TFAM
-
Official Full Name
transcription factor A, mitochondrial -
Overview
This gene encodes a key mitochondrial transcription factor containing two high mobility group motifs. The encoded protein also functions in mitochondrial DNA replication and repair. Sequence polymorphisms in this gene are associated with Alzheimers and Parkinsons diseases. There are pseudogenes for this gene on chromosomes 6, 7, and 11. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2012] -
Synonyms
TFAM;transcription factor A, mitochondrial;TCF6;MTTF1;MTTFA;TCF6L1;TCF6L2;TCF6L3;transcription factor 6;transcription factor 6-like 1;transcription factor 6-like 3;mitochondrial transcription factor 1;mitochondrial transcription factor A;transcription factor 6-like 2 (mitochondrial transcription factor)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
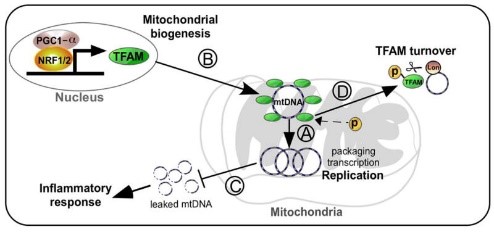
Fig1. Working model explaining how TFAM could impact the progression of neurodegenerative diseases through alteration of mtDNA dynamics. (Inhae Kang, 2018)
What is TFAM protein?
TFAM (transcription factor A, mitochondrial) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10q21. TFAM is a multifunctional DNA-binding protein that plays a crucial role in the maintenance and expression of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). It is essential for cellular bioenergetics and the survival of cells. TFAM contributes to mtDNA maintenance and expression, impacting the cellular energy production and the structural organization of mtDNA within the mitochondria. The TFAM protein is consisted of 246 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 29.1 kDa.
What is the function of TFAM protein?
TFAM is a protein that plays a critical role in regulating mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) transcription and replication. It is a member of the mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) family, which includes other proteins that also regulate mtDNA transcription and replication. TFAM is located in the nucleus and mitochondria, where it binds to mtDNA and promotes its transcription and replication. It also helps to protect mtDNA from damage and degradation. TFAM is essential for normal mitochondrial function, as it is required for the production of the mitochondrial proteins that are necessary for energy production.
TFAM Related Signaling Pathway
TFAM may transmit signals between organelles by regulating calcium ion levels. For example, it can regulate calcium ion signaling by influencing the dynamics of mitochondria-associated membrane structures. The reduction of TFAM can promote the release of mitochondrial DNA into the cytoplasm and activate the cGAS-STING signaling pathway, thus triggering the stress response of the cell. TFAM helps organize and protect the mitochondrial genome by binding to mtDNA. It is also involved in the process of mitochondrial DNA replication and transcription.
TFAM Related Diseases
Because TFAM proteins play a key role in regulating transcription and replication of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), mutations in TFAM genes may lead to mitochondrial diseases. These diseases include mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like onset syndrome (MELAS), Leigh syndrome, and others. Some studies have shown that the expression level of TFAM protein in tumor cells generally increases, which may be related to the increased energy requirements of tumor cells. The expression level of TFAM protein may change in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. TFAM protein may be related to the occurrence and development of cardiovascular diseases. For example, some studies have found that TFAM protein expression levels in cardiomyocytes increase significantly after a myocardial infarction.
Bioapplications of TFAM
In drug development, the recombinant TFAM protein can be used as a target for drug screening, helping researchers evaluate the impact of potential drugs on mitochondrial function, especially in the fields of neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic diseases, and tumor therapies. Since mitochondrial function is closely related to the aging process, TFAM protein is also an important research object in anti-aging research. By regulating the activity of TFAM, it may help to delay the aging process. The recombinant form of the TFAM protein could also be used to develop diagnostic tools to help doctors assess the status of mitochondrial function in patients, especially in the diagnosis of mitochondrial diseases or diseases related to mitochondrial dysfunction.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Natalya Kozhukhar, 2019
Mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) plays an important role in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) transcription and replication. In some experimental settings, TFAM expression parallels parameters of mitochondrial biogenesis, which led to a widespread acceptance of TFAM as marker of mitochondrial biogenesis. The researchers modulated TFAM expression in several experimental systems and observed that it fails to consistently parallel mtDNA copy number and expression of mtDNA-encoded polypeptides. They suggest that the use of TFAM as a marker of mitochondrial biogenesis should be avoided outside of systems in which its performance has been carefully validated.
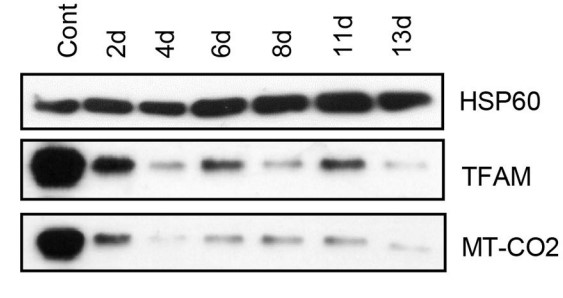
Fig1. TFAM and MT-CO2 protein expression.
 overexpression in human cells.jpg)
Fig2. Effects of endogenous human mitochondrial transcription factor A (hTFAM) overexpression in human cells.
