FUCA1
-
Official Full Name
fucosidase, alpha-L- 1, tissue -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a lysosomal enzyme involved in the degradation of fucose-containing glycoproteins and glycolipids. Mutations in this gene are associated with fucosidosis (FUCA1D), which is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease. A pseudogene of this locus is present on chr 2. -
Synonyms
FUCA1;fucosidase, alpha-L- 1, tissue;tissue alpha-L-fucosidase;Alpha L fucosidase I;Alpha L fucoside fucohydrolase;Alpha-L-fucosidase 1;Alpha-L-fucosidase I;Alpha-L-fucoside fucohydrolase 1;FUCA;FUCO_HUMAN;Tissue alpha L fucosidase;OTTHUMP00000003009
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- Fc
- His
- SUMO
- Non
- T7
- T8
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
Background
What is FUCA1 Protein?
FUCA1 is a type of enzyme that's crucial for breaking down a sugar called fucose, which is present in various parts of the body. This breakdown process is essential because it helps regulate different biological functions, including how cells interact with each other. Researchers are also looking into FUCA1 because of its possible role in cancer, as changes in its activity might influence how cancer cells grow and spread.What is the Function of FUCA1 Protein?
FUCA1 is an enzyme that plays a key role in breaking down the sugar fucose in the body. This process is important because it helps manage various biological activities, like cell-to-cell communication and immune responses. FUCA1 acts like a molecular pair of scissors, cutting fucose molecules from larger structures. By doing this, it influences how cells stick together and interact, which can impact tissue maintenance and even how the body responds to cancer. Scientists are interested in FUCA1 because changes in its function might affect cancer development, making it a potential target for new treatments.FUCA1 Related Signaling Pathway
The FUCA1 protein is involved in signaling pathways that regulate how cells grow, communicate, and interact with their environment. One critical pathway influenced by FUCA1 involves the breakdown of fucose, a sugar molecule. By removing fucose, FUCA1 can affect how proteins on the cell surface behave, which in turn influences how cells send and receive signals. This can impact important processes like cell adhesion, where cells stick together, and signaling pathways that can trigger cell growth or death. These pathways are especially significant when it comes to cancer, as the way cells communicate and grow is often altered in tumors. Scientists believe that by understanding FUCA1's role in these pathways, new strategies could be developed for cancer treatment, focusing on how altering this enzyme's activity might change cell signaling and tumor progression.FUCA1 Related Diseases
FUCA1 is an enzyme that breaks down a sugar called fucose, and problems with this enzyme can lead to certain diseases. One condition linked to FUCA1 is fucosidosis, a rare genetic disorder where the body accumulates too much fucose because the enzyme isn't working right. This disorder can result in developmental delays, fragile bones, and immune issues. FUCA1 is also under study for its connection to cancer since lower levels have been found in some tumors. This suggests FUCA1 might play a role in how quickly cancer grows or spreads. Researchers are exploring how targeting FUCA1 could lead to new treatments for these health issues.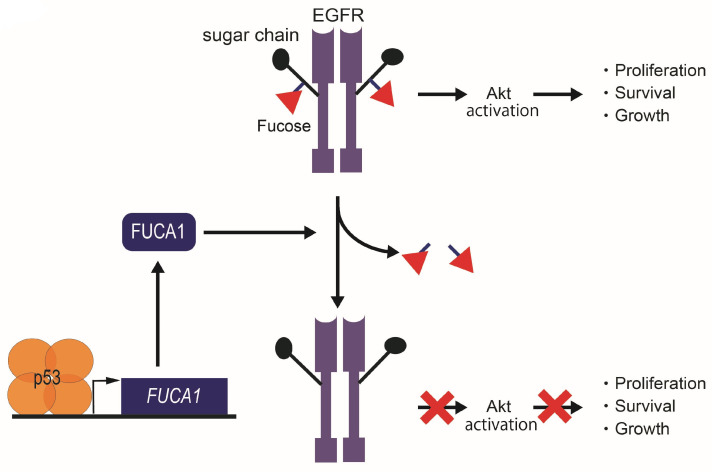
Fig1. Tumor suppression function in cancer cells by the p53-FUCA1 axis. (Die Hu, 2024)
Bioapplications of FUCA1
FUCA1 has potential bioapplications in medical and research fields due to its role in breaking down the sugar fucose. In diagnostics, measuring FUCA1 levels could help in detecting certain diseases, like some cancers, where its activity is altered. In therapeutics, FUCA1 might be targeted to develop treatments, especially for conditions like cancer and genetic disorders such as fucosidosis. By enhancing or mimicking FUCA1's activity, it might be possible to reduce harmful sugar build-up or modify cell interactions linked to disease. In research, FUCA1 provides insight into cellular processes, making it a valuable tool for studying cell behavior and developing new strategies for disease management.Case Study
Case Study 1: Vecchio G. et al. Oncotarget. 2017
Glycans with α-L-fucose play a key role in cell interactions. High glycan levels on cells are often linked to cancer. The enzyme FUCA-1, which degrades fucose, is less active in aggressive tumors. Its inactivity might alter proteins that help cancer spread. FUCA-1 is higher in normal thyroids but lower in aggressive thyroid cancers. Boosting FUCA-1 in cells reduces invasiveness, highlighting its role in cancer.-
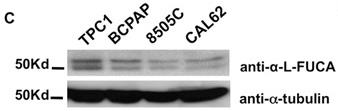 Fig1. a-L-FUCA-1 enzymatic activity of cell extracts from TPC-1, BCPAP, 8505C, and CAL62 cell lines.
