Active Recombinant Human AHCY Protein, 1-432aa, N-His tagged
| Cat.No. : | AHCY-727H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant human AHCY protein (1-432aa), fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E. coli, and purified by using proprietary chromatography techniques. This enzyme is validated for AHCY activity application. |
| Availability | April 18, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 1-432aa |
| Description : | Adenosylhomocysteinase (AHCY) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydrolysis of S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) to adenosine (Ado) and L-homocysteine (Hcy). It regulates the intracellular SAH concentration thought to be important for transmethylation reactions. Deficiency in this protein is one of the different causes of hypermethioninemia. |
| Form : | Liquid |
| Bio-activity : | Specific activity is > 300 pmol/min/mg. |
| Molecular Mass : | 49.8 kDa (452aa) confirmed by MALDI-TOF |
| AA Sequence : | MGSSHHHHHHSSGLVPRGSHMSDKLPYKVADIGLAAWGRKALDIAENEMPGLMRMRERYSASKPLKGARIAGCLHMTVETAVLIETLVTLGAEVQWSSCNIFSTQDHAAAAIAKAGIPVYAWKGETDEEYLWCIEQTLYFKDGPLNMILDDGGDLTNLIHTKYPQLLPGIRGISEETTTGVHNLYKMMANGILKVPAINVNDSVTKSKFDNLYGCRESLIDGIKRATDVMIAGKVAVVAGYGDVGKGCAQALRGFGARVIITEIDPINALQAAMEGYEVTTMDEACQEGNIFVTTTGCIDIILGRHFEQMKDDAIVCNIGHFDVEIDVKWLNENAVEKVNIKPQVDRYRLKNGRRIILLAEGRLVNLGCAMGHPSFVMSNSFTNQVMAQIELWTHPDKYPVGVHFLPKKLDEAVAEAHLGKLNVKLTKLTEKQAQYLGMSCDGPFKPDHYRY. |
| Purity : | > 95% by SDS-PAGE |
| Applications : | Enzyme Activity, and protein assay by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Store at -20 to -80 centigrade. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Concentration : | 1 mg/mL (determined by Bradford assay). |
| Storage Buffer : | Phosphate-Buffered Saline (pH 7.4) containing 20% glycerol, No DTT. |
| Gene Name | AHCY adenosylhomocysteinase [ Homo sapiens (human) ] |
| Official Symbol | AHCY |
| Synonyms | AHCY; adenosylhomocysteinase; S adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase; SAHH; adoHcyase; S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase; S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase; |
| Gene ID | 191 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000687 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000678 |
| MIM | 180960 |
| UniProt ID | P23526 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| AHCY-418H | Recombinant Human Adenosylhomocysteinase, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ABRA-2621H | Recombinant Human ABRA protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| AHCY-403M | Recombinant Mouse AHCY Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| AHCY-2H | Recombinant Human S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase | +Inquiry |
| AHCY-455H | Recombinant Human AHCY Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| AHCY-8964HCL | Recombinant Human AHCY 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Huang W, et al. Autophagy. 2022
S-adenosine homocysteine (SAH) is important in the processing of methionine. The enzyme adenosine homocysteine (AHCY) helps convert SAH to homocysteine and adenosine. Within the AHCY group, AHCYL1 works like a "sensor" to slow down autophagy through PIK3C3. Specifically, the C-terminus of AHCYL1 binds to SAH, thereby enhancing the binding of the N-terminus to the catalytic domain of PIK3C3 to achieve inhibition. This mechanism has been verified in vivo, indicating that SAH can also serve as a signaling molecule. This study revealed a new SAH-AHCYL1-PIK3C3 regulatory pathway that can sense the level of SAH in cells and inhibit autophagy without relying on MTORC1.

Fig1. Exogenous AHCYL1 readily binds with endogenous PIK3C3.
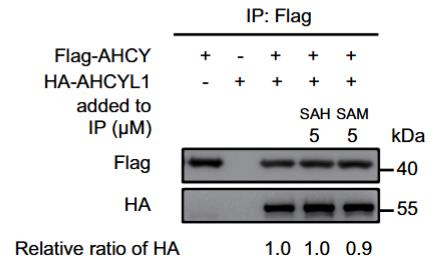
Fig2. SAH has no effect on the interaction between AHCYL1 and AHCY.
