Recombinant Canine ANGPTL1 protein(Glu197-Asp491), hFc-tagged
| Cat.No. : | ANGPTL1-162C |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Canine ANGPTL1 (E2RQY3) (Glu197-Asp491) was expressed in HEK293 with the Fc region of Human IgG1 at the N-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Canine |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | Fc |
| Protein Length : | Glu197-Asp491 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant canine ANGPTL1/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 555 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 62.4 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 64 and 38 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| ANGPTL1-001H | Recombinant Human ANGPTL1 Protein, His tagged | +Inquiry |
| ANGPTL1-2061H | Recombinant Human ANGPTL1, Fibrinogen-like Domain, FLAG-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ANGPTL1-1086HF | Recombinant Full Length Human ANGPTL1 Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ANGPTL1-1637M | Recombinant Mouse ANGPTL1 Protein | +Inquiry |
| Angptl1-1704M | Recombinant Mouse Angiopoietin-like 1 | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| ANGPTL1-001CCL | Recombinant Canine ANGPTL1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Kuo TC, et al. J Clin Invest. 2013
Angiopoietin-like protein 1 (ANGPTL1) plays a significant role in regulating angiogenesis, and recent studies indicate that it influences not only endothelial cells but also tumor cell activities. In a study involving 102 lung cancer patients, ANGPTL1 levels were negatively associated with tumor invasion, lymph node spread, and adverse clinical outcomes. ANGPTL1 was found to inhibit the migration, invasion, and metastatic potential of lung and breast cancer cell lines in vitro and to decrease metastasis in mice with cancer cell lines engineered to overexpress ANGPTL1. The overexpression of ANGPTL1 also hindered the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by downregulating the zinc-finger protein SLUG. Furthermore, a microRNA screen identified that ANGPTL1 downregulated SLUG through the upregulation of miR-630, which is mediated by an integrin α(1)β(1)/FAK/ERK/SP1 pathway.
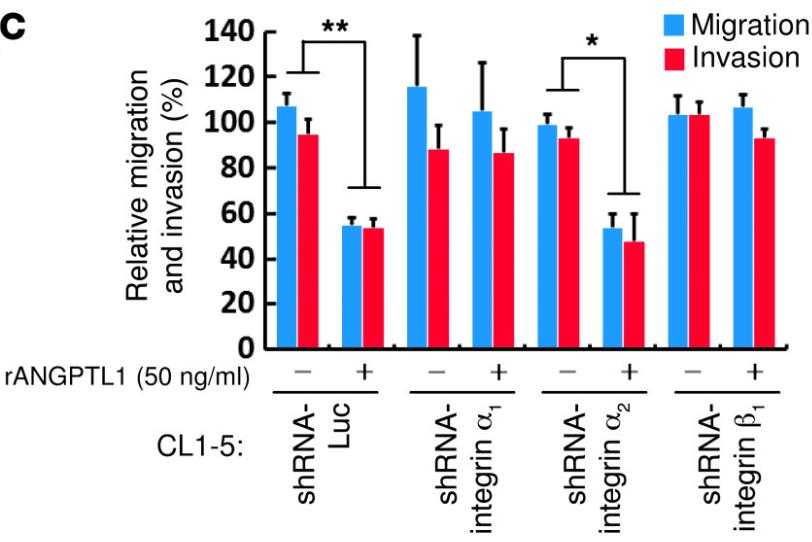
Fig1. Measurement of the migration and invasion of CL1-5 cells infected with shRNA-Luc, shRNA-integrin α1, shRNA-integrin α2, and shRNA-integrin β1 after treating with 50 ng/ml rANGPTL1.
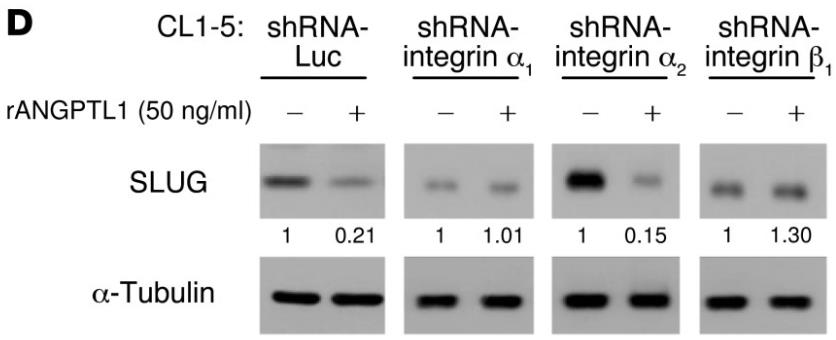
Fig2. Western blot analysis of SLUG in CL1-5 cells infected with shRNA-Luc, shRNA-integrin α1, shRNA-integrin α2, and shRNA-integrin β1 by treating with 50 ng/ml rANGPTL1.
