LRPAP1
-
Official Full Name
low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein associated protein 1 -
Overview
LRPAP1 is involved with trafficking of certain members of the LDL receptor family including LRP1 and LRP2. It is a glycoprotein that binds to the alpha-2-macroglobulin receptor, as well as to other members of the low density lipoprotein receptor family. It acts to inhibit the binding of all know ligands for these receptors, and may prevent receptor aggregation and degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby acting as a molecular chaperone. It may be under the regulatory control of calmodulin, since it is able to bind calmodulin and be phosphorylated by calmodulin-dependent kinase II. -
Synonyms
LRPAP1;low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein associated protein 1;LRPAP1;RAP;MRAP;A2RAP;HBP44;A2MRAP;OTTHUMP00000115346;MGC138272;low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein associated protein 1;alpha-2-macroglobulin receptor-associated protein;alpha-2-MRAP;lipoprotein receptor associated protein;alpha-2-macroglobulin receptor-associated protein 1;low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-associated protein 1;low density lipoprotein-related protein-associated protein 1 (alpha-2-macroglobulin receptor-associated protein 1)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Chicken
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- Insect Cells
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- Myc
- GST
- GFP
- DDK
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is LRPAP1 protein?
LRPAP1 gene (LDL receptor related protein associated protein 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 4 at locus 4p16. LRPAP1 is also known as receptor-associated protein (RAP). It is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone protein and an inhibitor of LDL receptor-associated protein 1 (LRP1) and related receptors. LRPAP1 is associated with a variety of physiological and pathological processes. In terms of virus infection, LRPAP1 is related to the escape mechanism of virus infection. In addition, inhibition or lack of LRPAP1 has been linked to a variety of neurodegenerative diseases. The LRPAP1 protein is consisted of 357 amino acids and LRPAP1 molecular weight is approximately 41.5 kDa.
What is the function of LRPAP1 protein?
The LRPAP1 protein, also known as Receptor-Associated Protein (RAP), functions as an endoplasmic reticulum chaperone and an inhibitor of LDL Receptor-Related Protein 1 (LRP1) and related receptors. It plays a role in the regulation of lipoprotein metabolism and has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases and immune responses, including the modulation of microglial phagocytosis, amyloid-beta aggregation, and the evasion of cellular innate immunity during viral infections.
LRPAP1 related signaling pathway
LRPAP1 plays a role in lipoprotein metabolism and has been linked to the regulation of the LDL Receptor-Related Protein 1 (LRP1). Recent research indicates that LRPAP1 is involved in the evasion of viruses from cellular innate immunity, particularly by binding to and triggering the degradation of IFNAR1, a key component in the interferon signaling pathway. This interaction facilitates virus escape from the host's immune response, highlighting a potential role for LRPAP1 in viral infections and immunity.
LRPAP1 related diseases
LRPAP1 has been implicated in several diseases, particularly neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. It plays a role in the microglial response, potentially regulating functions such as phagocytosis and amyloid-beta aggregation. Furthermore, LRPAP1 is noted for its involvement in the immune response, including facilitating virus evasion from cellular innate immunity. Research also indicates that LRPAP1 may be a key player in the micropapillary pattern metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma, suggesting a role in cancer progression.
