TNFSF15
-
Official Full Name
tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 15 -
Overview
TL1A, also known as TNF ligand-related molecule 1, vascular endothelial growth inhibitor, and TNF ligand superfamily member 15, is a type II membrane protein with a predicted molecular weight of 28 kD. TL1A can also be found as a secreted protein as a res -
Synonyms
TNFSF15;tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 15;tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15;MGC129934;MGC129935;TL1;TL1A;TNF ligand related molecule 1;TNF superfamily ligand TL1A;vascular endothelial cell growth inhibitor;vascular endothelial growth inhibitor 192A;VEGI;VEGI192A;TNF ligand-related molecule 1;vascular endothelial growth inhibitor-192A
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- HEK293
- E.coli
- N-His-Avi
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- Flag
- His
- rFc
- Non
- Fc
- Avi
- mFc
- hIgG4
- T7
Background
What is TNFSF15 protein?
TNFSF15 gene (TNF superfamily member 15) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 9 at locus 9q32. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. This protein is abundantly expressed in endothelial cells, but is not expressed in either B or T cells. The expression of this protein is inducible by TNF and IL-1 alpha. This cytokine is a ligand for receptor TNFRSF25 and decoy receptor TNFRSF21/DR6. It can activate NF-kappaB and MAP kinases, and acts as an autocrine factor to induce apoptosis in endothelial cells. This cytokine is also found to inhibit endothelial cell proliferation, and thus may function as an angiogenesis inhibitor. The TNFSF15 protein is consisted of 251 amino acids and TNFSF15 molecular weight is approximately 28.1 kDa.
What is the function of TNFSF15 protein?
TNFSF15, also known as TL1A, is a cytokine that plays a role in immune responses and inflammation. It is involved in T-cell activation and the promotion of proinflammatory cytokine production, which can exacerbate conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. TNFSF15 can also facilitate the differentiation and polarization of macrophages towards the M1 phenotype, which has anti-tumor properties, suggesting its potential role in cancer immunotherapy.
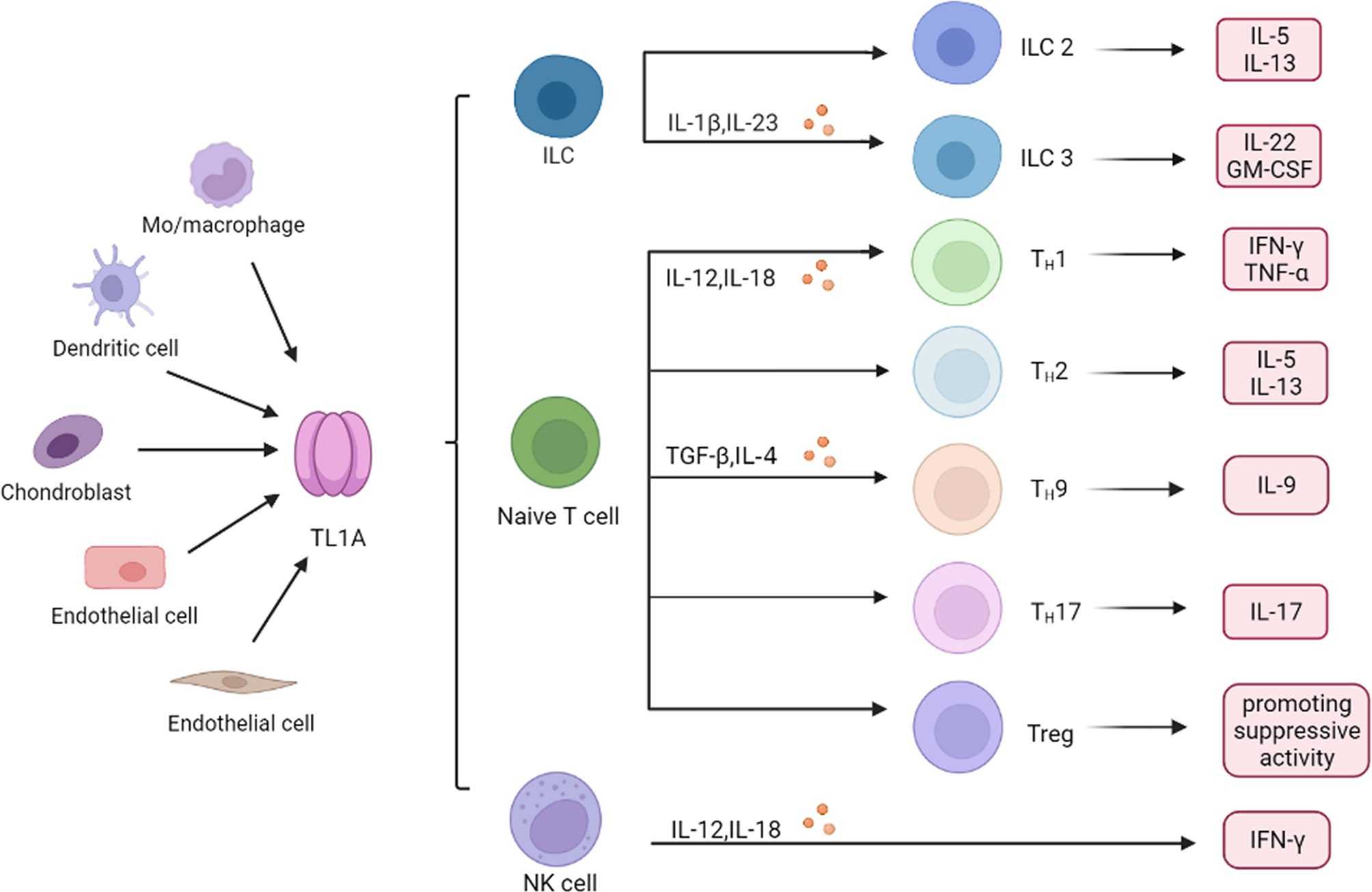
Fig1. Role of TL1A in immune cells. (Wang-Dong Xu, 2022)
TNFSF15 related signaling pathway
