Active Native Human C1q Protein
| Cat.No. : | C1Q-20H |
| Product Overview : | Native Human C1q was purified from pooled normal human plasma. |
| Availability | April 16, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Human Serum |
| Tag : | Non |
| Description : | The C1q complex is potentially multivalent for attachment to the complement fixation sites of immunoglobulin. The sites are on the CH2 domain of IgG and, it is thought, on the CH4 domain of IgM. The appropriate peptide sequence of the complement fixing site might become exposed following complexing of the immunoglobulin, or the sites might always be available, but might require multiple attachment by C1q with critical geometry in order to achieve the necessary avidity. |
| Form : | Frozen liquid |
| Bio-activity : | >1,000,000 C1H50 units/mg |
| Molecular Mass : | 410,000 Da (18 chains) |
| Purity : | ≥98% by SDS PAGE |
| Applications : | C1q is used to coat ELISA plates to capture and quantitate immune complexes in clinical samples. |
| Storage : | -70°C or below. Avoid freeze/thaw. |
| Concentration : | 1.0 mg/mL |
| Storage Buffer : | 10 mM HEPES, 300 mM NaCl, pH 7.2 |
| Preservative : | None, 0.22 μm filtered. |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| C1Q-20H | Active Native Human C1q Protein | +Inquiry |
| C1q-04M | Native Mouse C1q Protein | +Inquiry |
| C1q-07R | Native Rat C1q Protein | +Inquiry |
| C1q-01M | Native Monkey C1q Protein | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Bally I, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013
Complement C1q, a key initiator of the classical complement pathway, is a multi-chain protein that detects various immune and non-immune targets. Researchers developed a method to produce recombinant human C1q (rC1q) in HEK 293-F cells, which includes an affinity tag for purification. The rC1q closely resembles natural serum C1q in structure and function, maintaining its flower-like shape and ability to bind C1s-C1r and recognize ligands like IgG and pentraxin 3. Mutational analysis of key lysine residues in the collagen-like region revealed that LysB61 and LysC58 are crucial for binding to C1s-C1r, with LysA59 playing a lesser role. We suggest LysB61 and LysC58 may form salt bridges with acidic calcium ligands in the CUB domains of C1r and C1s.
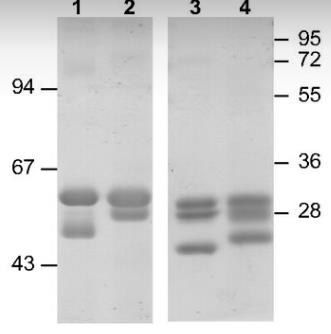
Fig1. SDS/PAGE analysis: lane 1, unreduced serum C1q; lane 2, unreduced WT rC1q; lane 3, reduced serum C1q; lane 4, reduced WT rC1q.
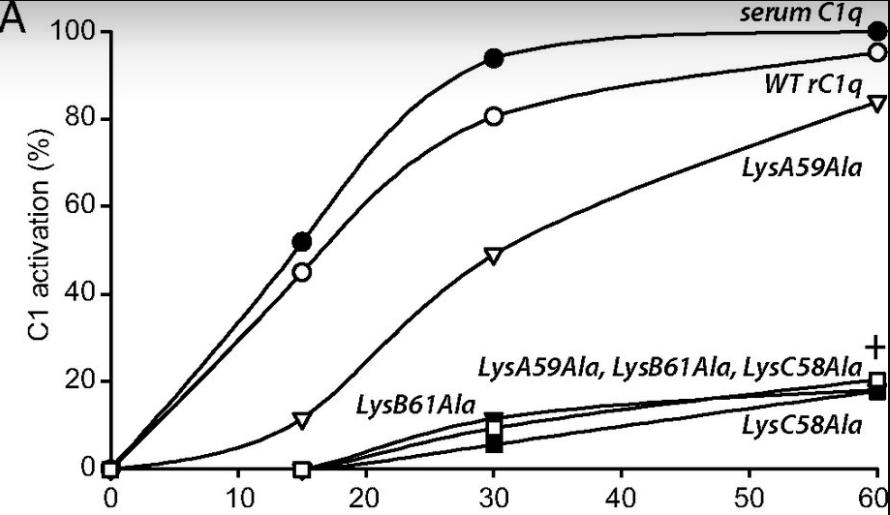
Fig2. Spontaneous activation.
Case 2: Yu Q, et al. iScience. 2023
The myelin sheath in the CNS is crucial for nerve impulse transmission. While microglia are implicated in myelin development, their exact role in early myelination remains unclear. This study shows that myelin formation in neural stem cells only happens with microglia-conditioned medium, and lacking C1q, a factor produced by microglia, causes myelination to fail. Supplementing with native human C1q protein can induce myelination in vitro. In a mouse model lacking C1q, a deficiency before myelination starts results in thinner myelin and a higher g-ratio, indicating impaired myelination.
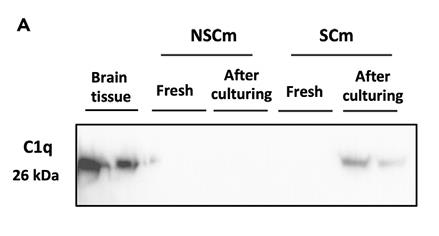
Fig1. IP and Western blot analysis of C1q expression in neural stem cell culture medium (NSCm) and spinal cord tissue culture medium (SCm).
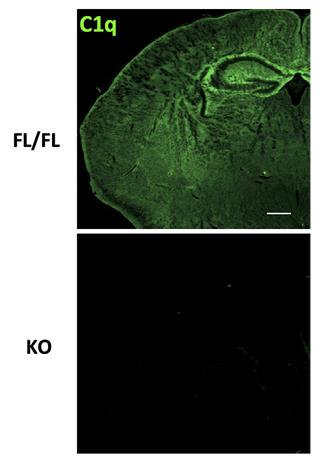
Fig2. Immunofluorescence staining of C1q and MBP expression in coronal brain sections of FL/FL and KO mice.
The C-terminal spherical header of C1q is responsible for recognizing various molecular structures, such as the Fc region of antibodies and marker molecules on the surface of apoptotic cells. The N-terminal gelatin-like tail is involved in effector mechanisms, such as interacting with receptors on the surface of immune cells. As a classical pathway recognition molecule in the complement system, C1q is of great significance for the study of immune response and related diseases.
Abnormal C1q function is associated with infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases and neurological diseases, so the determination of its level is important for the diagnosis of these diseases. C1q can be used in the screening process for drug development to assess a drug's potential impact on the immune system. C1q is involved in regulating the activity of immune cells and clearing apoptotic cells by binding to cell surface receptors.
In recent years, studies have revealed the role of C1q in more physiological and pathological processes, such as protein homeostasis maintenance in the aging brain and pro-angiogenic properties in endometriosis. These findings offer the possibility of developing new treatments.
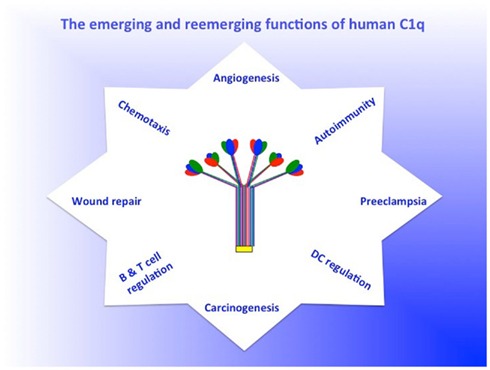
Fig1. The emerging and reemerging functions of C1q. (Berhane Ghebrehiwet, 2012)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All C1q Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All C1q Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


