Recombinant Human AMY2A protein(Met1-Leu511), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | AMY2A-8569H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human AMY2A (P04746) (Met1-Leu511) was expressed in HEK293 with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 1-511 a.a. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human AMY2A consists of 507 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 57.3 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 53-58 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | AMY2A amylase, alpha 2A (pancreatic) [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | AMY2A |
| Synonyms | AMY2A; amylase, alpha 2A (pancreatic); AMY2, amylase, alpha 2A; pancreatic; pancreatic alpha-amylase; glycogenase; alpha-amylase; found in the pancreas; pancreatic amylase 2A; pancreatic amylase alpha 2A; amylase, pancreatic, alpha-2A; 1,4-alpha-D-glucan glucanohydrolase; PA; AMY2; AMY2B; |
| Gene ID | 279 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000699 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000690 |
| MIM | 104650 |
| UniProt ID | P04746 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| AMY2A-697R | Recombinant Rhesus AMY2A protein, hFc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| AMY2A-3520H | Recombinant Human AMY2A protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| AMY2A-56C | Recombinant Cynomolgus AMY2A, His tagged | +Inquiry |
| AMY2A-535H | Recombinant Human AMY2A protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| AMY2A-194C | Recombinant Cynomolgus AMY2A, Fc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| AMY2A-8353H | Native Human AMY2A | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| AMY2A-001CCL | Recombinant Cynomolgus AMY2A cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| AMY2A-1351HCL | Recombinant Human AMY2A cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Date K, et al. J Cell Biochem. 2020
Alpha-amylase, essential for breaking down starch, is primarily present in the pancreas and salivary glands. Its presence in other tissues is unclear in origin, as it may be locally produced or derived from the pancreas or salivary glands. The role of alpha-amylase outside these glands remains uncertain. Research has shown its expression in intestinal cells, with high mRNA levels in the duodenum, second only to the pancreas. It's active in Caco-2 intestinal cells but not in their medium, and its expression increases with cell culture duration. This enzyme, showing activity specific to small intestine cells, aligns with AMY2B, a pancreatic alpha-amylase form. Blocking its expression affects cell growth and differentiation.
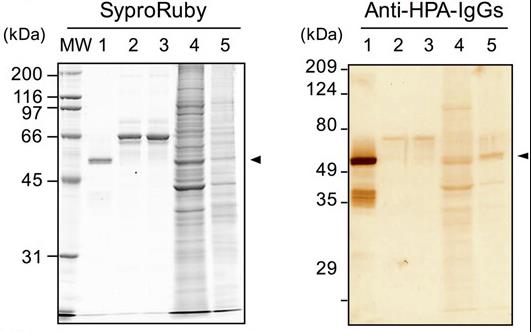
Fig1. Western-blotting for α-amylase.
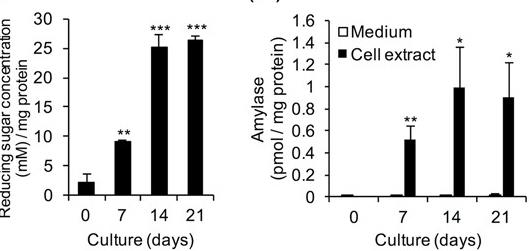
Fig2. Enzymatic activity of α-amylase.
Case 2: Date K, et al. J Biol Chem. 2015
Alpha-amylase, a key enzyme in the pancreas, aids in breaking down starch for energy. It specifically binds to N-glycans on intestinal membranes, crucial for starch digestion, but high concentrations can inhibit glucose absorption through the SGLT1 transporter. The exact mechanism to halt this inhibition was unclear. This research identified that in non-fasted pigs, alpha-amylase is internalized from pancreatic secretions and digested in lysosomes, a process blocked by alpha-mannoside. In human intestinal cells, tagged alpha-amylase was tracked along this degradation pathway. This mechanism aids in controlling glucose levels post-meal and supports intestinal cell renewal by supplying necessary amino acids.