Case 2: Boczki P, et al. Adipocyte. 2024
AHCY is essential in the methionine cycle, controlling how cells methylate. It's known to affect how different cells grow and change, like in cancers and stem cells. In fat tissue development, APCs need to grow and mature properly, which often goes wrong in obesity. To see if AHCY influences APC growth and development, we reduced its activity in human and mouse APCs in the lab. The findings show that cutting down AHCY activity with a chemical called AdOx or through specific genes lowers APC growth and numbers. It also hampers their development into mature fat cells and lessens the markers of fat cell maturity. A full DNA check in human APCs showed that blocking AHCY alters DNA methylation in genes tied to fat cell development and growth pathways.

Fig1. Inhibition of AHCY leads to reduced expression of proliferation markers CCND1 and PCNA.
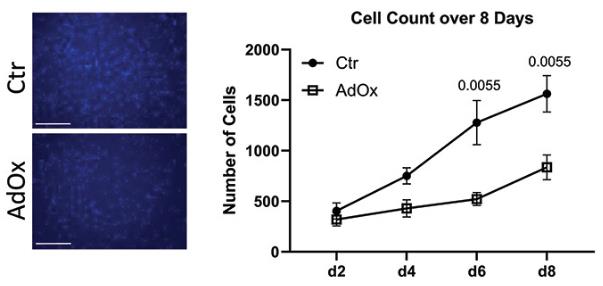
Fig2. Inhibition of AHCY reduces number of cells as indicated by counting of Hoechst-stained cell nuclei.
Adenosylhomocysteinase, also known as AHCY, plays an essential role in converting S-adenosylhomocysteine into adenosine and homocysteine. This process is important for keeping the balance necessary for cellular methylation, which supports numerous biological activities like the modification of DNA, RNA, and proteins. The enzyme is conserved across many species, highlighting its fundamental importance in living organisms. AHCY's activity supports the regulation of gene expression and normal cellular operations, making it crucial in both health and disease contexts.
In various fields like research and industry, Recombinant Human AHCY Protein is highly valued for its role in influencing key biochemical pathways. Researchers use it to explore how metabolic activities and gene expression are connected to enzyme functions. In the industrial arena, AHCY is important for crafting effective enzymatic methods used in creating pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals. For production, particularly in biotechnology, it is crucial in enabling the synthesis of compounds requiring accurate enzyme action. The protein's wide-ranging applications contribute significantly to scientific progress and industrial innovation.
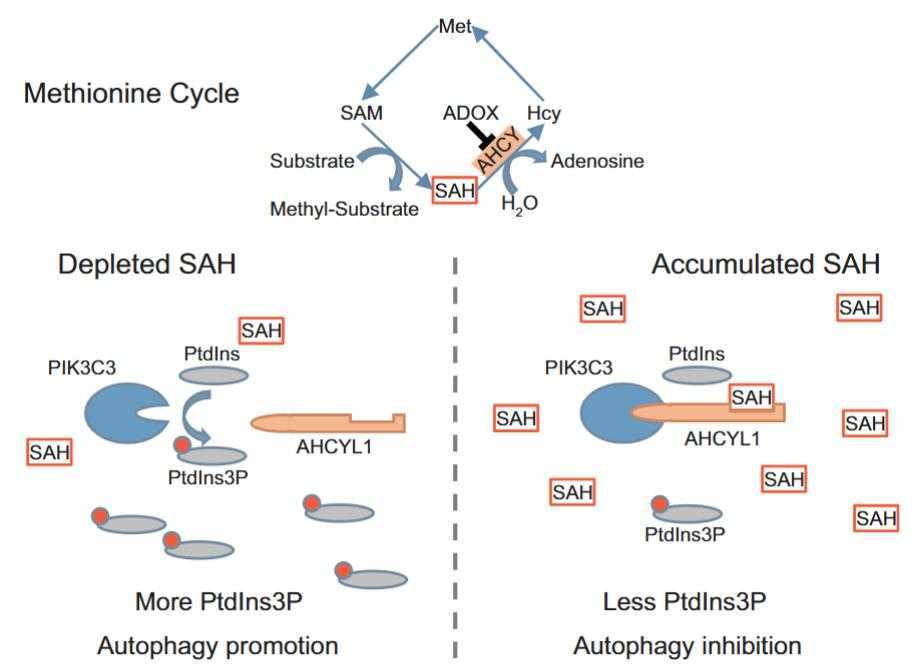
Fig1. AHCYL1 senses the intracellular SAH to control autophagy. (Wei Huang, 2022)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All AHCY Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All AHCY Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


