Recombinant Human ACO1 protein(Met1-Lys889), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | ACO1-2489H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human ACO1 (P21399) (Met 1-Lys 889) was expressed in Insect Cells, with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Insect Cells |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 1-889 a.a. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% gly, 2mM DTT. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human ACO1 consists of 908 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 101 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 90 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | ACO1 aconitase 1, soluble [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | ACO1 |
| Synonyms | ACO1; aconitase 1, soluble; IREB1; cytoplasmic aconitate hydratase; IREBP; IRP1; IRE-BP 1; aconitate hydratase; citrate hydro-lyase; iron regulatory protein 1; ferritin repressor protein; iron-responsive element binding protein 1; iron-responsive element-binding protein 1; ACONS; IREBP1; |
| Gene ID | 48 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_002197 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_002188 |
| MIM | 100880 |
| UniProt ID | P21399 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| ACO1-0264H | Recombinant Human ACO1 Protein (Lys26-Ile243), N-His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACO1-1193M | Recombinant Mouse ACO1 Protein | +Inquiry |
| ACO1-911H | Recombinant Human ACO1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACO1-110R | Recombinant Rat ACO1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACO1-3458Z | Recombinant Zebrafish ACO1 | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| ACO1-510HCL | Recombinant Human ACO1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Zhu T, et al. Front Oncol. 2022
ACO1 and IREB2 proteins are like sensors for iron levels in the body and play a big role in how our cells manage iron. In kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC), the levels of these proteins drop significantly, which is bad news for patient survival. Even though we know they are important, there's still a lot to uncover about why their expression goes down in this type of cancer and what that means clinically. Researchers looked at data from different studies and used bioinformatics tools to get a clearer picture. They assessed patient survival using tools like the Kaplan-Meier plotter and dug into their connection with ferroptosis using The Cancer Genome Atlas for KIRC. They also examined tumor immune infiltration via platforms like CIBERSORT and TIMER. Tests on renal cancer cells with inhibitors for ACO1 and IREB2, combined with the drug sorafenib, revealed that stopping these genes from working helped reduce cell death.

Fig1. Survival curves of ACO1 were shown for overall survival (OS).

Fig2. ACO1 or IREB2 inhibitor pretreatment reduces sorafenib-induced and rapamycin-induced cell death in renal cancer cells.
Case 2: Wang J, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2022
Iron-sulfur clusters are crucial for various cell processes, with ISCA2 being key in building these clusters. It's known that ISCA2 is active when red blood cells form, but how it exactly works isn't clear. To explore this, scientists used RNA interference to reduce ISCA2 in specific blood cancer cells. They discovered that without ISCA2, important cell structures weaken, causing harmful molecules to build up and damage cells, stopping them from growing properly. This situation also messes with enzymes that help produce heme, a vital component in red blood cells, by increasing iron levels unusually. So, lacking ISCA2 throws a wrench in red blood cell development and heme production, by indirectly lowering the activity of a key enzyme.

Fig1. An EMSA experiment based on near-infrared fluorescence was used to test the activity of IRP1.
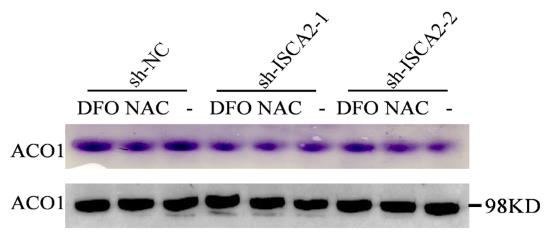
Fig2. The activity of c-aconitase after adding NAC and DFO was analyzed by the in-gel activity assay.
The Human ACO1 protein, better known as aconitase 1 or iron-responsive element binding protein 1 (IRP1), is key to how cells manage iron and balance it throughout the body. It's crucial for keeping heme synthesis in check, which is vital for hemoglobin production in our red blood cells. ACO1 is super important across different species and plays a big role in the citric acid cycle, a key player in energy production within cells. Recent research has even linked different versions of the ACO1 gene with varying hemoglobin levels, emphasizing its role in how we make red blood cells. Aside from its duties in metabolism, ACO1 has a hand in regulating iron, making it a prime target for treating issues like iron imbalance or anemia. Plus, it hangs out in different cell parts like the mitochondria and the cytosol, showcasing its versatile role in our cells. Unlocking ACO1's structure and function is critical in crafting therapies for diseases tied to iron metabolism or heme production troubles.
In the lab and industry, recombinant human ACO1 protein is a real game-changer. It's pivotal in studying cell metabolism, how cells respond to oxidative stress, and iron regulation, serving as a crucial tool for scientists trying to decipher cell functions. Its applications don't stop there; it's also paving the way for new treatments targeting metabolic disorders and related health issues. In the industrial realm, ACO1 aids in fine-tuning biological processes, boosting production efficiency, and sparking innovation, especially in the biotech and pharmaceutical sectors.
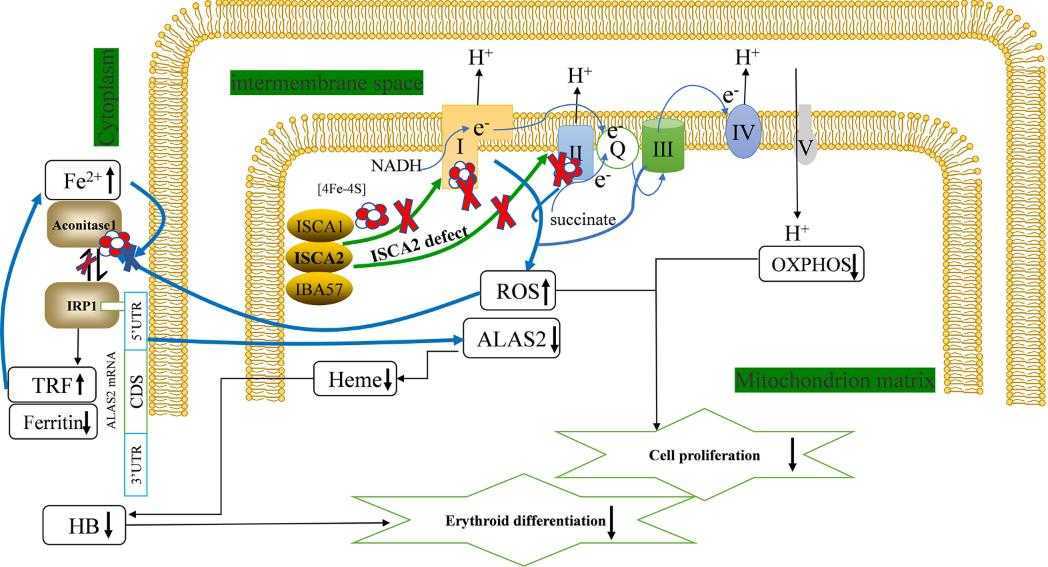
Fig1. Diagram of ISCA2 affecting cell proliferation and erythroid differentiation. (Jing Wang, 2022)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All ACO1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All ACO1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


