HIF1A
-
Official Full Name
hypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit (basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor) -
Overview
Hypoxia, a condition of low tissue O2 concentration, plays an important role in normal physiological processes and tumor formation. Under hypoxic conditions mammalian cells up regulate the expression of hypoxic genes, including induction of angiogenesis and a switch to anaerobic metabolism, in order to survive. HIF-1 (Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1) is one of the key regulators of the transcriptional response to oxygen deprivation (1). HIF-1 is composed of two subunits, HIF-1alphaand HIF-1beta also known as aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT)) that are members of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) (bHLH-PAS) family of transcription factors. HIF-1 is essential for angiogenesis, embryonic development, and is associated with tumor progression, erythropoiesis, vascular development/remodeling, vasodilation, and glucose/energy metabolism. The over expression of HIF-1alphahas been demonstrated in many common human cancers including prostate and breast, in which HIF-1alpha levels are associated with increase vascularitry and tumor progression. Besides physiological hypoxia, genetic abnormalities frequently detected in human cancers, such as loss of function mutations (Von Hippel-Lindau, p53, and PTEN), are associated with induction of HIF1 activity and expression of HIF-1-inducible genes (1). -
Synonyms
HIF1A;hypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit (basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor);hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha;bHLHe78;HIF 1alpha;HIF1;MOP1;PASD8;HIF-1-alpha;member of PAS protein 1;ARNT interacting protein;ARNT-interacting protein;member of PAS superfamily 1;PAS domain-containing protein 8;basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS protein MOP1;class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 78;hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha isoform I.3;hypoxia-inducible factor 1, alpha subunit (basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor);HIF-1alpha;HIF1-ALPHA
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Cattle
- Pig
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- Insect Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- Non
- S
- MBP
- ABP
- Strep
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
Background
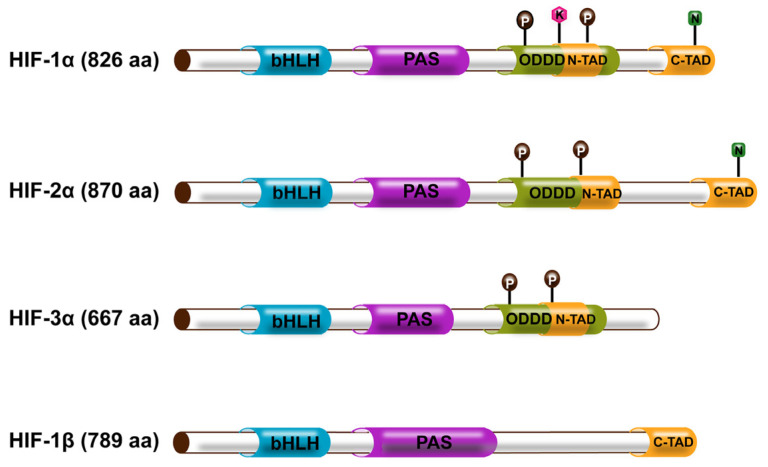
Fig1. The structure of the HIF family. (Jiaqian You, 2023)
What is HIF1A Protein?
HIF1A gene (hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 14 at locus 14q23. This gene encodes the alpha subunit of transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1), which is a heterodimer composed of an alpha and a beta subunit. HIF-1 functions as a master regulator of cellular and systemic homeostatic response to hypoxia by activating transcription of many genes, including those involved in energy metabolism, angiogenesis, apoptosis, and other genes whose protein products increase oxygen delivery or facilitate metabolic adaptation to hypoxia. HIF-1 thus plays an essential role in embryonic vascularization, tumor angiogenesis and pathophysiology of ischemic disease. The HIF1A protein is consisted of 826 amino acids and HIF1A molecular weight is approximately 92.7 kDa.
What is the Function of HIF1A Protein?
The HIF1A protein is a transcription factor that primarily plays a role in the cell's response to hypoxic environments. HIF1A binds to the promoter region of specific genes and regulates the expression of these genes, which are normally involved in hypoxia response, angiogenesis, energy metabolism, and cell survival. HIF1A promotes the formation of new blood vessels by activating the expression of genes such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) to meet the oxygen demand of hypoxic tissues. Under hypoxia conditions, HIF1A can promote the expression of glycolytic-related enzymes and enhance the ability of cells to produce energy through the glycolytic process. HIF1A can affect the survival of cells in hypoxic environment by regulating the balance of anti-apoptotic factors and pro-apoptotic factors. HIF1A plays a role in tissue repair processes, such as regulating inflammatory responses and cell proliferation during wound healing.