Fig1. a-L-FUCA-1 enzymatic activity of cell extracts from TPC-1, BCPAP, 8505C, and CAL62 cell lines. -
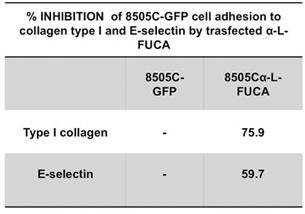 Fig2. Inhibition of 8505C cells adhesion to collagen type I and to E-selectin by endogenous α-L-FUCA-1.
Fig2. Inhibition of 8505C cells adhesion to collagen type I and to E-selectin by endogenous α-L-FUCA-1.
Case Study 2: Ezawa I. et al. Cancer Sci. 2016
The p53 protein stops tumors by turning on specific genes. Researchers found a new p53 target gene, FUCA1, which makes fucosidase. Though usually a lysosomal protein, FUCA1 works best outside lysosomes and at normal body pH. Since fucosylation is linked to cancer, we checked FUCA1's role in it. Overexpressing FUCA1, but not its inactive form, stopped cancer cell growth and caused cell death. FUCA1 also lowered fucosylation and the activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, slowing related signaling paths. FUCA1 mutations appear in some cancers, its levels drop in large intestine cancer, and less FUCA1 means a worse cancer outlook.-
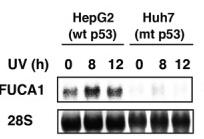 Fig3. HepG2 or Huh7 cells were subjected to UV treatment.
Fig3. HepG2 or Huh7 cells were subjected to UV treatment. -
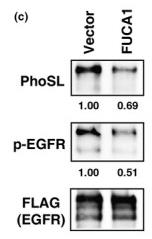 Fig4. COS7 cells were co-transduced with EGF receptor (EGFR)-FLAG and FUCA1 or control vector.
Fig4. COS7 cells were co-transduced with EGF receptor (EGFR)-FLAG and FUCA1 or control vector.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FUCA1-7730H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FUCA1-7730H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Fuca1-7731M)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Fuca1-7731M)
Involved Pathway
FUCA1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FUCA1 participated on our site, such as Other glycan degradation,Lysosome, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FUCA1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Lysosome | AP1M1,AP1M3,LITAF,CLN3,CTSSB.2,AP4E1,ATP6V1H,GGA1,IGF2R,CTSW |
| Other glycan degradation | FUCA1.2,NEU2,HEXB,NEU3.5,MAN2B2,NEU3.3,MAN2C1,ENG-1,GBA,NEU3 |
-
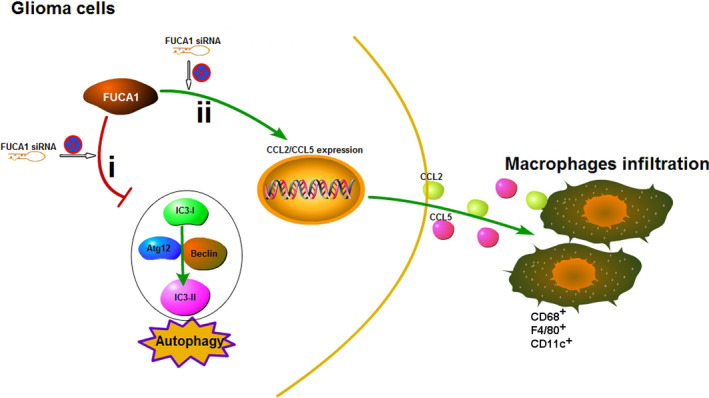 Fig1. Schematic representation of the processes involved in the effects of α‐l‐fucosidase 1 (FUCA1) on glioma development. (Lixia Xu, 2020)
Fig1. Schematic representation of the processes involved in the effects of α‐l‐fucosidase 1 (FUCA1) on glioma development. (Lixia Xu, 2020) -
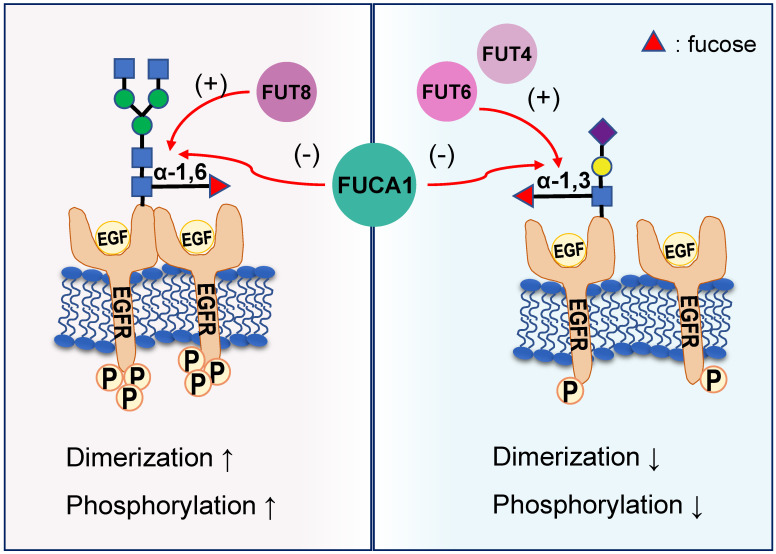 Fig2. Different EGFR fucosylation sites lead to different EGFR activation. (Jinxing Fu, 2022)
Fig2. Different EGFR fucosylation sites lead to different EGFR activation. (Jinxing Fu, 2022)
Protein Function
FUCA1 has several biochemical functions, for example, alpha-L-fucosidase activity,fucose binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FUCA1 itself. We selected most functions FUCA1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FUCA1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| fucose binding | FUOM,FUCA2,SELP |
| alpha-L-fucosidase activity | FUCA1.1,FUCA2,FUCA1.2 |
Interacting Protein
FUCA1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FUCA1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FUCA1.
MARK2;USP21;VAV2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