TNFSF15 is a cell surface receptor that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. It is mainly expressed in immune cells, such as T cells, B cells and dendritic cells. When TNFSF15 binds to its ligand, it can activate downstream signaling pathways, including NF-κB, MAPK, and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways, thereby regulating a variety of biological processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, and inflammation. In addition, TNFSF15 is also involved in the regulation of the immune system, such as promoting the activation and proliferation of T cells, and regulating the production of antibodies to B cells.
TNFSF15 related diseases
TNFSF15, also known as TL1A, is a protein involved in immune responses and is associated with diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. It plays a role in the activation of T cells and the promotion of proinflammatory cytokine production, which can lead to inflammation. Additionally, TNFSF15 is linked to autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and has been implicated in cancer immunotherapy strategies, where it can facilitate the differentiation and polarization of macrophages toward an M1 phenotype, inhibiting tumor growth. Furthermore, variations in TNFSF15 have been correlated with the immune response and prognosis in esophageal cancer.
Bioapplications of TNFSF15
TNFSF15, also known as TL1A, is primarily involved in immune responses and inflammation, playing a significant role in conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It stimulates T-cell activation and the production of proinflammatory cytokines, which can exacerbate gut inflammation. Furthermore, TNFSF15 has been found to promote the differentiation and polarization of macrophages toward the M1 phenotype, which has anti-tumor properties, suggesting its potential use in cancer immunotherapy. Additionally, it may serve as a predictive biomarker for immunotherapy outcomes in esophageal cancer.
Case Study
Case Study 1: S Jin, 2012
TL1A, a cytokine related to TNFα, is associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This study explored how TL1A triggers inflammation in CD4+ T cells, distinct from TNFα. Researchers discovered that TL1A directly stimulates proinflammatory cytokines, including TNFα, from CD4+CD161+ T cells, which are unresponsive to TNFα. This effect is not blocked by anti-TNFα, suggesting a direct action. Importantly, CD161 and TL1A are specifically elevated in gut biopsies of IBD patients, not in peripheral blood, indicating that TL1A acts both upstream and independently of TNFα in gut inflammation.
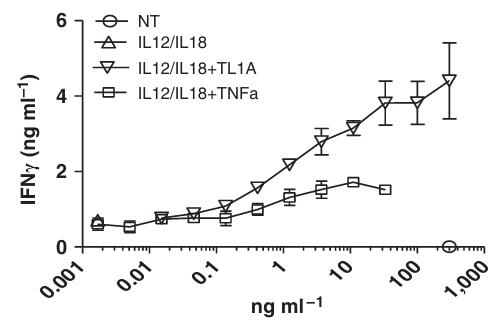
Fig1. Supernatants were analyzed for IFNγ expression by AlphaLISA.