HIF1A Related Signaling Pathway
At normal oxygen levels, HIF-1α is hydroxylated by proline hydroxylase (PHDs) and binds to the Von Hippel-Lindau protein (pVHL) before being ubiquitinated, leading to its degradation via the proteasome pathway. Under hypoxic conditions, PHDs activity is inhibited, and HIF-1α is stabilized and transferred to the nucleus. HIF-1α binds to HIF-1β to form heterodimers, which bind to hypoxic response elements (HRE) on its target genes, promoting the transcription and expression of these genes. HIF1A activates a series of adaptive responses that focus on upregulating transcriptional cascades beneficial for tissue protection and adaptation, including protective effects on multiple organs under acute hypoxia conditions. HIF1A stability and activity are affected by factors associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, including TCA cycling, electron transport chain components, and mitochondrial respiration, and HIF1A activation can in turn affect mitochondrial function.
HIF1A Related Diseases
HIF1A is highly expressed in a variety of solid tumors and hematological malignancies, promoting tumor cell proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, metabolic reprogramming and immune escape, and is a potential target for tumor therapy. HIF1A is involved in the hypoxia response of the cardiovascular system, affects energy metabolism and angiogenesis, and is closely related to the development of cardiovascular diseases. It is also associated with a variety of organ diseases, such as lung disease, liver disease, bone disease and so on. HIF1A is involved in erythrocyte production by regulating the expression of EPO, and the regulation of its activity is helpful for the treatment of anemic diseases such as renal anemia.
Bioapplications of HIF1A
Drug development based on HIF1A signaling pathway is actively underway, including prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors, HIF-1α protein stable modifier enzymes, etc., which show potential in the treatment of renal anemia, tumors, etc. As a key regulator of tumor adaptation to hypoxic microenvironment, HIF1A has become a hot target of anti-tumor drug research by regulating the expression of many target genes related to tumor cell proliferation, survival, angiogenesis and metastasis. Targeting HIF1α or its interaction with p300 can inhibit tumor growth, and related inhibitors are already in drug development and clinical trials. HIF1A regulates the expression of erythropoietin (EPO), and related drugs such as Roxallistat treat renal anemia through the HIF1A pathway, which has been undergoing clinical trials in China.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Wei Kou, 2018
The aim of this study was to survey the effect of hypoxia on the Th17 response in AR patients by investigating the action of hypoxia-influenced signaling pathways on Th17 differentiation. 23 AR patients and 15 healthy controls were recruited for this study. The amount of ARNT combined with either HIF-1α or AhR was determined after the exposure of 2-(1H-Indol-3-ylcarbonyl)-4-thiazolecarboxylic acid methyl easter (ITE) with normoxia and hypoxia. The results showed that HIF-1α and AhR expression were higher in CD4+T cells from AR patients than in those from healthy controls. In a hypoxic environment, the expression of HIF-1α was elevated in CD4+T cells of both AR patients and healthy controls. These effects were arisen from HIF-1α out-competing AhR for ARNT binding which limited the activity of the AhR pathway.
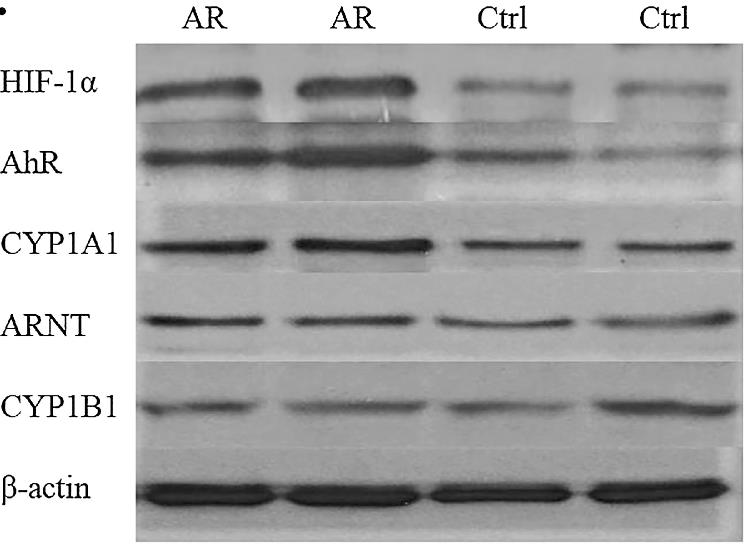
Fig1. The protein expression of HIF-1α, AhR and CYP1A1 in AR patients and controls were detected by western blotting.
