IDO1
-
Official Full Name
indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 -
Overview
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is an enzyme that is responsible for converting tryptophan to kynurenines. IDO is expressed by a wide variety of tissues and IDO can be upregulated by interferon gamma. IDO modulates levels of the amino acid tryptophan, which is vital for cell growth, but is also involved in the suppression of the immune response. IDO may be involved in thesuppression of the immune response to tumours and blocking the IDO pathway may be a potential target for immunotherapy. -
Synonyms
IDO1;indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1;IDO, INDO, indoleamine pyrrole 2,3 dioxygenase;indole 2,3-dioxygenase;indolamine 2,3 dioxygenase;indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase;IDO;INDO;IDO-1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- Yeast
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- DDK
- Myc
- Fc
Background
What is IDO1 protein?
IDO1 gene (indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 8 at locus 8p11. This gene encodes indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) - a heme enzyme that catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in tryptophan catabolism to N-formyl-kynurenine. This enzyme acts on multiple tryptophan substrates including D-tryptophan, L-tryptophan, 5-hydroxy-tryptophan, tryptamine, and serotonin. This enzyme is thought to play a role in a variety of pathophysiological processes such as antimicrobial and antitumor defense, neuropathology, immunoregulation, and antioxidant activity. The IDO1 protein is consisted of 403 amino acids and IDO1 molecular weight is approximately 45.3 kDa.
What is the function of IDO1 protein?
IDO1 is an enzyme that plays a key role in the tryptophan metabolic pathway by catalyzing the conversion of tryptophan to the N-form of tryptophan, which is the first step in tryptophan degradation. IDO1 plays a role in a variety of biological processes, including modulating immune responses, influencing cell proliferation and differentiation, and playing a role in certain pathological states such as cancer and autoimmune diseases. In immune regulation, IDO1 inhibits T cell activity by depleting tryptophan, potentially affecting immune escape mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. In addition, the activity of IDO1 is also related to the maternal immune tolerance to the embryo during pregnancy.
IDO1 related signaling pathway
The IDO1 protein is involved in the regulation of tryptophan metabolism through its enzyme activity, thus affecting a variety of signaling pathways. In terms of immune regulation, IDO1 degrades tryptophan to produce kynuridine, a metabolite that can inhibit the proliferation and activation of T cells, thereby potentially promoting immune escape in the tumor microenvironment. In addition, activation of IDO1 can promote the formation of regulatory T cells (Tregs), further suppressing the immune response. During pregnancy, IDO1 contributes to maternal immune tolerance to the embryo. Signaling in IDO1 also involves interactions with a variety of cytokines and immune receptors, such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and interleukin (ILs) signaling pathways, affecting inflammatory responses and immune cell function. The activity of IDO1 is regulated by a variety of factors, including activation of its transcription factors such as NF-κB and STAT3, as well as interactions with co-stimulatory molecules and cell surface receptors.
IDO1 related diseases
IDO1 is associated with many diseases, especially closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors. In the tumor microenvironment, the high expression of IDO1 is associated with tumor immune escape, which inhibits the activity of immune cells and promotes tumor growth by consuming tryptophan and producing the metabolite kynuridine. IDO1 expression is increased in a variety of tumor tissues, such as breast cancer, colorectal cancer, liver cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, lung cancer, endometrial cancer, melanoma, pancreatic cancer, osteosarcoma, and its up-regulated expression is positively correlated with poor prognosis and tumor progression and metastasis. In addition, IDO1 also plays a role in Alzheimer's disease, and its inhibitors may help restore glucose metabolism in the brain's astrocytes and improve cognitive function.
