CEBPB
-
Official Full Name
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), beta -
Overview
The protein encoded by this intronless gene is a bZIP transcription factor which can bind as a homodimer to certain DNA regulatory regions. It can also form heterodimers with the related proteins CEBP-alpha, CEBP-delta, and CEBP-gamma. The encoded protein is important in the regulation of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses and has been shown to bind to the IL-1 response element in the IL-6 gene, as well as to regulatory regions of several acute-phase and cytokine genes. In addition, the encoded protein can bind the promoter and upstream element and stimulate the expression of the collagen type I gene. -
Synonyms
CEBPB;CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), beta;TCF5;CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta;C/EBP beta;CRP2;IL6DBP;interleukin 6 dependent DNA binding protein;LAP;liver enriched transcriptional activator protein;NFIL6;nuclear factor of interleu
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is CEBPB Protein?
CEBPB gene (CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 20 at locus 20q13. The CEBPB protein, short for CCAAT enhancer binding protein β, is like a multitasking performer inside cells. Part of the basic leucine zipper family, it steps in to control gene activity by latching onto specific DNA spots. It's a key player in how cells grow, change, and fend off invaders, really making its mark in fat cell formation, inflammation, and immune function. Aside from flipping genes on or off, it can buddy up with other proteins to fine-tune gene activity even further. It's also involved in how cells handle stress, move through growth cycles, and decide when to die. But when CEBPB doesn't work right, it can be linked to various health issues like metabolic problems, inflammation, and cancer. The CEBPB protein is consisted of 345 amino acids and CEBPB molecular weight is approximately 36.1 kDa.
What is the Function of CEBPB Protein?
CEBPB, short for CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta, is a transcription factor in cells doing a bunch of important tasks. It's part of the bZIP family, which means it helps control gene expression by attaching to certain DNA bits. This protein is really important for things like cell growth, immune responses, and especially in making fat cells and handling inflammation. What's cool about CEBPB is that it can either kickstart genes into action or slow them down, often teaming up with other transcription helpers. Plus, it jumps in when cells are stressed, helping manage the cell cycle and prompting cell death when needed. When CEBPB goes off track, it can be linked to issues like metabolism problems, inflammation, and even cancer.
CEBPB Related Signaling Pathway