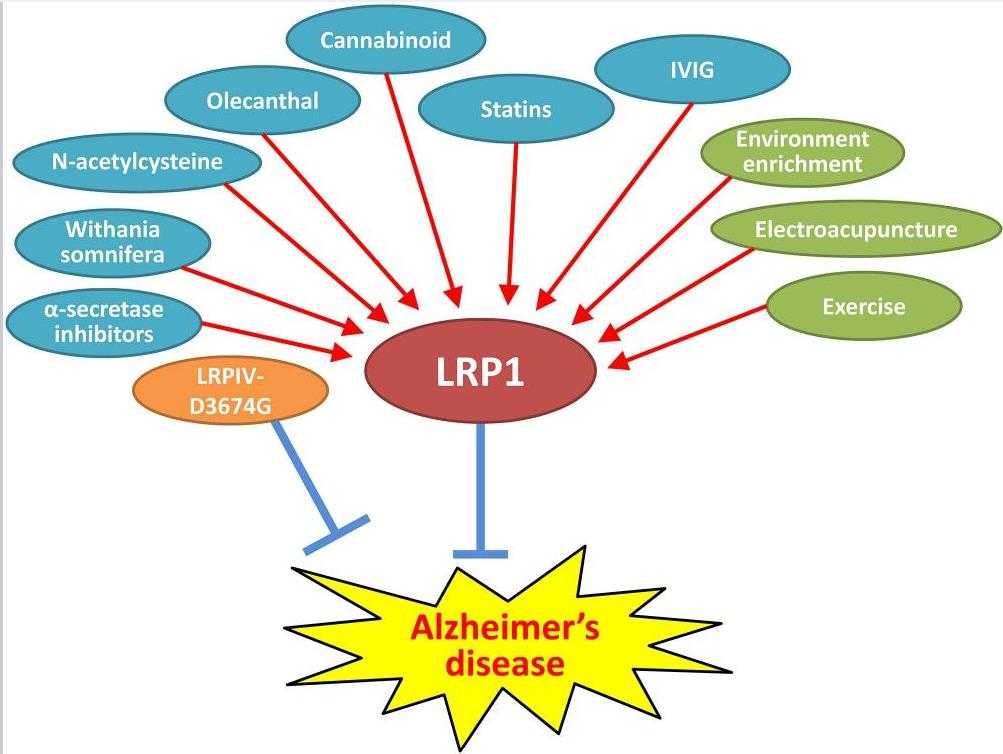
Fig1. Potential therapeutics for AD targeting LRP1. (Mitsuru Shinohara, 2017)
Bioapplications of LRPAP1
LRPAP1 plays a crucial role in various bioapplications, particularly in the field of cancer research. It is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, making it a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of certain types of cancer. Additionally, LRPAP1 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease, as it interacts with the amyloid precursor protein (APP) and affects its processing and clearance. The modulation of LRPAP1 activity may therefore hold promise for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for these diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Huangcan Li, 2023
Interferon (IFN) signaling is key to fighting pathogens, but viruses often disrupt this process internally. This research reveals a new external mechanism: the SARS-CoV-2 and EV71 viruses increase production of LRPAP1, which binds to and degrades the IFNAR1 receptor, enhancing viral infections. A small LRPAP1 peptide can mimic this effect, promoting viral infections, while the LRPAP1 inhibitor α2M can prevent it.
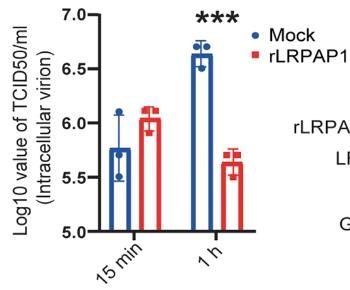
Fig1. Intracellular virions were harvested and subjected to viral titration.
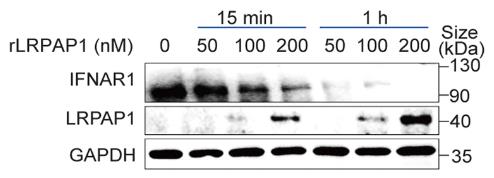
Fig2. Immunoblots of lysates in HEK-293T cells which were treated with the indicated concentration of rLRPAP1 for 15 min or 1 h.
Case Study 2: Kyle M Reid, 2023
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-associated protein 1 (LRPAP1), also known as receptor associated protein (RAP), is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone that inhibits LDL receptor related protein 1 (LRP1). It is unclear if LRPAP1 is physiologically released to regulate LRP1 and cell functions. This study using microglial cell lines found that LRPAP1 is released when cells are activated by lipopolysaccharide or stressed by tunicamycin. This LRPAP1 inhibits microglial phagocytosis and amyloid-beta (Aβ) uptake and aggregation. Thus, extracellular LRPAP1 may regulate microglial functions and Aβ pathology, suggesting it could broadly modulate cell functions.

Fig3. LRPAP1 release into the wells of treated CHME3 cultures, represented as nanomolar concentration.