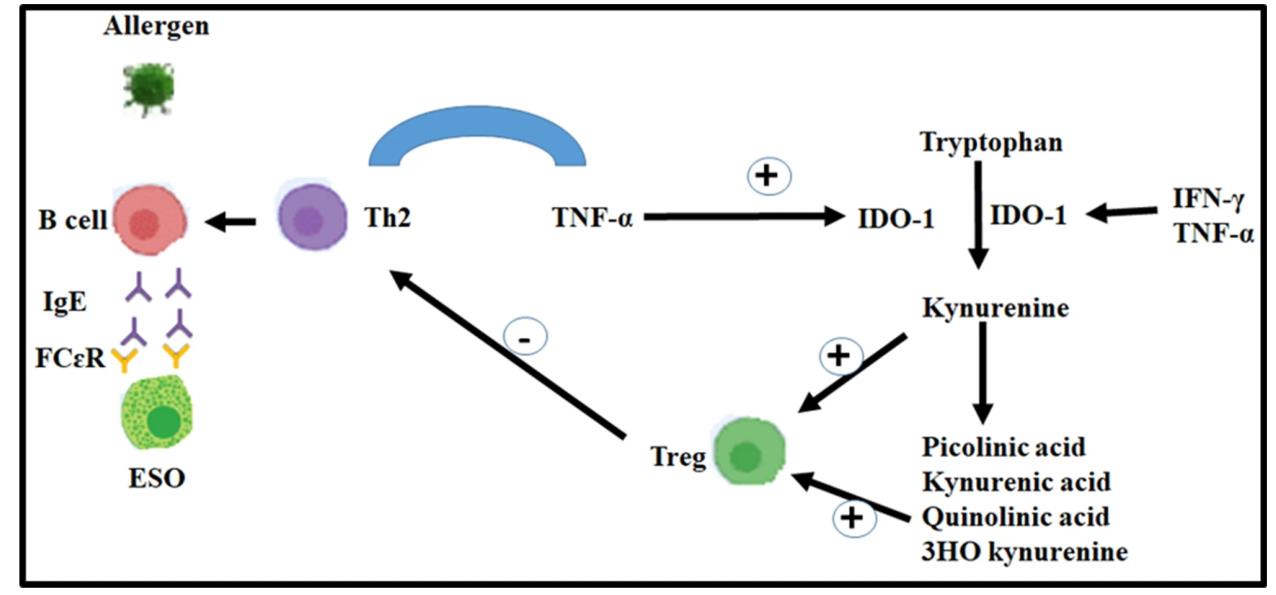
Fig1. The production of cytokines, such as TNF-α, in the process of allergic diseases causes the production of IDO enzymes. (Seyed-Alireza Esmaeili, 2022)
Bioapplications of IDO1
It is mainly used to study the biological function of the enzyme IDO1 and its role in disease, especially its key role in cancer immune escape. In drug development, rhIDO1 is used to screen for small molecule compounds that can inhibit its activity, which could become novel therapies for certain types of cancer. For example, through high-throughput screening of natural product libraries, researchers have identified a number of new IDO1 inhibitors that show inhibitory activity against rhIDO1 and may have the potential to be developed into anticancer drugs.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Chengtao Sun, 2022
Despite aggressive treatments, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) can be lethal due to its aggressive nature. The enzyme IDO1, which drives the kynurenine pathway in the immune system, may help cancer cells evade destruction when overactive. Its specific impact on DLBCL is not well understood. This research found higher IDO1 levels in DLBCL, linked to worse outcomes and lower survival rates. Blocking IDO1 reduced DLBCL cell growth in lab tests and slowed tumor formation in living organisms. IDO1 inhibition lowered MDM2 and raised TP53 levels in OCI-Ly10 cells, as shown by RNA sequencing. This suggests that IDO1 inhibition could decrease MDM2, a p53 suppressor, and restore p53 in DLBCL cells, leading to cell cycle halt and cell death. It also triggered apoptosis, with increased PUMA and BAX, and decreased BCL2 and BCL-XL. Furthermore, p21, a p53 target, increased during cell cycle arrest.
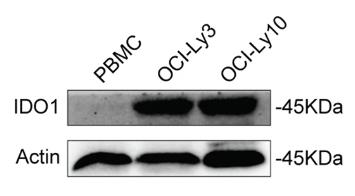
Fig1. WB analysis of IDO1 protein expression in OCI-Ly3, OCI-Ly10, and PBMCs.
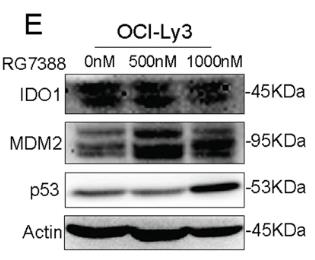
Fig2. WB of OCI-Ly3 cells treated with RG7388 for 24 h.
