Tnfrsf10b
-
Official Full Name
tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10b -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily, and contains an intracellular death domain. This receptor can be activated by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TNFSF10/TRAIL/APO-2L), and transduces an apoptosis signal. Studies with FADD-deficient mice suggested that FADD, a death domain containing adaptor protein, is required for the apoptosis mediated by this protein. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms and one non-coding transcript have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009] -
Synonyms
TNFRSF10B;tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10b;DR5;CD262;KILLER;TRICK2;TRICKB;ZTNFR9;TRAILR2;TRICK2A;TRICK2B;TRAIL-R2;KILLER/DR5;tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 10B;Fas-like protein;death receptor 5;cytotoxic TRAIL receptor-2;TNF receptor superfamily member 10b;apoptosis inducing receptor TRAIL-R2;apoptosis inducing protein TRICK2A/2B;TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2;death domain containing receptor for TRAIL/Apo-2L;tumor necrosis factor receptor-like protein ZTNFR9;p53-regulated DNA damage-inducible cell death receptor(killer)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Cynomolgus
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Rat
- HEK293
- Human Cells
- E.coli
- Sf21 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- Non
- hIgG4
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- mFc
Background
What is TNFRSF10B Protein?
TNFRSF10B, or DR5/ TRAIL receptor 2, is part of the TNF receptor family and works with TRAIL to jumpstart the cell's self-destruct sequence, apoptosis. It has this special "death domain" inside the cell that's crucial for sending out the self-destruct signal. Mostly found on the cell surface, TNFRSF10B has fingers in many cellular pies, especially when it comes to responding to immune signals and regulating cell death. It's a big player in cancer biology too, since tweaking its pathway could help trigger cancer cell death, making it a hot target for therapy. TNFRSF10B is involved in immune responses and inflammation, making it a major focal point in studying diseases with disrupted processes.
What is the Function of TNFRSF10B Protein?
TNFRSF10B, otherwise known as DR5 or TRAIL-R2, is a receptor on cell surfaces that kicks off apoptosis when it hooks up with the TRAIL ligand. This bonding starts a caspase chain reaction, ultimately leading to controlled cell death. This process is crucial for keeping cell balance and is especially important in cancer situations, where activating this protein can help wipe out tumor cells. Because of its role in cell death, TNFRSF10B is seen as a potential target for cancer treatments that aim to kill off cancer cells while leaving healthy ones unaffected.
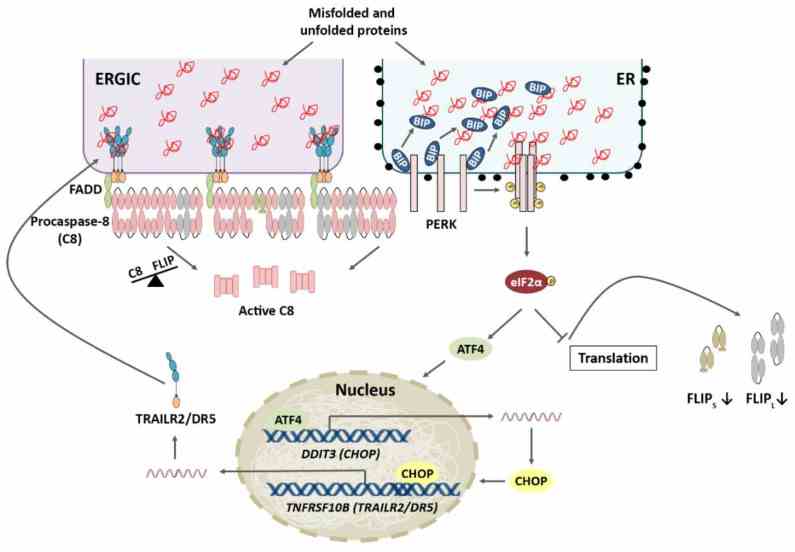
Fig1. TRAILR2/DR5 upregulation and FLIP downregulation are both required for ER stress-induced apoptosis. (Rocío Mora-Molina, 2022)
TNFRSF10B Related Signaling Pathway
TNFRSF10B, also known as DR5 or TRAIL-R2, plays a crucial role in the extrinsic route of apoptosis. Once activated by its ligand TRAIL or specific antibodies, it kickstarts a chain reaction leading to cell death. This involves pulling in adapter proteins like FADD and caspases to form the Death-Inducing Signal Complex (DISC). Initiator caspases get activated, chopping downstream effectors and setting off apoptosis. The activation of caspase-8, a major move in this pathway, can be held back by the FLICE-like inhibitor protein (CFLAR) to stop it from joining DISC. TNFRSF10B's signaling is a hot topic in cancer research because it might help target and eliminate cancer cells while sparing the healthy ones.
