Recombinant Human CA4 Protein(Met1-Lys283), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CA4-237H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CA4 Protein(NP_000708.1) (Met1-Lys283) without the pro peptide was expressed in CHO with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | CHO |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | Met1-Lys283 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Bio-activity : | Measured by its esterase activity.The specific activity is >10 pmol/min/μg. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human CA4 consists of 276 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and has a predicted molecular mass of 31.7 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, rh CA4 migrates as approximately 34 and 19 kDa band. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | ≥ 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. ≥ 95 % as determined by SEC-HPLC. |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | CA4 carbonic anhydrase IV [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CA4 |
| Synonyms | CA4; carbonic anhydrase IV; retinitis pigmentosa 17 (autosomal dominant) , RP17; carbonic anhydrase 4; CAIV; Car4; CA-IV; carbonic dehydratase IV; carbonate dehydratase IV; RP17; |
| Gene ID | 762 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000717 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000708 |
| MIM | 114760 |
| UniProt ID | P22748 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CA4-7835H | Recombinant Human CA4 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Car4-364R | Recombinant Rat Car4 Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CA4-3839H | Recombinant Human CA4, His tagged | +Inquiry |
| CAR4-1133R | Recombinant Rat CAR4 Protein | +Inquiry |
| CA4-10621H | Recombinant Human CA4, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CA4-001HCL | Recombinant Human CA4 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| CA4-2069HCL | Recombinant Human CA4 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| CA4-2501MCL | Recombinant Mouse CA4 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Datta R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009
Mutations in the CA IV gene linked to autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (RP17) were studied, focusing on R69H and R219S mutations. The R219S mutation significantly reduced enzyme activity, while R69H did not, hinting that enzyme loss isn't the main issue. Both mutations caused improper protein processing and retention inside cells, leading to stress in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and apoptosis. Similar to the R14W variant found in initial RP17 cases, these mutations disrupt ER function. The toxic gain of function by inducing ER stress and cell death appears to be the disease mechanism. Notably, treating affected cells with dorzolamide, a CA inhibitor, helped mitigate this stress, suggesting potential therapeutic use to prevent blindness in RP17.
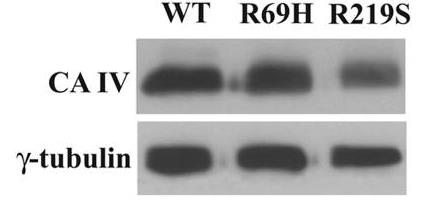
Fig1. Total protein (12.5 μg) from COS-7 cells was subjected to reducing SDS/PAGE and blotted either with CA IV antibody.
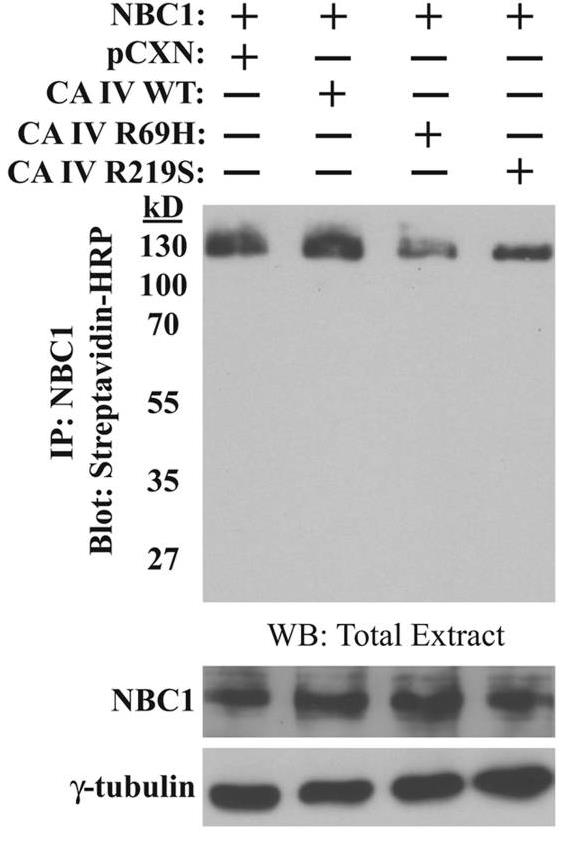
Fig2. Dominant-negative effects of R69H and R219S CA IV on cell-surface expression of NBC1.
Case 2: Okamoto S, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2024
When human nasal epithelial cells (c-hNECs) with CAIV are exposed to a CO2/HCO3–free solution, their intracellular pH (pHi) remains high at 7.64, in contrast to bronchial cells (c-hBECs) without CAIV, which have a pHi of 7.10. This high pHi in c-hNECs, driven by increased HCO3- influx through CAIV and Na+/HCO3- cotransport, results in no rise in the frequency or amplitude of ciliary beating. Upon applying the Zero-CO2 solution, the pHi, and subsequently, the ciliary beating parameters decrease in c-hNECs due to the high pHi, whereas in c-hBECs, both parameters increase with the lower pHi. The study highlights that interactions between CAIV and NBC are crucial for HCO3- influx regulation, which maintains stable ciliary function in nasal epithelial cells, particularly during low CO2 exposure, such as respiration.