Case 2: Wang D, et al. J Neuroimmunol. 2024
In this study, researchers explored the impact of exosomal ANGPTL1 on glioblastoma (GBM) angiogenesis and its underlying mechanisms. Using bioinformatics, human GBM cell lines, and a xenograft mouse model, we found that exosomal ANGPTL1 (e-ANGPTL-Exos) from bone mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing ANGPTL1 could inhibit GBM progression and angiogenesis by reducing VEGFA expression and blocking the VEGFR2/Akt/eNOS pathway. This effect was reversed by VEGFA overexpression, but the VEGFR2 inhibitor vandetanib could counteract this, suggesting a potential therapeutic approach for GBM.
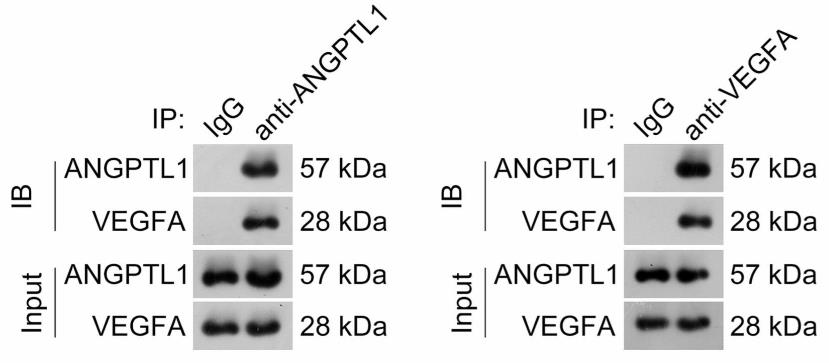
Fig1. Assessment of the interaction between ANGPTL1 and VEGFA in U87 cells by co-IP.
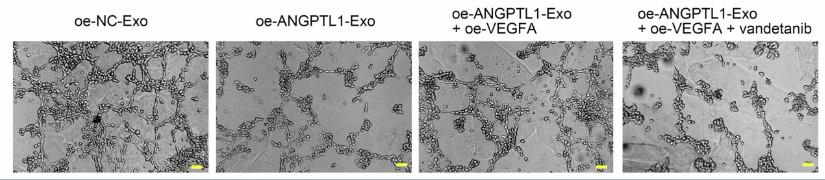
Fig2. Assessment of the angiogenesis of U87 cells by tube generation assay.
ANGPTL1 (Angiopoietin-like protein 1) is a member of the angiopoietin-like protein family and plays an important role in a variety of biological processes, including angiogenesis, inflammatory response, lipid metabolism and tumor development. Abnormal function of ANGPTL1 is associated with a variety of diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease and metabolic diseases.
Recombinant Canine ANGPTL1 protein is an important biomolecular tool with a wide range of applications in scientific research and biomedicine. ANGPTL1 is a member of the angiopoietin-like protein family and is involved in key biological processes such as angiogenesis, inflammatory response, lipid metabolism and tumor development. In scientific research, this recombinant protein is used to study the role of ANGPTL1 in oncology, angiogenesis, inflammation and signal transduction, helping scientists to gain a deeper understanding of its mechanisms in cell growth, differentiation and disease development. In addition, it is also used to build disease models and develop new therapeutic strategies, especially in the treatment of cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
In the field of biomedicine, the applications of recombinant ANGPTL1 protein include drug development, detection of disease markers and as an additive for cell culture to promote cell proliferation and differentiation. It is also used in functional analyses, such as assessing cell migration and angiogenesis, providing an important tool for developing new therapeutic approaches. These applications demonstrate that recombinant ANGPTL1 protein not only advances the understanding of related diseases, but also provides a valuable resource for the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
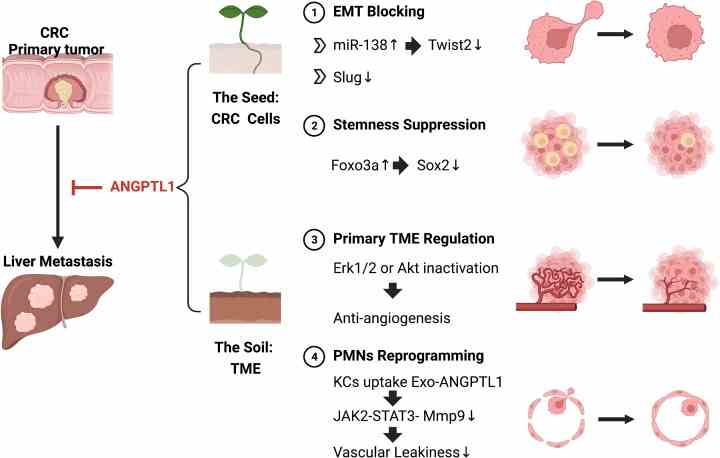
Fig1. The possible mechanisms for ANGPTL1 attenuating CRC liver metastasis. (Kai Jiang, 2022)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All ANGPTL1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All ANGPTL1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