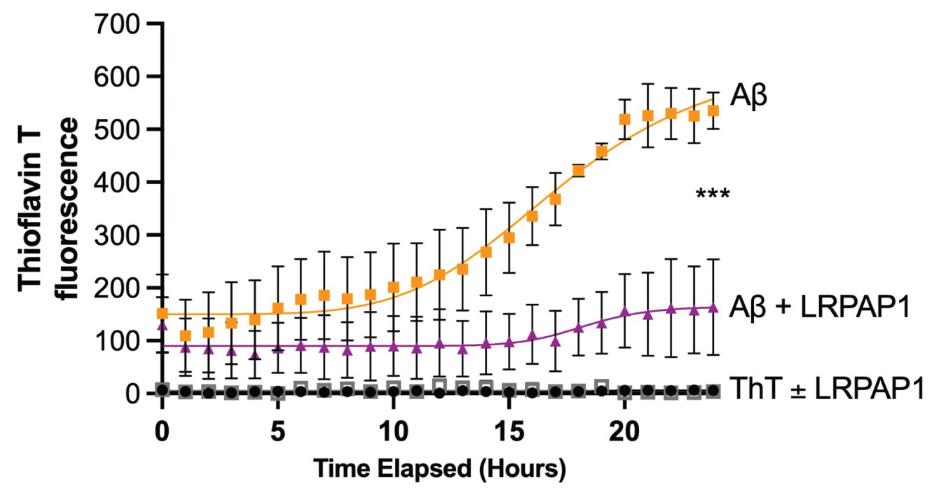
Fig4. LRPAP1 inhibits fibrillization of Aβ.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LRPAP1-6640H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LRPAP1-4687H)
Involved Pathway
LRPAP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LRPAP1 participated on our site, such as Lissencephaly gene (LIS1) in neuronal migration and development,Reelin signaling pathway,Signaling events mediated by the Hedgehog family, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LRPAP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Lissencephaly gene (LIS1) in neuronal migration and development | NDEL1,MAP1B,DYNLT1,DAB1,KATNA1,VLDLR,NUDC,DCX |
| Reelin signaling pathway | VLDLR,DAB1,MAP1B |
| Signaling events mediated by the Hedgehog family | PTHLH |
Protein Function
LRPAP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, asialoglycoprotein receptor activity,heparin binding,lipase binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LRPAP1 itself. We selected most functions LRPAP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LRPAP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | GYPC,DCUN1D5,PFKM,CCNK,TRPC5,ZC4H2,SVIL,E2F8,RAB33B,BLNK |
| low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding | DNAJA1,LANCL1,DKK1,AP2M1,MESDC2,SACS,CRP,ARRB2,LDLRAP1,SNX17 |
| asialoglycoprotein receptor activity | ASGR1,ASGR2 |
| heparin binding | AAMP,UBE4A,ECM2,HDGF,CYR61,SELL,FGF2,HRG,VEGFAA,CCL7 |
| lipase binding | FAF2,APOA5,APOB,PLIN5,GPIHBP1 |
| receptor antagonist activity | ESR2,AGTR2,ADH7,DKK1,IL18BP |
| unfolded protein binding | RP2,CLPXA,DNAJB2,AIPL1,CCT6B,HSPA6,PFDN6,HSPD1,CHAF1B,DNAJB6 |
| very-low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding | PCSK9,APOEA,APOE,APOEB,Reln |
Interacting Protein
LRPAP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LRPAP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LRPAP1.
VLDLR;LPL;LRP1;SMAD2;SORL1;PPM1G;RANBP2;POLA2;RTN4;ETV7;SUMO3;Lrp4;SORT1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Singh, NK; Banerjee, BD; et al. APOE and LRPAP1 gene polymorphism and risk of Parkinson's disease. NEUROLOGICAL SCIENCES 35:1075-1081(2014).
- Fred, RG; Boddeti, SK; et al. Imatinib mesylate stimulates low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1-mediated ERK phosphorylation in insulin-producing cells. CLINICAL SCIENCE 128:17-28(2015).


