Madcam1
-
Official Full Name
mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is an endothelial cell adhesion molecule that interacts preferentially with the leukocyte beta7 integrin LPAM-1 (alpha4beta7), L-selectin, and VLA-4 (alpha4beta1) on myeloid cells to direct leukocytes into mucosal and inf -
Synonyms
MADCAM1;mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1;mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1;MACAM1;MAdCAM-1;hMAdCAM-1;mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Yeast
- His
- Fc
- Non
- SUMO
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- GST
- Flag
Background
What is MADCAM1 protein?
MADCAM1 gene (mucosal vascular addressin cell adhesion molecule 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19p13. The protein encoded by this gene is an endothelial cell adhesion molecule that interacts preferentially with the leukocyte beta7 integrin LPAM-1 (alpha4beta7), L-selectin, and VLA-4 (alpha4beta1) on myeloid cells to direct leukocytes into mucosal and inflamed tissues. It is a member of the immunoglobulin family and is similar to ICAM1 and VCAM1. At least seven alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different protein isoforms have been found for this gene, but the full-length nature of some variants has not been determined. The MADCAM1 protein is consisted of 382 amino acids and MADCAM1 molecular weight is approximately 40.2 kDa.
What is the function of MADCAM1 protein?
MADCAM1 protein is an endothelial cell adhesion molecule mainly expressed in mucosal and inflammatory tissues. It interacts with the β7 integrin LPAM-1 (α4β7), L-selectin, and VLA-4 (α4β1) on the surface of white blood cells to guide white blood cells into the mucosa and inflammatory tissue. MADCAM1 is a member of the immunoglobulin family, similar to ICAM1 and VCAM1. Mutations in MADCAM1 are associated with a variety of diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and certain eye diseases. In inflammatory bowel disease, MADCAM1 promotes the migration of T cells with "gut homing" properties to the gut by interacting with α4β7 integrin. In addition, MADCAM1 also plays a role in regulating the homing and retention of lymphocytes in mucosal tissues, and plays an important role in maintaining mucosal immunity and promoting inflammatory response.
MADCAM1 related signaling pathway
MADCAM1 mediates homing and adhesion of immune cells, especially T cells, by interacting with α4β7 integrins on the surface of white blood cells. MADCAM1 expression is regulated by a variety of cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), which involves multiple signaling pathways, including tyrosine kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). Increased expression of MADCAM1 in inflammatory bowel disease and other autoimmune diseases promotes the inflammatory response and recruitment of immune cells. In addition, MADCAM1 also plays a role in certain cancers, neurological diseases, and eye diseases. These findings suggest that MADCAM1 plays an important role in signaling mechanisms in a variety of pathophysiological processes.
MADCAM1 related diseases
MADCAM1 is a key immune cell adhesion molecule, especially expressed on the surface of vascular endothelial cells in the intestinal mucosa, and interacts with α4β7 integrin to regulate the migration of immune cells such as lymphocytes. MADCAM1 plays a role in a variety of diseases, including inflammatory bowel diseases (such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis), and its targeted drugs (such as Vederizumab and SHP647) are being developed to treat these diseases. MADCAM1 has also been linked to liver diseases such as hepatitis, where loss of MADCAM1 or β7 integrin mitigated experimental immune-mediated hepatitis. In addition, MADCAM1 also plays a role in intestinal immune regulation and may be involved in other diseases such as autoimmune diseases and intestinal tumors.
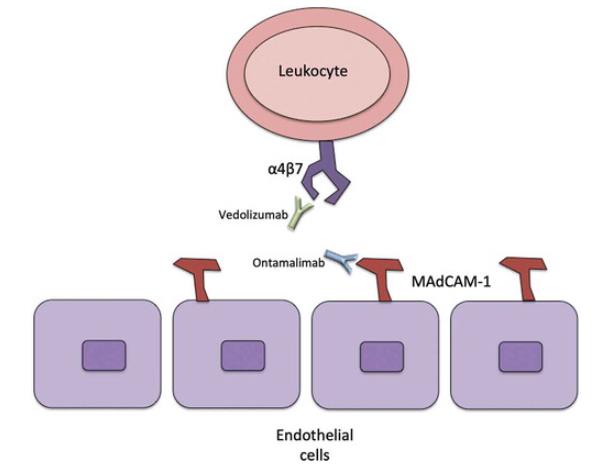
Fig1. Vedolizumab binds to the α4β7 integrin on leukocytes inhibiting its interaction with MAdCAM-1 on endothelial cells. (Sherman Picardo, 2019)
Bioapplications of MADCAM1
The expression of MADCAM1 on the surface of intestinal mucosal vascular endothelial cells makes it a key molecule in regulating immune cell migration. It plays a role in mediating the inflammatory response by interacting with α4β7 integrin on the surface of immune cells and promoting the directed migration of immune cells to the intestinal mucosa. Antibody drugs targeting MADCAM1, such as Vedolizumab, are able to specifically inhibit this interaction, reducing intestinal homing of inflammatory cells and effectively relieving IBD symptoms such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. In addition, the role of MADCAM1 in eye diseases has also received attention, and studies have suggested that it may be related to the pathogenesis of certain eye diseases. These findings suggest that MADCAM1 plays a central role in regulating immune responses and promoting inflammatory processes, and is a potential target for the treatment of related diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Kun Peng, 2021
Patients with IBD may have eye symptoms, but the cause is unknown. By giving mice oral DSS to induce chronic colitis and using ERG to assess retinal function, abnormal ERG amplitude was found in mice with colitis, accompanied by severe degeneration of bipolar and ganglion cells, while outer retinal neurons were less affected. In addition, the retinal inflammatory response is enhanced during colitis, including microglial activation, lymphocyte infiltration, and cytokine/chemokine production. MAdCAM-1 is upregulated in retinal microvessels, especially in superficial and deep plexiform areas, and recruits intestinal homing CD4+ T cells to co-locate with bipolar and ganglion cells during colitis. Accordingly, depletion of CD4+ T cells in vivo or blocking MAdCAM-1 significantly reduced retinal inflammation and neurodegenerative changes caused by colitis.
