Recombinant Full Length Nadh-Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Chain 3(Nad3) Protein, His-Tagged
| Cat.No. : | RFL36476RF |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Full Length NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 3(NAD3) Protein (O21273) (1-122aa), fused to N-terminal His tag, was expressed in E. coli. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Reclinomonas americana |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | His |
| ProteinLength : | Full Length (1-122) |
| Form : | Lyophilized powder |
| AA Sequence : | MNTMILSEYLSVLIFFIFSFGLSCIILGLSYVLATQNADTEKLSPYECGFNPFDDARGAF DVRFYLVAILFIIFDLEVAFLFPWAVALSDVTIFGFWTMFIFLLILTVGFIYEWKKGALD WE |
| Purity : | Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Applications : | SDS-PAGE |
| Notes : | Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week. |
| Storage : | Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Storage Buffer : | Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0 |
| Reconstitution : | We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference. |
| Gene Name | NAD3 |
| Synonyms | NAD3; NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 3; NADH dehydrogenase subunit 3 |
| UniProt ID | O21273 |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| KS-01G | Active Native Goat KS Protein | +Inquiry |
| Lectin-1769D | Active Native Dolichos Biflorus Agglutinin Protein, Biotinylated | +Inquiry |
| PNLIP-1175P | Native Porcine Pancreatic Lipase | +Inquiry |
| UMOD-91P | Native Porcine UMOD | +Inquiry |
| Apotransferrin-36M | Native Mouse Apotransferrin | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| C16orf13-8258HCL | Recombinant Human C16orf13 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
| PDCD6-3359HCL | Recombinant Human PDCD6 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
| CPM-1711MCL | Recombinant Mouse CPM cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| CD274-2735HCL | Recombinant Human CD274 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| NMNAT2-001HCL | Recombinant Human NMNAT2 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Chowdhry S, et al. Nature. 2019
Here researchers show that tissue context is the major determinant of dependence on the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) metabolic pathway in cancer. By analysing more than 7,000 tumours and 2,600 matched normal samples of 19 tissue types, coupled with mathematical modelling and extensive in vitro and in vivo analyses, they identify a simple and actionable set of 'rules'. If the rate-limiting enzyme of de novo NAD synthesis, NAPRT, is highly expressed in a normal tissue type, cancers that arise from that tissue will have a high frequency of NAPRT amplification and be completely and irreversibly dependent on NAPRT for survival. By contrast, tumours that arise from normal tissues that do not express NAPRT highly are entirely dependent on the NAD salvage pathway for survival. Amplification of NAPRT is shown to generate a pharmacologically actionable tumour cell dependence for survival. Dependence on another rate-limiting enzyme of the NAD synthesis pathway, NAMPT, as a result of enhancer remodelling is subject to resistance by NMRK1-dependent synthesis of NAD.
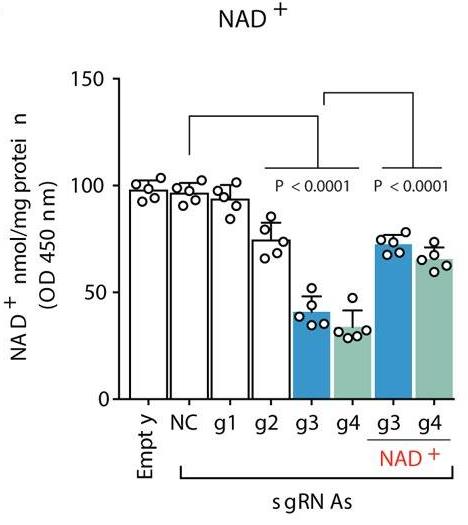
Fig1. NAD+ levels.
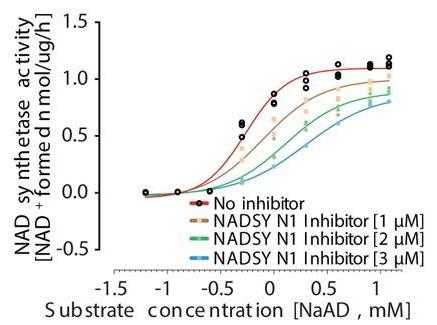
Fig2. NAD synthetase activity of human recombinant enzyme.
