Recombinant Full Length Rhizobium Radiobacter Putative K(+)-Stimulated Pyrophosphate-Energized Sodium Pump(Hppa) Protein, His-Tagged
| Cat.No. : | RFL21678RF |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Full Length Rhizobium radiobacter Putative K(+)-stimulated pyrophosphate-energized sodium pump(hppA) Protein (Q8VPZ0) (1-189aa), fused to N-terminal His tag, was expressed in E. coli. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Rhizobium radiobacter |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | Full Length (1-189) |
| Form : | Lyophilized powder |
| AA Sequence : | AGGIAEMAELGPEVRKTTDKLDSVGNTTAAIAKGFAIGSAALTALALFTAFAEEIAKNPK LTGLLVDGHLVVNLTEPGVIIGIFLGATLPFLVCAFTMEAVGKAAFEMIEEVRRQFREIP GIMEGTGRPDYAKCVDISTKAAIREMMLPGVFAVGAPLIVGFLLGAKALAGFLAGVTASG VLLAIFSPS |
| Purity : | Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Notes : | Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week. |
| Storage : | Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage Buffer : | Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0 |
| Reconstitution : | We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference. |
| Gene Name | hppA |
| Synonyms | hppA; vppA; Putative K(+-stimulated pyrophosphate-energized sodium pump; Membrane-bound sodium-translocating pyrophosphatase; Pyrophosphate-energized inorganic pyrophosphatase; Na(+-PPase; Fragment |
| UniProt ID | Q8VPZ0 |
Case 1: Abe K, et al. Nat Commun. 2021
Gastric H+,K+ -ATPase undergo electroneutral 1H+/1K+ exchange through ATP hydrolysis on the membrane. Previous structural analysis of the E2-P transition state blocked by H+,K+ -ATPase K+ revealed that the enzyme binds only one K+ at the second cation-binding site, in contrast to the blocking of two K+ ions at the cation-binding sites I and II of the closely related Na+,K+ -ATPase. Na+ and K+ -ATPase mediate electrogenic 3Na+/2K+ transport across membranes. Researchers show a series of crystal structures and cryo-electron microscopic structures of H+,K+ -ATPase mutants that are altered near the first binding site, based on the structure of the sodium pump. We gradually constructed mutants, finally through five mutations to obtain a double K+ binding H+,K+ -ATPase, including direct coordination of K+ amino acids (Lys791Ser, Glu820Asp), amino acids that indirectly contribute to the formation of cation-binding sites (Tyr340Asn, Glu936Val) and isomerically stable K+ blocking conformation (Tyr799Trp). The 2.6-A-resolution cryo-electron microscopic structure of this quintuple mutant in K+ enclosed E2-P state clearly shows two independent densities of cation-binding sites.
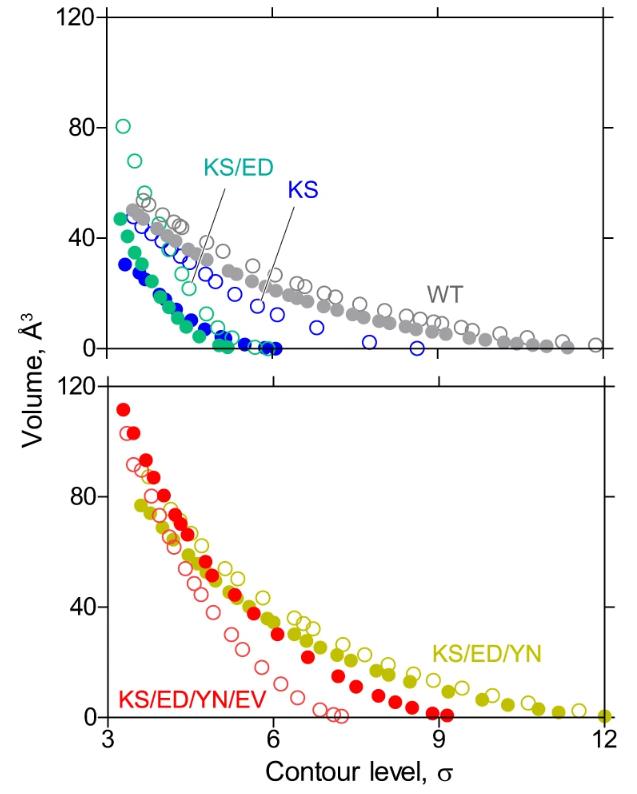
Fig1. Trends in the anomalous Rb+ densities.