Case Study 2: Xin Fang, 2022
IDO1, an enzyme that drives tryptophan metabolism and has immunosuppressive effects, may also influence the expression of NKG2D ligands (NKG2DL) on tumor cells by modulating ADAM10, an enzyme involved in shedding NKG2DL. This study in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) showed a negative link between IDO1 expression and NKG2DL, and a positive one with ADAM10. IDO1 seemed to regulate ADAM10 and NKG2DL expression through the IDO1-Kyn-AhR pathway. Mice lacking IDO1 had slower tumor growth and better NK cell function. Both IDO1 inhibitors and a combination of these inhibitors with NK cells showed enhanced therapeutic effects in NSCLC.
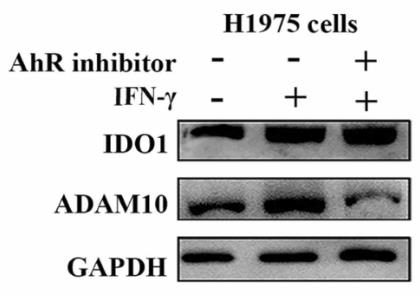
Fig3. Western blot analysis of the expressions of IDO1 and ADAM10 in H1975 cells treated with IFN-γ + SR1.
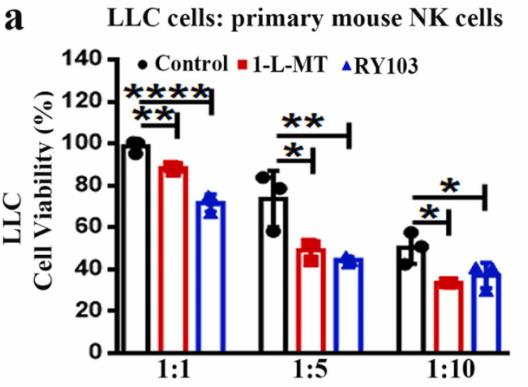
Fig4. The viabilities of LLC cells in the cocultures of IDO1 inhibitor pretreated LLC cells with NK cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (IDO1-008H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (IDO1-101HFL)
Involved Pathway
IDO1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways IDO1 participated on our site, such as Tryptophan metabolism,Metabolic pathways,African trypanosomiasis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with IDO1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolic pathways | ASNS,HOGA1,ACOX2,SGMS2,B4GALNT1,MMAB,POLR2GL,MGAT4A,DNMT3B,CHPT1 |
| Tryptophan metabolism | ALDH3A2A,IL4I1,KYNU,GCDHB,ALDH9A1B,ALDH7A1,AANAT,CCBL2,ASMT,AOX4 |
| African trypanosomiasis | THOP1,ICAM1,PRKCG,IFNG,HBB,IL10,TNF,FAS,PRKCB,LAMA4 |
Protein Function
IDO1 has several biochemical functions, for example, electron carrier activity,heme binding,indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by IDO1 itself. We selected most functions IDO1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with IDO1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metal ion binding | ZNF193,RBM26,TRIM2A,MBNL1,PTGS2,CYP2K18,FREM1,ZFAT,NT5C3L,AGBL1 |
| tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase activity | TDO2B,TDO2A,TDO2,IDO2 |
| indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity | IDO2 |
| electron carrier activity | SDHB,ACOX1,COX7A1,GRXCR1,CYCSB,ME2,GCDH,ACADS,CYP19A1,SH3BGRL3 |
| heme binding | HBB-B2,CYP2D9,CYP2B6,CYP46A1,PTGIS,CYP21A1,CYP19A1A,HBA2,CYP2D6,CYP4B1 |
Interacting Protein
IDO1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with IDO1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of IDO1.
q8d0v8_yerpe;PPP1R16A;DDX24;TERF2IP
Resources
Research Area
Cancer Drug TargetsInflammatory Mediators
MDSC Intracellular Signaling Factors
Immune Checkpoints
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Theate, I; van Baren, N; et al. Extensive Profiling of the Expression of the Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase 1 Protein in Normal and Tumoral Human Tissues. CANCER IMMUNOLOGY RESEARCH 3:161-172(2015).
- Kang, W; Marasco, WA; et al. Anti-tat Hutat2:Fc mediated protection against tat-induced neurotoxicity and HIV-1 replication in human monocyte-derived macrophages. JOURNAL OF NEUROINFLAMMATION 11:-(2014).