TNFRSF10B Related Diseases
TNFRSF10B, which you might also know as DR5 or TRAIL-R2, pops up in a bunch of health issues, mostly when we're talking about cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. It's got a big part to play in head and neck cancer, possibly pushing things along when there are changes or deletions in its chromosomal neighborhood. In Parkinson's disease, TNFRSF10B seems to mess with movement by affecting how microglia throw out exosomal α-synuclein, which could end up harming nerves. It's also in the mix with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, kicking off cell death, and it's tangled up in other neurodegenerative stuff like amyloid-beta build-up, spinal cord injury, and brain ischemia. Because of how it drives cell death, or apoptosis, it's seen as a player in conditions where TNFRSF10B goes a bit overboard, making it an interesting target for therapy.
Bioapplications of TNFRSF10B
TNFRSF10B has a bunch of bio uses, especially in research and making stuff in the industry. In the research world, it's a big deal for figuring out its structure and how it works, which is super helpful for coming up with new ways to fight diseases like head and neck cancer. People use computer tools to check out genes more precisely and quickly, and they even use virtual methods to hunt down new possible drug candidates that target TNFRSF10B. On the production side, especially in making biopharmaceuticals, studying TNFRSF10B can lead to new cancer drugs. Bioinformatics plays a key role here by breaking down how this protein interacts with new inhibitors, which is a big step in designing and making new drugs. Plus, understanding how TNFRSF10B interacts with other proteins helps figure out its part in disease pathways, paving the way for new treatments. In short, TNFRSF10B applications range from modeling its structure to screening in virtual spaces, holding great promise for pushing forward medical treatment advancements and drug manufacturing.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Dapeng Zhao, 2024
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is pretty common in China. TNFRSF10B, a receptor crucial for triggering cell death and managing chemo, still has unclear regulation.To dig into chemo resistance in TNBC, folks looked at RNA-Seq data from the GEO database. They used RT-PCR and Western blotting to peek at TNFRSF10B's mRNA and protein levels. They also ran a bunch of tests like CCK-8 and colony formation to see how cells were growing, while Annexin V/7-AAD staining helped them figure out how much the cells were diving into apoptosis. Another layer of analysis involved examining TNFRSF10B on cell membranes using Western blot and immunofluorescence. The study found that TNFRSF10B is often reduced in TNBC, impacting prognosis. Elevating its levels can slow TNBC growth and boost chemosensitivity. Additionally, activating endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) heightens TNFRSF10B presence on cell surfaces, which triggers apoptosis.
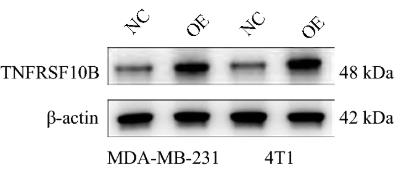
Fig1. Overexpressing plasmids upregulated the expression of TNFRSF10B.
