Recombinant Human CASP14 Protein, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CASP14-1168H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CASP14 Protein(NP_036246.1) (Ser 2-Gln 242) was expressed in E. coli, with a polyhistide tag at the N-terminus. |
| Availability | April 19, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | Ser 2-Gln 242 |
| Tag : | N-His |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human CASP14 consisting of 248 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 28.5 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 30 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Purity : | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | CASP14 caspase 14, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CASP14 |
| Synonyms | CASP14; caspase 14, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase; caspase 14, apoptosis related cysteine protease; caspase-14; apoptosis related cysteine protease; MGC119078; MGC119079; MICE; CASP-14; apoptosis-related cysteine protease; caspase 14, apoptosis-related cysteine protease; |
| Gene ID | 23581 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_012114 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_036246 |
| MIM | 605848 |
| UniProt ID | P31944 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CASP14-2750M | Recombinant Mouse CASP14 Protein | +Inquiry |
| CASP14-2925HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CASP14 Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CASP14-3637H | Recombinant Human CASP14 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CASP14-0853H | Recombinant Human CASP14 Protein (Met1-Gln242), N-His tagged | +Inquiry |
| Casp14-690M | Recombinant Mouse Casp14 Protein, His/GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CASP14-145HCL | Recombinant Human CASP14 lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Al-Shabrawey M, et al. Mol Vis. 2012
The study examined caspase-14 levels in the retina under normal and diabetic conditions to understand its role in high glucose-induced cell death. Using PCR and western blot, researchers found caspase-14 in various retinal cells, with diabetic retinopathy increasing its levels, especially in blood vessels. High glucose elevated caspase-14, resulting in higher cell death and increased cleaved PARP-1 and caspase-3 levels in cells overexpressing caspase-14.

Fig1. Western blot analysis of caspase-14 in BRECs infected with adenovirus expressing caspase-14 and GFP.
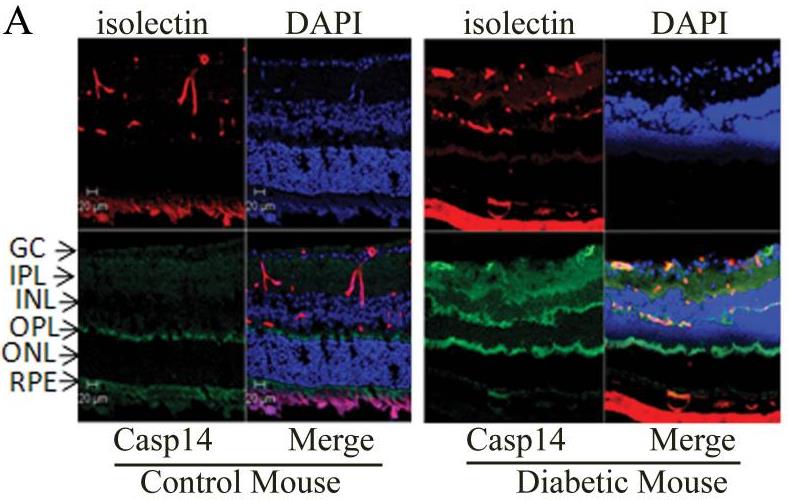
Fig2. Immunofluorescence reaction using specific antibody against caspase-14 (green).
Case 2: Pistritto G, et al. Cell Death Differ. 2002
Caspase-14, part of the caspase family involved in apoptosis, doesn't cleave typical substrates and is largely expressed in keratinocytes after birth. However, this research shows it's also present in simple epithelial cells from the breast, prostate, and stomach. Its expression increases in high-density and suspension cultures due to transcriptional activation, without being cleaved during apoptosis. Forced expression in keratinocytes doesn't affect cell death either. Unlike other conditions, calcium-induced differentiation in keratinocytes doesn't boost caspase-14, highlighting its role in both simple and complex epithelia and regulated by cell density or matrix interactions.

Fig1. Upregulation of caspase-14 expression in high confluent cultures.
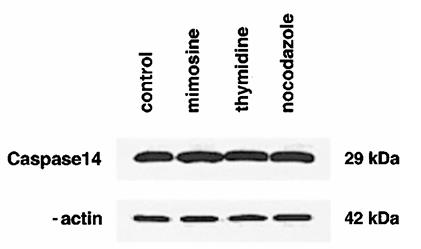
Fig2. Immunoblot analysis of caspase-14 in lysates from synchronized MCF-7 cultures.
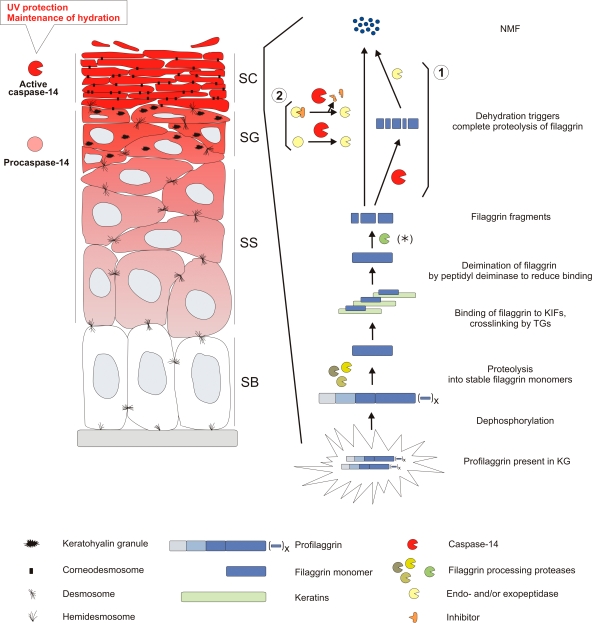
Fig1. Caspase-14 protects the skin against UVB photo damage and water loss and is involved in the processing of (pro)filaggrin. (Geertrui Denecker, 2008)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CASP14 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CASP14 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