CEBPB is central to cell signaling, particularly in inflammation and immune responses. This transcription factor impacts the cell cycle, growth, and differentiation by controlling gene expression. It works through pathways like NF-kB, MAPK, and Jak-STAT, which are linked to inflammation. CEBPB doesn't just bind directly to DNA to start or stop gene activity; it also teams up with other transcription factors to tweak various signaling pathways. This makes it crucial in conditions like metabolic issues, inflammation, and cancer, showing how versatile it is in complex biological systems.
CEBPB Related Diseases
CEBPB is a transcription factor deeply involved in controlling gene expression, playing a big role in cell growth, differentiation, and immune reactions. It helps manage pathways like NF-kB, MAPK, and Jak-STAT that are key to our body's defense systems. When these pathways get disrupted, it can lead to health issues like metabolic disorders, inflammatory diseases, or cancers. CEBPB doesn't just regulate genes on its own; it also partners with other transcription factors to tweak different signaling pathways, making it central to many health conditions. By diving into how CEBPB operates, researchers see a lot of promise in targeting it for therapies to tackle these complex diseases.
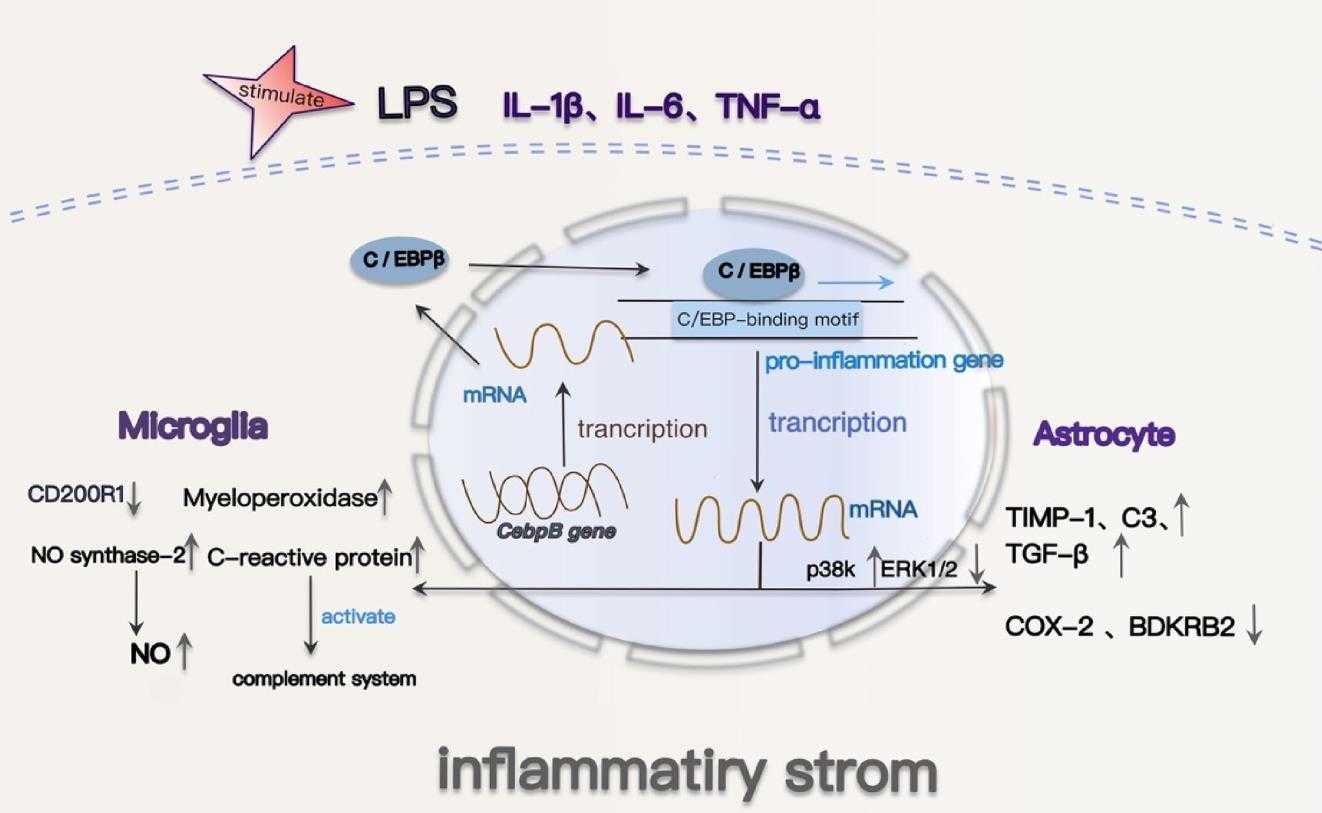
Fig1. C/EBPβ regulates signaling pathways associated with brain inflammation in AD. (Qing Yao, 2024)
Bioapplications of CEBPB
CEBPB is a transcription factor that plays a big role in controlling genes tied to cell growth, differentiation, and inflammation response. It's key in the NF-kB, MAPK, and Jak-STAT pathways—major players in immune function and inflammation. When these pathways go off track, it can lead to things like metabolic issues, inflammatory diseases, and cancer. CEBPB does its thing by either latching onto DNA directly or teaming up with other transcription factors to steer these pathways. This makes it a hot topic in research for tackling complex diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Britt A. Sterken, 2022
The transcription factor C/EBPβ plays a crucial role in the development of mammary glands and tissue changes during lactation. It can be translated into three different protein forms: C/EBPβ-LAP1, -LAP2, and -LIP, each with unique functions. The smaller LIP variant lacks certain domains and acts as an inhibitor to the other forms by competing for DNA binding. Excessive LIP expression is linked to increased cell growth in mammary tissue and appears in aggressive, hormone receptor-negative breast cancers. By altering the balance between these forms in cancer cells, researchers found that increasing LAP levels decreases the cancer cells' ability to migrate and invade, whereas LIP overexpression in normal cells boosts migration. Reducing CEBPB in cancer cells leads to less migration and affects genes related to cell movement and structure, hinting that the balance between these protein forms influences how breast cancer cells spread.
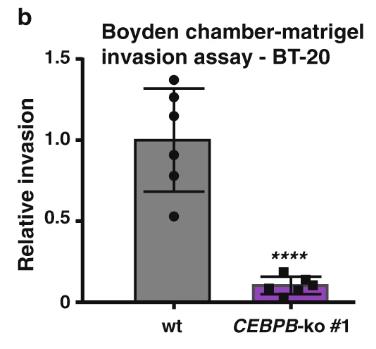
Fig1. Bar graph with representative quantification of 3D Boyden chamber-matrigel invasion assay using BT-20 wt and BT-20 CEBPB-ko clone.
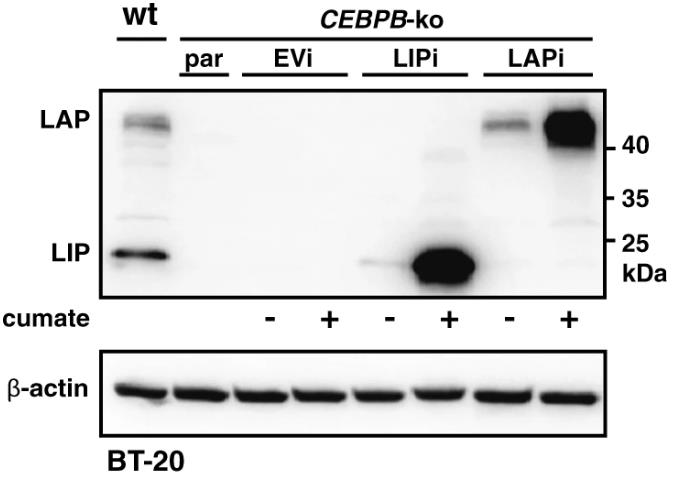
Fig2. Immunoblot showing the expression of LAP and LIP and β-actin as loading control in BT-20 CEBPB-ko clone.