Case 2: Yang Y, et al. Plant Physiol. 2017
RNA editing plays a key posttranscriptional role in gene expression. However, the importance and regulation of RNA editing in several critical agronomic processes are not well understood, a notable example of which is fruit ripening. Here, researchers analyzed the expression profile of 33 RNA editing factors and identified 11 putative tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) fruit ripening-related factors. Knocking out SlORRM4 expression using a clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats CRISPR-associated protein 9 genome editing strategy delayed tomato fruit ripening by lowering respiratory rate and ethylene production. Moreover, the loss of SlORRM4 function significantly reduced RNA editing of many mitochondrial transcripts, leading to low-level expression of some core subunits that are critical for mitochondrial complex assembly (i.e. Nad3, Cytc1, and COX II).
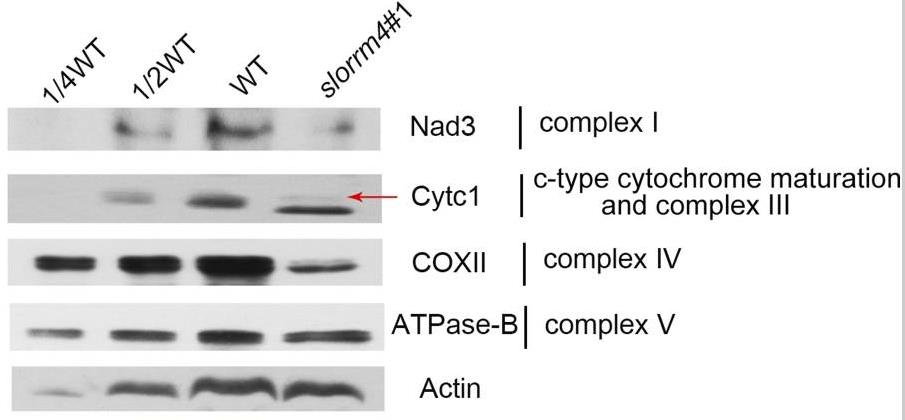
Fig1. Levels of core subunits of the mitochondrial complex were reduced.
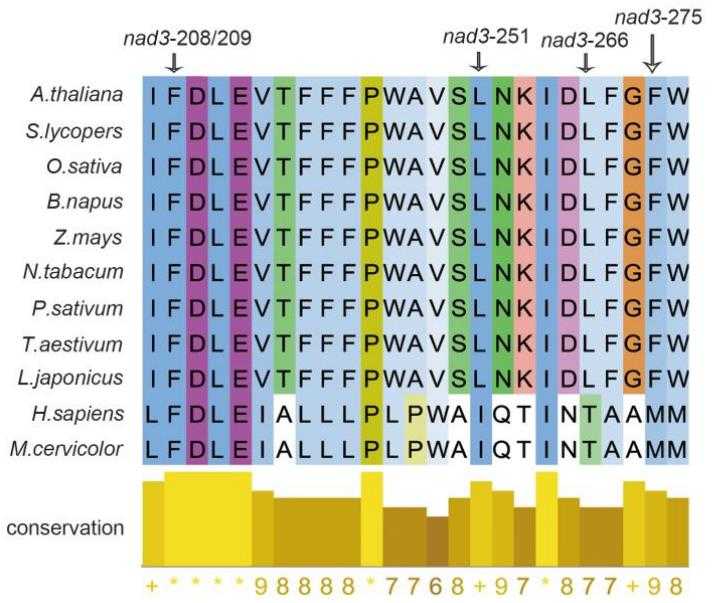
Fig2. Editing of nad3 at five position leads to restoration of several residues in tomato.
Nadh-ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Chain 3 (NAD3) is a component of the NADH dehydrogenase Complex (Complex I) in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. NAD3 protein plays an important role in cellular energy metabolism. Here are some of the applications and research areas of NAD3 protein:
1. Study on disease model. NAD+ levels are associated with a variety of neurodegenerative diseases, and the role of NAD3 protein in maintaining NAD+ levels may have potential implications for the treatment of these diseases. The role of NAD3 protein in maintaining mitochondrial function makes it an important target for the study of diseases associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. The central role of NAD+ in cell metabolism makes it relevant to a variety of metabolic diseases, and the study of NAD3 protein contributes to understanding the pathogenesis of these diseases.
2, disease treatment research. The role of NAD3 protein in the NAD+ synthesis pathway makes it a potential target for drug development, especially when developing drugs against NAD+ metabolically dependent tumors. Studying the function of the NAD3 gene through gene-editing techniques, such as CRISPR/Cas9, may help develop gene therapies for specific genetic diseases. NAD+, as a substrate of NAD-dependent enzymes, links cell metabolism with DNA damage repair and epigenetic regulation.
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All NAD3 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All NAD3 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