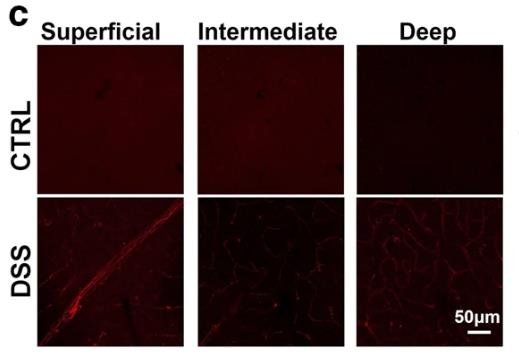
Fig1. Shown was MAdCAM-1 expression in the three vascular plexuses and MAdCAM-1+ vessels were calculated in each plexus.
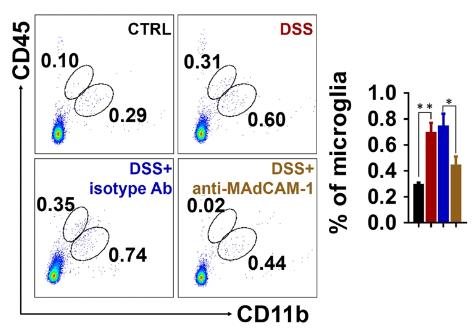
Fig2. Microglia infiltration was analyzed by flow cytometry.
Case Study 2: T Oshima, 2001
MAdCAM-1 is an endothelial cell adhesion molecule that controls lymphocyte migration to the intestinal mucosa. Although MAdCAM-1 is known to play a role in chronic intestinal inflammation, the regulatory mechanisms of its expression have been poorly studied. Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) was found to induce MAdCAM-1 mRNA and protein expression in a dose - and time-dependent manner by activating tyrosine kinase, p42/44, p38 MAPK, and NF-κB/PARP signaling pathways. In addition, the distribution of MAdCAM-1 between endothelial cells is regulated by cytokines such as TNF-α, a process that involves the activation of MAPKs and NF-κB.
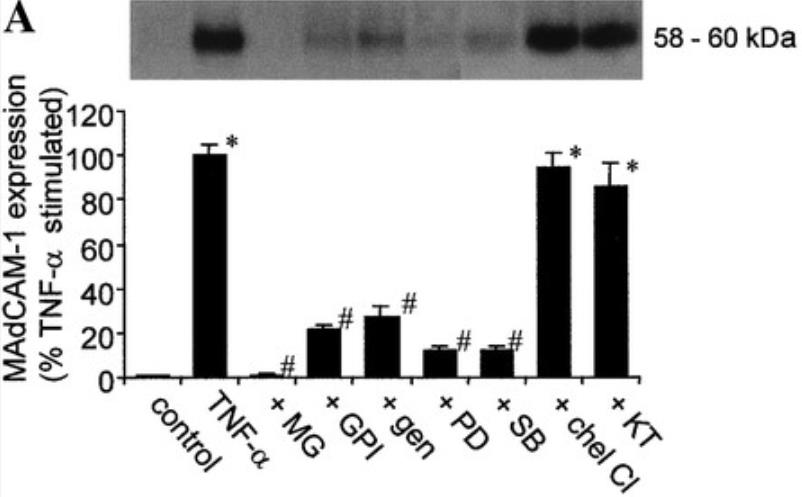
Fig3. Effect of signal transduction blockers on mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule (MAdCAM) in bEnd.3 cells.
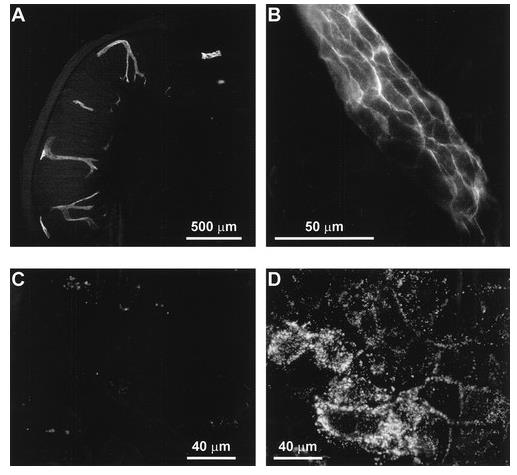
Fig4. Immunofluorescent staining of MAdCAM on SVEC.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MADCAM1-3983H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MADCAM1-2538H)
Involved Pathway
Madcam1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Madcam1 participated on our site, such as Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs),Intestinal i,ne network for IgA production, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Madcam1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | PVRL3,HLA-DRB3,CLDN22,HLA-DRB4,CLDN17,Itgam&Itgb2,GLYCAM1,CD8B1,CLDNC,Icosl |
| Intestinal i | HLA-DRA,HLA-DRB5,ITGB7,PIGR,HLA-DOB,TNFSF13,TGFB1A,CD80,HLA-DMA,HLA-DOA |
| ne network for IgA production | CCL25B,HLA-DRB1,TNFSF13,CCL28,BLB1,HLA-DPB1,LTBR,CD80,IL4,HLA-DOA |
Protein Function
Madcam1 has several biochemical functions, for example, integrin binding involved in cell-matrix adhesion. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Madcam1 itself. We selected most functions Madcam1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Madcam1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
Madcam1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Madcam1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Madcam1.
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