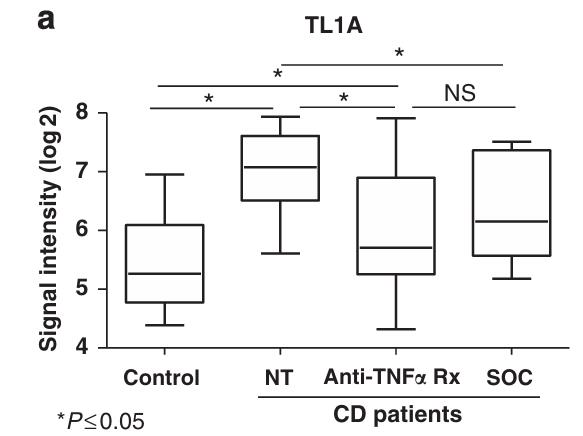
Fig2. Expression of TL1A analyzed by microarray.
Case Study 2: Yahui Ding, 2020
The clinical application of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) is hindered by the difficulty of expanding them outside the body, and umbilical cord blood (UCB) is an alternative source. However, the low count of HSC in a single UCB unit restricts its use. Our study shows that TNFSF15, a tumor necrosis factor superfamily member, can promote the expansion of UCB-derived HSCs, which are then able to successfully engraft in bone marrow of NOD/SCID or NOG mice upon transplantation. The treated HSCs have a higher rate of repopulating cells in the injected tibiae compared to the control group. Moreover, TNFSF15 treatment leads to increased expression of Notch pathway signaling proteins in UCB-HSCs.
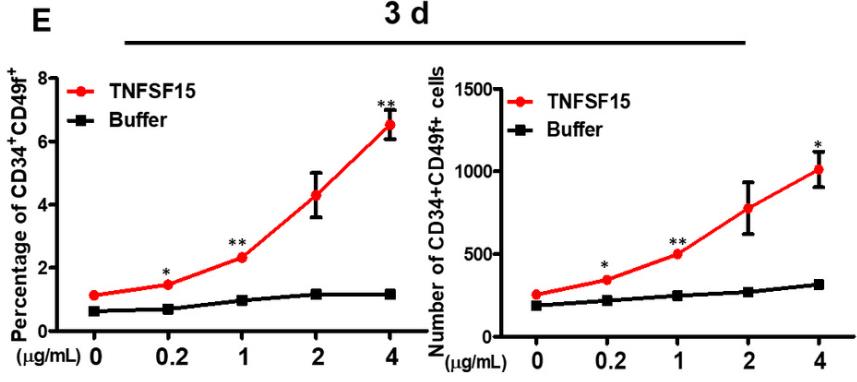
Fig3. Percentages and absolute number of CD34+CD49f+ cells in CD34+ cells treated with various concentrations of TNFSF15.
Fig4. Frequencies of cobblestone area-forming cells (CAFC) after the treatment of TNFSF15.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TNFSF15-150HB)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TNFSF15-1071H)
Involved Pathway
TNFSF15 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TNFSF15 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TNFSF15 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | IFNA8,IL18R1,CCL11,LTBR,MPL,IFNW1,CCL19,PF4V1,TGFB2,IL18RAP |
Protein Function
TNFSF15 has several biochemical functions, for example, cytokine activity,death receptor binding,receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TNFSF15 itself. We selected most functions TNFSF15 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TNFSF15. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| cytokine activity | KITLG,IL5,IFNL3,FAM3C,GREM2,Ifna15,IFNA5,BMP6,GDF11,IL16 |
| tumor necrosis factor receptor binding | BRE,CD40LG,TRAP1,TNFSF10,TNFSF8,TNFSF14,TNFSF10L,TRAF1,TNFSF13B,TRADD |
| death receptor binding | PRDM4,NOL3,MYD88,FADD,TMBIM1,BID,Fasl,CASP8,FASLG,CFLAR |
| receptor binding | ANKRD13C,LAMA3,PTK2AB,MLN,LAMA4,SLC39A1,Fert2,CADM4,PTK2AA,PVRL2 |
Interacting Protein
TNFSF15 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TNFSF15 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TNFSF15.
TNFSF15 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Death Receptor–Ligand SystemDeath Ligands
Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)
Co-stimulatory Molecules
Immune Checkpoints
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Xu, SZ; Lee, SH; et al. Effects of dietary selenium on host response to necrotic enteritis in young broilers. RESEARCH IN VETERINARY SCIENCE 98:66-73(2015).
- Xu, SZ; Lee, SH; et al. Dietary sodium selenite affects host intestinal and systemic immune response and disease susceptibility to necrotic enteritis in commercial broilers. BRITISH POULTRY SCIENCE 56:103-112(2015).



