MTAP
-
Official Full Name
methylthioadenosine phosphorylase -
Overview
MTAP is an enzyme that is essential for the salvage pathway for both adenine and methionine synthesis. MTAP catalyzes the cleavage of 5'-methylthioadenosine into adenine and 5-methylthio-D-ribose-1-phosphate. Adenine is then used to generate AMP whereas 5 -
Synonyms
MTAP;methylthioadenosine phosphorylase;S-methyl-5-thioadenosine phosphorylase;c86fus;MSAP;MTAPase;MTA phosphorylase;MeSAdo phosphorylase;5-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Cynomolgus
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is MTAP protein?
MTAP gene (methylthioadenosine phosphorylase) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 9 at locus 9p21. MTAP is an enzyme involved in cellular metabolism that plays a key role in the remedial synthesis pathway of purines and methionine. MTAP is involved in cellular energy balance, DNA synthesis and protein synthesis by catalyzing the conversion of methionine (MTA) to adenosine and methionine. In a variety of tumors, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), MTAP expression is often abnormal, and its deletion is closely related to tumor occurrence, development, and clinical prognosis. The MTAP protein is consisted of 283 amino acids and MTAP molecular weight is approximately 31.2 kDa.
What is the function of MTAP protein?
The MTAP protein functions primarily in the methionine salvage pathway, where it catalyzes the conversion of 5'-deoxy-5'-(methylthio)adenosine (MTA), a byproduct of polyamine synthesis, back into adenine and methionine. This process is crucial for the recycling of these essential molecules and maintaining cellular methionine pools, which are vital for protein synthesis, DNA methylation, and numerous other metabolic processes. The loss or dysfunction of MTAP can disrupt these pathways, potentially leading to various pathological conditions, including certain types of cancer.
MTAP related signaling pathway
The MTAP protein is involved in the methionine salvage pathway, a critical metabolic process that recycles methionine from the byproduct 5'-deoxy-5'-(methylthio)adenosine (MTA). This pathway is essential for maintaining cellular methionine pools, which are vital for protein synthesis, DNA methylation, and polyamine synthesis. Dysregulation of this pathway due to MTAP dysfunction can lead to imbalances in these processes, contributing to carcinogenesis and other pathological conditions.
MTAP related diseases
MTAP dysfunction is associated with several diseases, most notably certain types of cancer, including gliomas and non-Hodgkin lymphomas. This association arises because MTAP plays a key role in the methionine salvage pathway, crucial for maintaining cellular methionine levels necessary for protein synthesis, DNA methylation, and other metabolic processes. Loss of MTAP function can disrupt these pathways, contributing to carcinogenesis. Additionally, MTAP deficiency can lead to increased susceptibility to infections due to its involvement in immune response regulation.
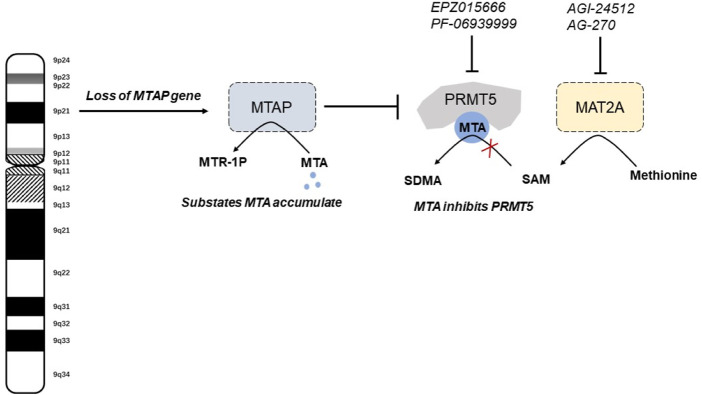
Fig1. The mechanisms of synthetic lethal vulnerabilities in MTAP-deleted tumors. (Na Fan, 2023)
Bioapplications of MTAP
Recombinant human Methionine Adenosyltransferase (rhMTAP) has significant bioapplications, particularly in enhancing methionine recycling and potentially ameliorating conditions associated with MTAP deficiency. By supplementing the methionine salvage pathway, rhMTAP can help maintain cellular methionine levels, crucial for protein synthesis and DNA methylation. This application holds promise for therapeutic interventions in diseases where MTAP dysfunction plays a role, such as certain cancers and other metabolic disorders.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Wen-Hsin Chang, 2023
MTAP deficiency, common in cancers, is linked to poor patient survival, but its impact on tumor progression is not fully understood. The comprehensive analysis revealed that MTAP loss alters tumor-intrinsic pathways, skews the immune environment in favor of tumor growth, and increases PD-L1 expression on cancer cells. This upregulation impairs T cell function, promoting exhaustion and reducing their tumor-killing capacity. In xenograft models, MTAP-deficient tumors showed enhanced growth, especially in immunocompetent mice, and were associated with reduced immune cell infiltration and an increased presence of immunosuppressive cells. These findings highlight the role of MTAP in modulating the tumor-immune interface and suggest potential therapeutic strategies targeting this deficiency.
