with LPS.
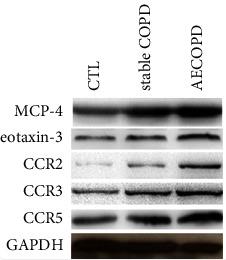
Fig2. Protein levels of MCP-4, eotaxin-3, and CCR2, 3, and 5 were examined in COPD and normal samples.
Case 2: Liang H, et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2024
Estrogen is linked to ovarian cancer, and our research shows it increases lncRNA SNHG17, a molecule that promotes cancer progression. SNHG17 helps activate M2 macrophages and facilitates cancer growth and spread by releasing CCL13 through the PI3K-Akt pathway. This process, driven by estrogen, suggests SNHG17 could be a marker and therapeutic target for treating ovarian cancer influenced by estrogen.
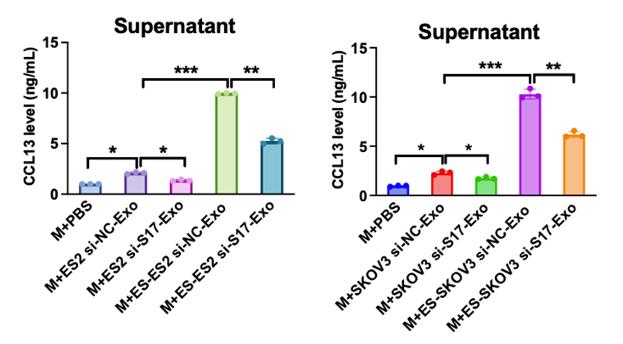
Fig1. CCL13 content was measured in the supernatant from macrophages incubated with exosomes.
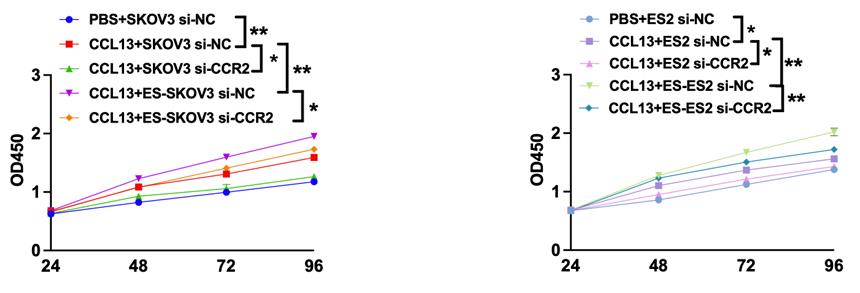
Fig2. Cell proliferation treated with CCL13 recombination protein.
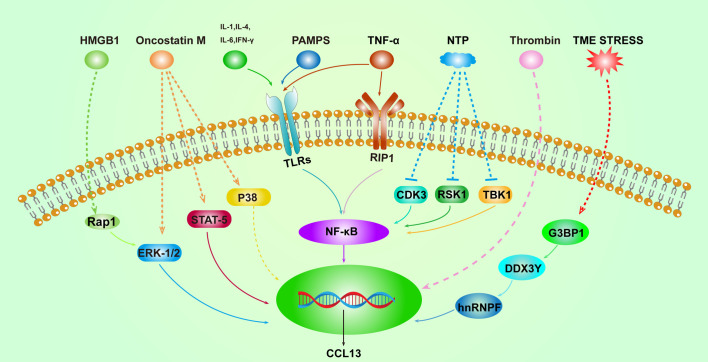
Fig1. Overview of the activation pathways of CCL13. (Laifu Li, 2023)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CCL13 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CCL13 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