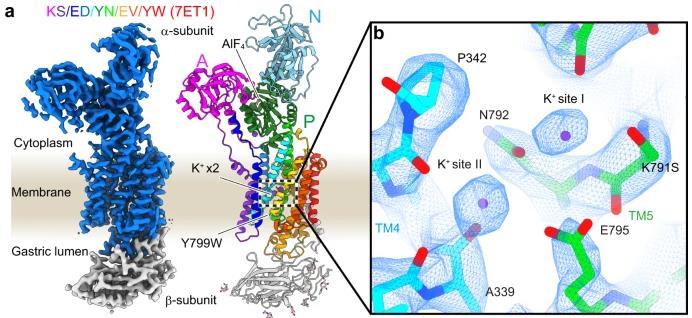
Fig2. Cryo-EM density map (left, blue, and gray surface, 5.5σ) and amino acid model of a quintuple mutant in the K+-occluded E2-AlF state.
Hppa protein is a membrane protein that is mainly expressed on the plasma membrane of bacterial cells. The protein uses pyrophosphate hydrolysis to drive sodium ion transport and is closely related to potassium ion homeostasis. The presence of this protein can help bacteria adapt to the changes of salt in the environment, and it is of great significance to study the environmental adaptability of bacteria.
Due to its special role in ion transport and energy conversion, the Hppa protein is considered a potential drug target that may be used to develop novel antimicrobial agents or growth regulators. Further research could explore its applications in industrial microbes or biotechnology, such as enhancing the salt tolerance of certain industrial strains or improving their energy efficiency. Through site-specific mutation or domain replacement, Hppa protein can be modified to enhance or inhibit some specific activities, which provides a powerful tool for studying its biological function.
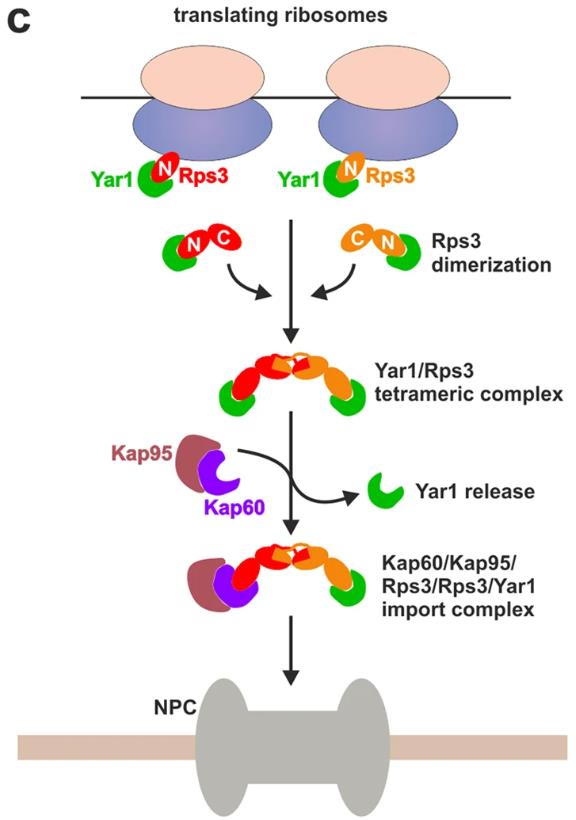
Fig1. Model describing the formation of the Yar1/Rps3/Rps3/Kap60/Kap95 import-complex that allows simultaneous targeting of an Rps3 dimer bound to one Yar1 chaperone into the nucleus. (Valentin Mitterer, 2016)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All hppA Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All hppA Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