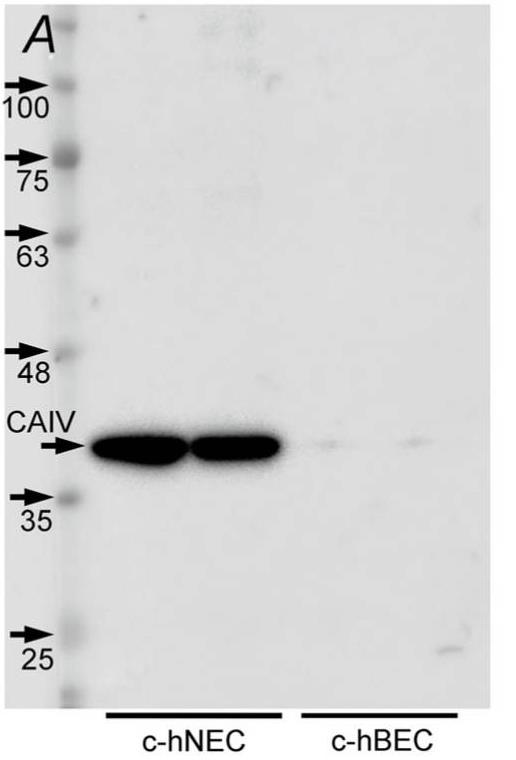
Fig1. The single band of CAIV (40 kDa) was detected in c-hNECs but faint in c-hBECs.
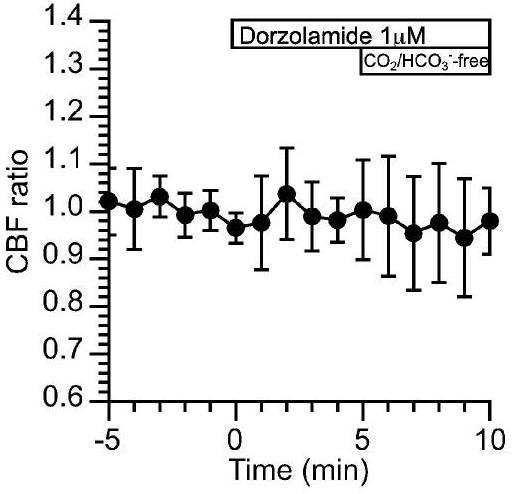
Fig2. Effects of dorzolamide (an inhibitor of CAII and CAIV) on CBF upon applying the Zero-CO2.
Human Carbonic Anhydrase IV (CA4) is essential for balancing acid and base in the blood and other tissues by helping with the hydration of carbon dioxide. Researchers use recombinant Human CA4 (rhCA4) to explore its enzyme functions and its roles in processes like breathing and maintaining acid-base balance. It's also being studied for its connection to inherited kidney issues related to bicarbonate transport and its ability to stabilize pH levels. Intriguingly, CA4 acts as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by interfering with the Wnt signaling pathway, making it a valuable tool in health and disease research.
On the industrial side, rhCA4 is used in drug discovery and cancer treatment development. It's produced in systems such as HEK293 cells and E. coli and tagged for easy purification. This recombinant protein assists in creating standardized research tools, which helps ensure experiments are reliable and repeatable. Additionally, rhCA4 is crucial for developing diagnostic tools and antibodies to detect and measure CA4 in biological samples, making it an important factor in understanding its functions and related diseases.
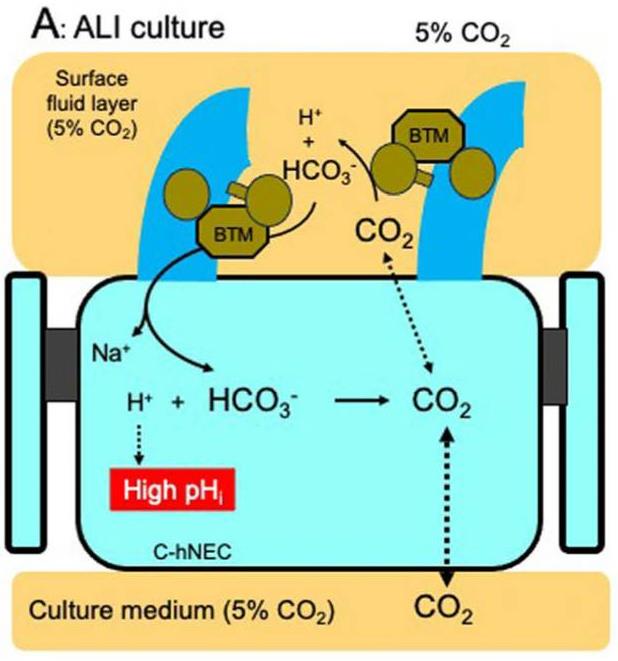
Fig1. Schematic diagrams of CBF and pHi regulation by CAIV in c-hNEC. (Shota Okamoto, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CA4 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CA4 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