Case Study 2: Wenyan Xu, 2019
MtDNA degradation has emerged as an essential quality control measure to maintain mtDNA and to cope with mtDNA damage resulting from endogenous and environmental factors. Among all types of DNA damage known, abasic (AP) sites, sourced from base excision repair and spontaneous base loss, are the most abundant endogenous DNA lesions in cells. In mitochondria, AP sites trigger rapid DNA loss; however, the mechanism and molecular factors involved in the process remain elusive. Herein, the researchers demonstrate that the stability of AP sites is reduced dramatically upon binding to a major mtDNA packaging protein, mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM). The half-life of AP lesions within TFAM-DNA complexes is 2 to 3 orders of magnitude shorter than that in free DNA, depending on their position. The TFAM-catalyzed AP-DNA destabilization occurs with nonspecific DNA or mitochondrial light-strand promoter sequence, yielding DNA single-strand breaks and DNA-TFAM cross-links. TFAM-DNA cross-link intermediates prior to the strand scission were also observed upon treating AP-DNA with mitochondrial extracts of human cells. In situ trapping of the reaction intermediates (DNA-TFAM cross-links) revealed that the reaction proceeds via Schiff base chemistry facilitated by lysine residues.
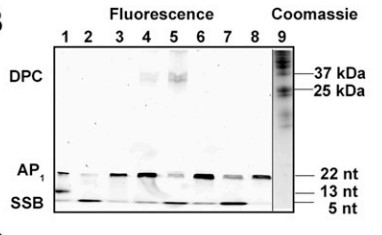
Fig3. TFAM induces the formation of DPCs and SSBs with AP1.
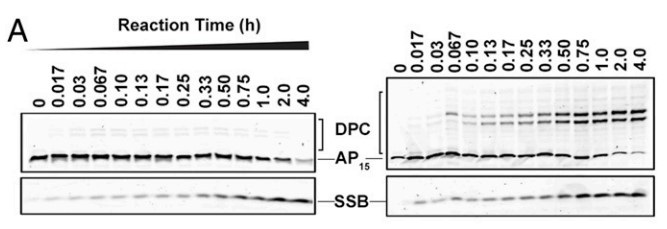
Fig4. Representative denaturing PAGE analysis of reactions of TFAM with AP15.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TFAM-654H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TFAM-6414H)
Involved Pathway
TFAM involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TFAM participated on our site, such as Huntingtons disease, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TFAM were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Huntingtons disease | UQCRC1,TP53,NDUFA3,DNAI1,DNALC4,POLR2H,CASP9,ATP5O,NDUFS1,TBP |
Protein Function
TFAM has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding, bending,RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding,chromatin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TFAM itself. We selected most functions TFAM had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TFAM. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| DNA binding, bending | HMGB3,FOXD1,FOXL1,SRY,HMGB1,LEF1,TOP2A,FOXD4,HHEX,CRIP1 |
| RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | PITX1,TCF3A,ELF1,NKX2-5,HOXA5,JDP2,NFE2L3,CEBPB,NFIA,ATF3 |
| heat shock protein binding | FKBP4,CDC37,DMPK,DNAJC9,DNAJA2,HDAC2,GRXCR2,DNAJA3B,FKBP5,TPR |
| chromatin binding | GATA2,TRIM37,NR5A1A,RNF20,ARID5A,HOXD10,NR5A1,DNAJC2,CCDC111,TMPOA |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | FOSL1,GCM1,GABPA,CREB3L1,ZIC3,KLF13,STAT3,BCL11B,PAX5,MEF2A |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | TULP4,ZNF165,SLC12A9,TFAP2C,DMRTC1C2,IRF1A,ZNF192,ATF4,FOXG1C,POU6F1 |
| protein binding | AVPI1,MAD2L2,MNAT1,NCKIPSD,CCDC25,ASCC1,FAM59A,ZKSCAN5,DRG2,RRS1 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | STAU1,CAST,MTERF,HIST1H4D,C14orf166,NPM3,ETF1,ACAA2,RBM34,CDC5L |
Interacting Protein
TFAM has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TFAM here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TFAM.
ARL6IP1;AGTRAP;TFB1M;C1qbp;TFB2M;MCC;IKBKE;TNIK;ssrna_cg
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Sotgia, F; Whitaker-Menezes, D; et al. Mitochondria "fuel" breast cancer metabolism Fifteen markers of mitochondrial biogenesis label epithelial cancer cells, but are excluded from adjacent stromal cells. CELL CYCLE 11:4390-4401(2012).
- Vadrot, N; Ghanem, S; et al. Mitochondrial DNA Maintenance Is Regulated in Human Hepatoma Cells by Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 beta and p53 in Response to Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha. PLOS ONE 7:-(2012).



