Recombinant Human ACP5 protein(Met1-Pro320), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | ACP5-240H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human ACP5 (NP_001602.1)(Met 1-Pro 320) was expressed in HEK293 with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Availability | April 16, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | Met1-Pro320 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The secreted recombinant human ACP5 comprises 310 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 35 kDa as estimated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Purity : | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | ACP5 acid phosphatase 5, tartrate resistant [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | ACP5 |
| Synonyms | ACP5; acid phosphatase 5, tartrate resistant; tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase type 5; tartrate resistant acid phosphatase; TRAP; TrATPase; tartrate-resistant acid ATPase; SPENCDI; |
| Gene ID | 54 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001111034 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001104504 |
| MIM | 171640 |
| UniProt ID | P13686 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| ACP5-38H | Recombinant Human ACP5 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACP5-240H | Recombinant Human ACP5 protein(Met1-Pro320), His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Acp5-928M | Recombinant Mouse ACP5 protein(Met1-Pro327), His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACP5-180H | Recombinant Human ACP5 Protein, GST-Tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACP5-7906R | Recombinant Rabbit ACP5 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| ACP5-2809HCL | Recombinant Human ACP5 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ACP5-2431MCL | Recombinant Mouse ACP5 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Yang S, et al. Mol Med. 2024
This study looked into how ACP5 might play a part in heart fibrosis after a heart attack. Researchers collected blood samples to check ACP5 levels and used a drug to block ACP5 in mice to see if it helped heal their hearts. They found that ACP5 levels were higher after a heart attack and that blocking it reduced heart scarring and improved heart function in mice. In lab tests with heart cells, the study showed blocking ACP5 slowed cell growth and changes, while boosting ACP5 did the opposite. The effects of ACP5 were linked to changes in a key cellular pathway (GSK3β/β-catenin), and it was found that ACP5 affects this pathway through ERK-related processes.
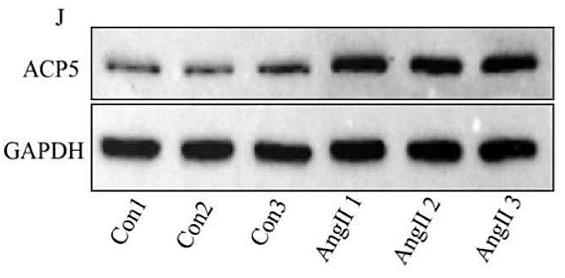
Fig1. CF Western blot analysis of ACP5 expression in different groups.

Fig2. Western blot analysis of the expression levels of p-ERK and ERK in ACP5-deficient CFs.
Case 2: Huang Y, et al. Cell Rep. 2022
Glioma-associated microglia/macrophages (GAMs) really play a big part in making glioblastomas (GBM) grow. Researchers looked into CCL18, a cytokine found in human GAMs, and why it matters for glioma growth. Since this can't be checked in regular mouse models, they came up with a method using human stem cell-derived microglia and glioma cells transplanted into mouse brain slices without their own microglia. CCL18 helps glioma cells grow and spread, with CCR8 acting as a receptor for CCL18 on these tumor cells. Also, ACP5 turns out to be key in the signaling process that pushes glioma growth along.
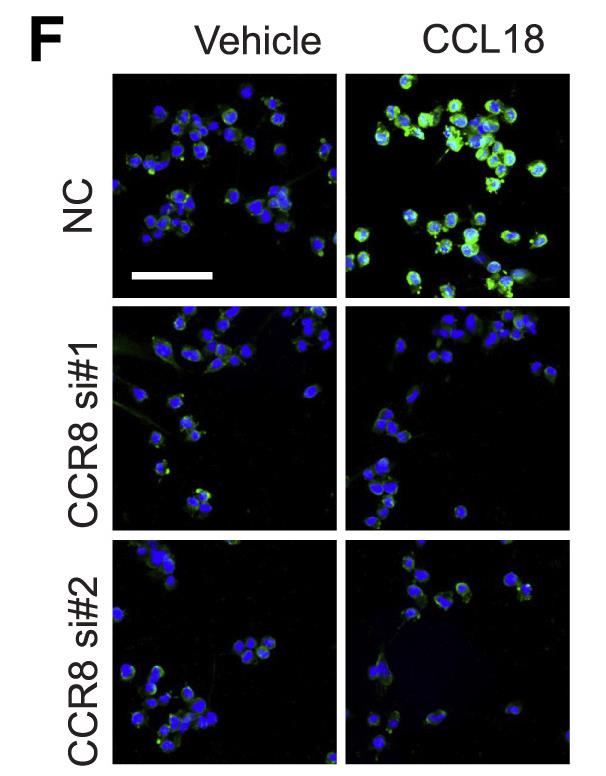
Fig1. ACP5 protein expression was detected by immunofluorescence (ACP5, green; DAPI, blue).

Fig2. Negative control (NC) and ACP5 siRNA (ACP5si) transfected glioma cell lines.
Human ACP5, also known as tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase, is a protein with a bunch of roles, from breaking down bone and generating reactive oxygen species to helping out immune cells like macrophages. It's key in bone development and works in osteoblast regulation. There are two forms of ACP5, with ACP5b being more active due to a process called proteolytic cleavage. This protein often shows up more in certain health issues, like Gaucher and Hodgkin diseases or some types of leukemia, hinting at its involvement there. Plus, it's linked with worsening pulmonary fibrosis by affecting β-catenin signaling, making it a possible target for treatments related to this disease.
Recombinant Human ACP5, or TRAP, is a handy protein across different fields. In research, it helps scientists understand bone metabolism and bone-related disorders like osteoporosis due to its link with osteoclast activity. In industry, it's used in tests that gauge bone resorption, aiding in the hunt for bone disease treatments. On the diagnostic front, ACP5 acts as a biomarker for spotting specific cancers and inflammatory conditions, playing a role in early detection and keeping tabs on how diseases progress. This versatility makes ACP5 a key player in research and clinical labs.

Fig1. Schematic illustration of the mechanisms of Acp5 in fibroblasts. (Yinan Hu, 2022)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All ACP5 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All ACP5 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