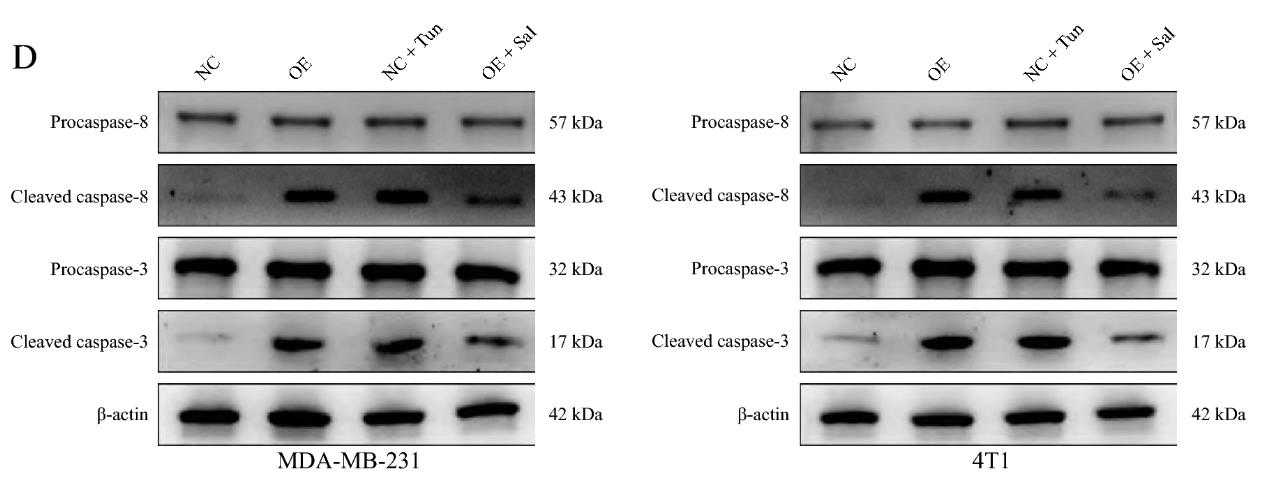
Fig2. Western blotting analysis revealed that TNFRSF10B promoted cleaved caspase‑8 and caspase‑3 protein expression levels.
Case Study 2: Gu-Choul Shin, 2016
Death receptors such as TNFSF10/TRAIL are crucial in triggering apoptosis for viral threat management, but viruses like hepatitis B often bypass this. The hepatitis B virus, for instance, uses its X protein (HBx) to mess with TNFSF10 receptor signaling by pushing for the breakdown of the TNFRSF10B/DR5 receptor through the autophagy pathway, allowing virus-infected cells to slip by unnoticed. We found that HBx significantly reduces TNFRSF10B levels in liver tissues from chronic hepatitis B patients and HBV or HBx-infected cell lines by shoving the receptor into lysosomes—not proteasomes—for degradation. Experiments showed HBx boosts autophagy by interacting directly with TNFRSF10B, guiding it into the early stages of autophagosome formation. Blocking autophagy makes HBx-infected liver cells more vulnerable to TNFSF10, pointing out HBx's dual role: acting like an autophagy receptor to gather TNFRSF10B with LC3B, and kicking autophagy into gear.
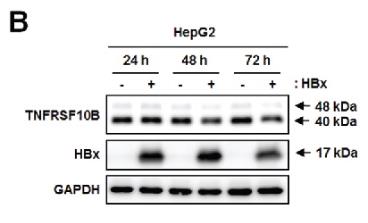
Fig3. TNFRSF10B expression at the indicated time points after transfection with the control or HBx plasmid in HepG2 cells was analyzed by immunoblot assay.