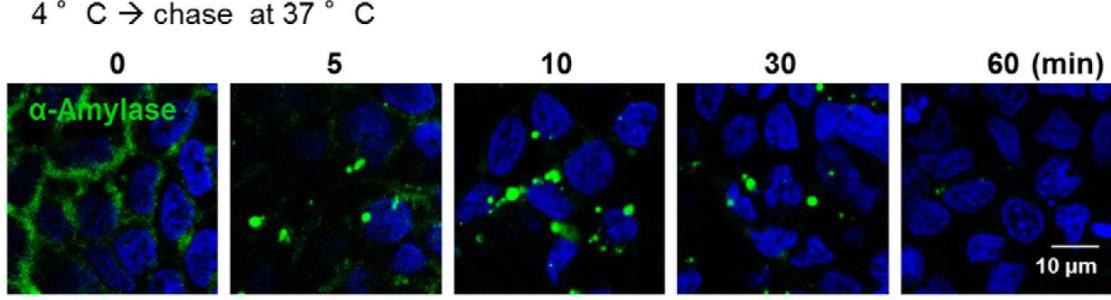
Fig1. Internalized pancreatic α-amylase decreased in Caco-2 cells.
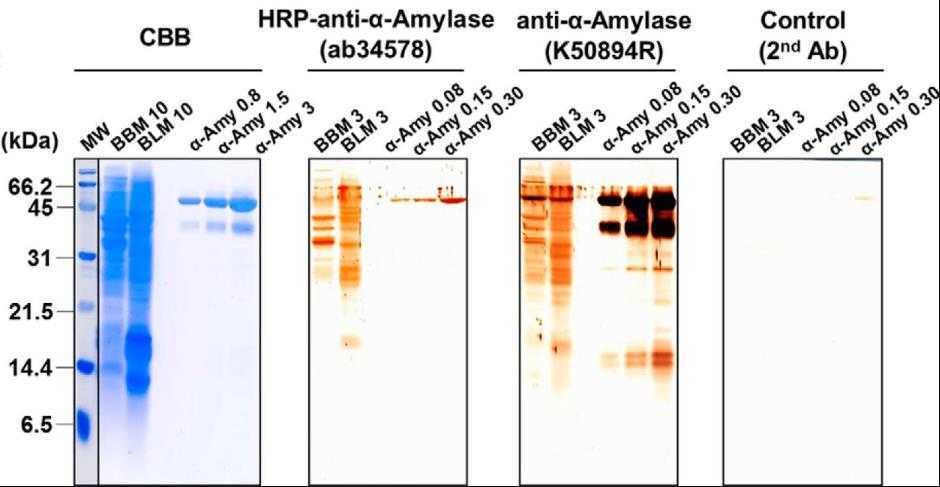
Fig2. The BBM and BLM fractions and α-amylase were separated by SDS-PAGE.
Human AMY2A protein, commonly known as pancreatic alpha-amylase, is vital in digestion by breaking down 1,4-alpha-glucoside bonds in oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, initiating the digestion of starches and glycogen. In research, recombinant Human AMY2A Protein finds numerous uses, such as in Western Blot assays to verify protein presence and size, in creating antibodies for immune-related studies, and in protein detection via ELISA to measure specific proteins. Moreover, it acts as a control in experiments, guaranteeing assay reliability and procedural effectiveness.
In industrial contexts, notably in the food and pharmaceutical markets, recombinant Human AMY2A Protein is essential. It aids the food sector by converting starch into simple sugars, thus modifying food texture and sweetness. In pharmaceuticals, it contributes to producing digestive enzymes and serves as a remedy for starch digestion disorders. The production of recombinant AMY2A Protein allows these processes to scale while ensuring consistency and quality control, which are crucial for industrial and commercial viability.
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All AMY2A Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All AMY2A Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