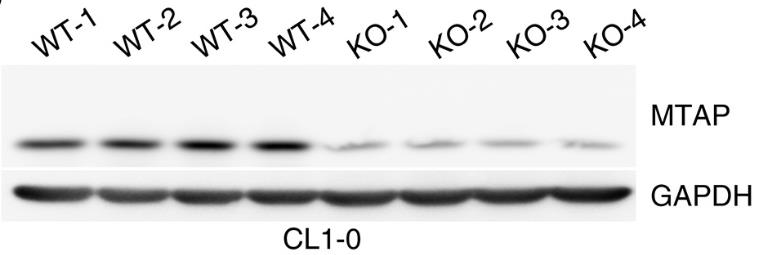
Fig1. MTAP protein expression levels in tumours isolated from NSG-SGM3 humanized mice.
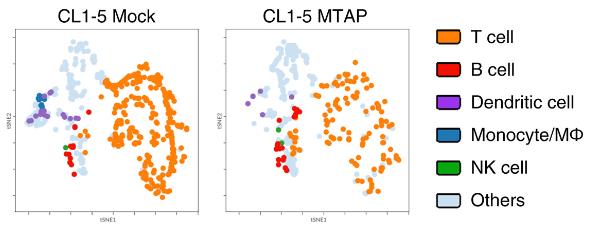
Fig2. ain sub-populations of CD45+ TILs from CL1-5 Mock/MTAP tumours of humanized mice.
Case Study 2: Landon J Hansen, 2019
MTAP deletion is common in glioblastoma and leads to significant epigenetic changes, including hypomethylation of stem cell regulatory genes like PROM1/CD133. This deficiency enhances the formation of glioma stem-like cells, marked by increased PROM1/CD133 expression, boosts tumorigenicity, and correlates with poor patient prognosis. Leveraging the dependency of these MTAP-deficient, CD133+ cells on purines, their depletion can be achieved by blocking _de novo_ purine synthesis, offering a potential therapeutic strategy.
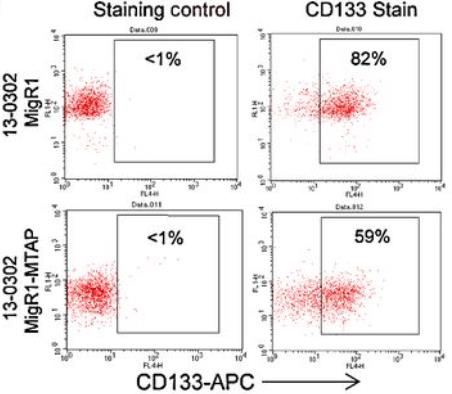
Fig3. Flow cytometry confirmed decreased surface CD133 expression following MTAP restoration.
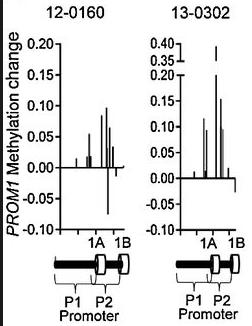
Fig4. Methylation probes in the PROM1 promoter have increased methylation beta value after MTAP restoration.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MTAP-386H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MTAP-5684H)
Involved Pathway
MTAP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MTAP participated on our site, such as Cysteine and methionine metabolism,Metabolic pathways, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MTAP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolic pathways | PIGH,ITPK1A,LPIN2,ATP5F1,PYCRL,ALOX15B,ackA,CYP2C8,CDS2,CKB |
| Cysteine and methionine metabolism | TST,GSS,DNMT3B,GOT2A,DNMT3AB,AHCYL1,MAT2AL,ENOPH1,MDH1,DNMT4 |
Protein Function
MTAP has several biochemical functions, for example, S-methyl-5-thioadenosine phosphorylase activity,phosphorylase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MTAP itself. We selected most functions MTAP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MTAP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| phosphorylase activity | TYMP,PYGMB,PYGMA |
| protein binding | OTUD7B,PIK3C3,ARHGAP1,EZR,SLA,RABGAP1,CENPL,EIF4EBP2,KAZN,BANP |
Interacting Protein
MTAP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MTAP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MTAP.
CENPH;LYRM1;NP;CDC25A;RELB;FOLH1;MAP1LC3A
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Chidlow, G; Wood, JPM; et al. Ocular Expression and Distribution of Products of the POAG-Associated Chromosome 9p21 Gene Region. PLOS ONE 8:-(2013).
- Meyer, S; Fuchs, TJ; et al. A Seven-Marker Signature and Clinical Outcome in Malignant Melanoma: A Large-Scale Tissue-Microarray Study with Two Independent Patient Cohorts. PLOS ONE 7:-(2012).