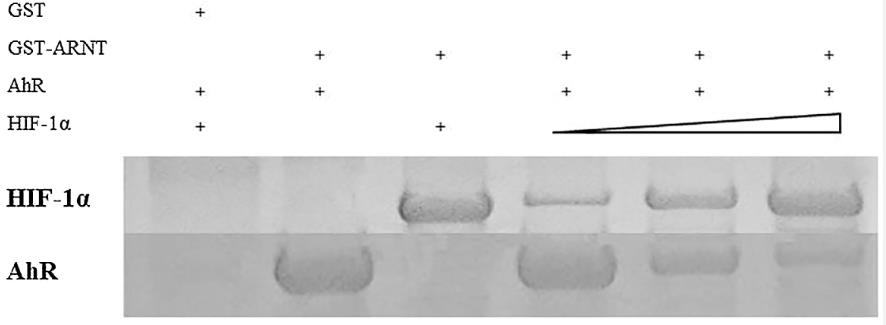
Fig2. Different amount of purified HIF-1α and AhR recombinant protein were analyzed by GST pull-down assay and Western Blotting.
Case Study 2: Yiting Geng, 2024
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted therapy is an important treatment for RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC), but the resistance mechanism remains unclear. Here, the differential expression of circRNAs between Cetuximab sensitive and resistant cell lines was analyzed using whole-transcriptome sequencing. The expression of circHIF1A was significantly higher in LIM1215-R than in LIM1215. When treated with Cetuximab, downregulation of circHIF1A level weakened the proliferation and clonal formation ability of LIM1215-R, caused more cells to enter G0-G1 phase, and significantly reduced the basal respiration, ATP production, and maximal respiration, as well as the glycolytic capacity and glycolytic reserve. Mechanistically, circHIF1A can upregulate the level of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 A (HIF1A) by competitively binding to miR-361-5p, inducing the overexpression of enzymes such as glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) and lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA). In a xenograft model, inhibition of circHIF1A expression increased the sensitivity to Cetuximab treatment.
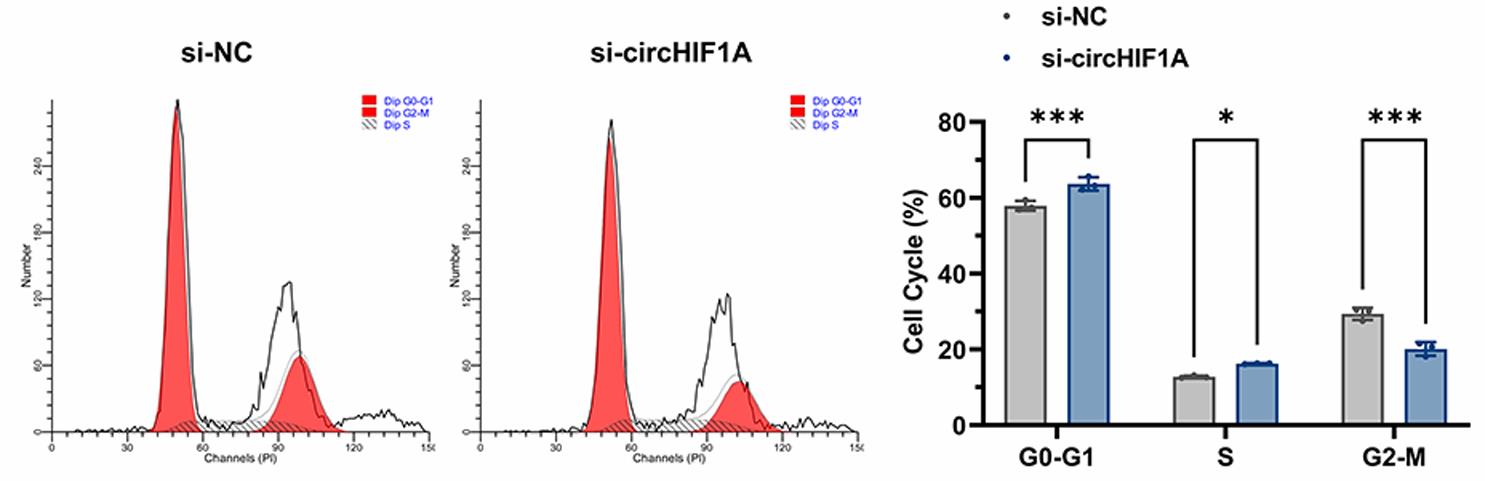
Fig3. The effect of circHIF1A levels on the cell cycle.