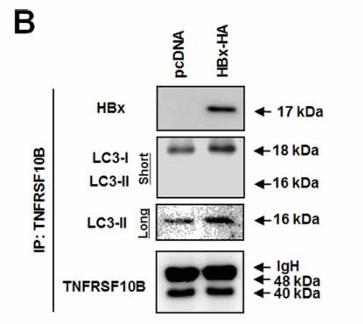
Fig4. Immunoprecipitation with anti-TNFRSF10B and anti-HA antibodies.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TNFRSF10B-7761H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TNFRSF10B-311H)
Involved Pathway
Tnfrsf10b involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Tnfrsf10b participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,p signaling pathway,Apoptosis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Tnfrsf10b were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Influenza A | NXF2,IFNA13,HLA-DQB1,IFNB1,OAS1,NFKBIB,HSPA8,HSPA1L,HLA-DRB4,IFN-a |
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | IFNA14,RAC2,Raet1c,BID,IFNA10,H60a,MICB,HLA-G,Fasl,KIR2DS3 |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | CSF2,TNFRSF9A,GM10591,IL-15RA,TGFB2,CCL20A.3,CSH,IL9,IL3RA,IL5 |
| p signaling pathway | SFN,PTENA,SESN1,CASP3B,BAI1,APAF1,PPM1DB,CCNE1,CCND2,CASP3A |
| Apoptosis | PIK3R3,HMGB2A,BAX,CAPN2,DSG1,XIAP,TNFRSF1A,PRKAR2AB,PRKACAA,IRAK3 |
| Measles | IFNGR1,CCND3,TRP53,MSN,HSPA1B,EIF2AK1,CCNE2,IRF3,NFKB1,TYK2 |
Protein Function
Tnfrsf10b has several biochemical functions, for example, TRAIL binding,protein binding,receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Tnfrsf10b itself. We selected most functions Tnfrsf10b had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Tnfrsf10b. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| TRAIL binding | TNFRSF10C,TNFRSF10D,TNFRSF10A,Tnfrsf22 |
| protein binding | BANF1,RPS11,IQCB1,MXD3,EAF2,RBMY1A1,DYNLRB1,TBX2A,TALDO1,CRYAB |
| tumor necrosis factor-activated receptor activity | TNFRSF10A,TNFRSF18,TNFRSF21,TNFRSFA,TNFRSF9,RELT,Tnfrsf26,CD27,TNFRSF8,NGFR |
| receptor activity | TNFRSF6B,NLGN3B,VMN1R40,BTLA,OGFRL2,GRIN2BB,RPA1,FOLR1,VMN1R49,KLRK1 |
Interacting Protein
Tnfrsf10b has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Tnfrsf10b here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Tnfrsf10b.
TNFSF10
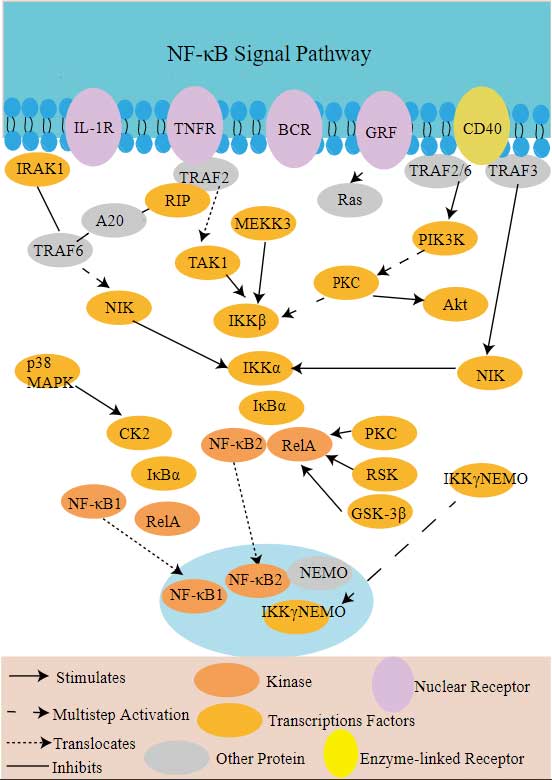
Tnfrsf10b Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Cancer Drug TargetsAdipocytokines
Endothelial Cell Markers
Death Receptor–Ligand System
TNF Receptor
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Seirafian, S; Prod'homme, V; et al. Human cytomegalovirus suppresses Fas expression and function. JOURNAL OF GENERAL VIROLOGY 95:933-939(2014).
- Meng, XW; Koh, BD; et al. Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibitors Sensitize Cancer Cells to Death Receptor-mediated Apoptosis by Enhancing Death Receptor Expression. JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 289:20543-20558(2014).