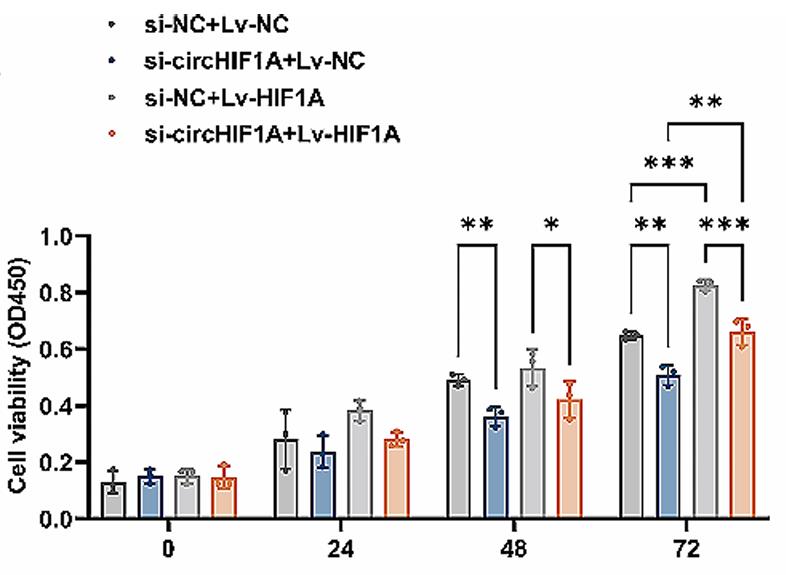
Fig4. Effect of HIF1A overexpression on the proliferation of LIM1215-R with circHIF1A downregulated.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (HIF1A-5279H)
.
.jpg )
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (HIF1A-01H)
Involved Pathway
HIF1A involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways HIF1A participated on our site, such as HIF- signaling pathway,mTOR signaling pathway,Thyroid hormone signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with HIF1A were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Proteoglycans in cancer | CAV1,CAV2,ARHGEF1,TLR2,RRAS2,CD44,TIMP3,TGFB1,IL12B,MMP9 |
| Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | MED27,GATA4,GSK3B,SIN3A,ATP1B3,MAPK1,MDM2,SLC9A1,SLC16A10,MTOR |
| mTOR signaling pathway | INS,RICTOR,EIF4E2RS1,RPS6,STK11,PDPK1,CAB39L,TSC1A,AKT2,IKBKB |
| Renal cell carcinoma | MET,HRAS,ARNT,RBX1,FH1,TGFB2,ARNT2,EGLN1,FLCN,TGFB3 |
| Choline metabolism in cancer | PIK3CG,PIP5K1A,AKT2,DGKD,HRAS,PLA2G4C,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,WASF1,PIK3CA,DGKA |
| HIF- signaling pathway | PRKCB,LTBR,NPPA,ERBB2,ENO2,PIK3R1,NOX3,LDHA,AKT1,TEK |
| Pathways in cancer | FZD10,PTEN,CDH1,MMP9,NRAS,FZD8,ARAF,ITGB1,Fasl,STK4 |
| Central carbon metabolism in cancer | MAPK1,TP53,SCO2,SIRT3,PIK3R3,RAF1,FGFR2,RET,PGAM2,C12orf5 |
Protein Function
HIF1A has several biochemical functions, for example, Hsp90 protein binding,enzyme binding,histone acetyltransferase binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by HIF1A itself. We selected most functions HIF1A had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with HIF1A. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| nuclear hormone receptor binding | BUD31,CRY1,SIRT1,MYOD1,TACC2,NCOA2,SNW1,TCF7L2,NRIP1,EP300 |
| transcription factor activity, transcription factor binding | CRY2,ASCL1B,LDB1A,LDB2B,TP63,MTA2,CRY1,LDB1B,ASCL1,NEUROG1 |
| enzyme binding | TSPAN17,SIRT3,POR,Slc4a2,HIST1H2AG,PRTN3,AKIRIN2,NOTCH1,TOP2A,SCARB2 |
| histone deacetylase binding | HDAC1,ZNHIT1,ANKRD1,TOP2A,SOD3,KAT2B,TAL1,MAPK8,CAMTA2,BRMS1L |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | SUMO2,TRIB1,FAF2,SNCAIP,CDC34B,HSPA1A,EGR2,HSPD1,ARRB1,USP2 |
| contributes_to transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II distal enhancer sequence-specific binding | ARNT |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | BATF,NFAT5,MYC,CEBPB,YBX1,ELF1,HOXA5,SIX1,SFPI1,PLAG1 |
| protein kinase binding | TOM1L1,MAP2K3,PTEN,CCNY,PFKFB2,PGAM1,ADRA2A,RPS3,SLC12A7,CALM |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific binding | SRF,REST,ATF2,BARX2,ALX4,RXRB,MAFK,MAFF,MAFB,CSRNP2 |
Interacting Protein
HIF1A has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with HIF1A here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of HIF1A.
VHL
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Mimouna, S; Bazin, M; et al. HIF1A regulates xenophagic degradation of adherent and invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC). AUTOPHAGY 10:2333-2345(2014).
- So, K; Chung, Y; et al. The effect of chronic prenatal hypoxia on the development of mature neurons in the cerebellum. JOURNAL OF NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS 5:-(2013).