Case Study 2: Hamood AlSudais, 2022
C/EBPβ is a transcription factor linked to aggressive tumor growth and poor prognosis in cancers. In advanced cancers, patients often experience cachexia, which is a severe muscle-wasting condition. This factor gets activated by signals from tumors that cause cachexia, leading to muscle wasting and hindering muscle repair. It plays a role in immune responses by promoting the production of secreted factors like cytokines. Due to its high levels in aggressive tumors contributing to cachexia, researchers are looking into C/EBPβ's involvement in producing these harmful tumor factors.
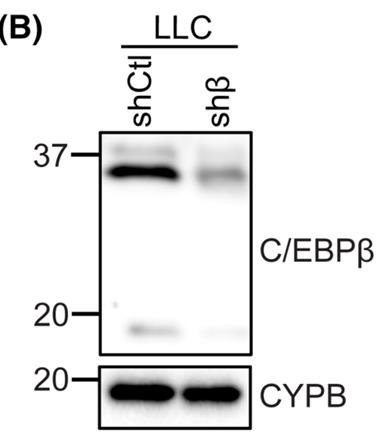
Fig3. C/EBPβ protein expression in Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells.
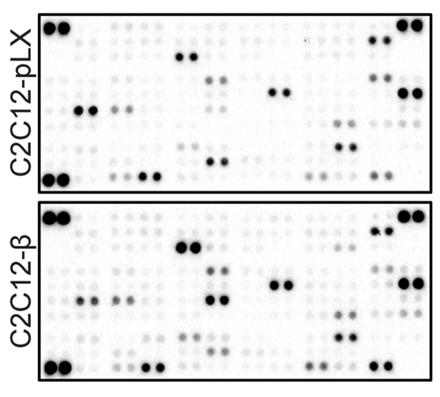
Fig4. Lysates from proliferating C2C12 cells retrovirally transduced with empty vector (pLX) or to express C/EBPβ (β).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CEBPB-1101H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (Cebpb-736M)
Involved Pathway
CEBPB involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CEBPB participated on our site, such as Adipogenesis,C-MYB transcription factor network,Cellular Senescence, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CEBPB were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| FOXA1 transcription factor network | NRIP1,CC10,POU2F1,NR2F2,NFIC,NFIB,CYP2C18,TFF1,NFIA,DSCAM |
| EGFR1 Signaling Pathway | USP6NL,ARF4,KRT17,RALBB,REPS2,EEF1A1,JUND,RALBP1,DNM1,SH2D3C |
| C-MYB transcription factor network | CEBPA,MYC,LECT2,TRIM28,PRTN3,ADORA2B,MYF6,MYB,ADA,YEATS4 |
| Adipogenesis | KLF6,GADD45A,E2F4,SPOCK1,GDF10,EBF1,CREB1,CDKN1A,NR2F1,STIL |
| Diurnally regulated genes with circadian orthologs | NCKAP1,TOB1,SF3A3,CRY1,ZFR,STBD1,CBX3,PURA,DAZAP2,EIF4G2 |
| Cellular responses to stress | ATG7,MOV10,RAD50,HIST1H1C,HIST4H4,NUP50,HSPA13,RBBP7,POT1,HMGA1-RS1 |
| Cellular Senescence | CBX6,PHC3,RNF2,MAPKAPK2B,AGO1,CDKN2D,CBX8A,IGFBP7,CDKN2B,CBX6A |
| Developmental Biology | SMAD3B,TRPC5,MYL9,PLXND1,NTN1A,EPHA10,KCNQ3,PITPNA,DUSP1,RASGRP1 |
Protein Function
CEBPB has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding,RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CEBPB itself. We selected most functions CEBPB had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CEBPB. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| chromatin binding | CREBBP,TRP53,CHD8,TOP2B,MBD5,MSL1A,REL,FANCM,NFATC2,MEIS1 |
| protein homodimerization activity | S100A6,SPATA24,EPHX2,MAP3K12,CSF1R,Fzd4,GCH1,KLHL7,GNB2L1,HEXB |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | WT1B,HMGB2,CBFA2T2,TAF5L,NR6A1B,ZNF334,FOXG1C,GLI4,FOXP3,ZFP12 |
| histone acetyltransferase binding | MYOCD,EID1,ZBTB7A,TRIP4,PAX6,MEF2A,EPAS1,TP53,CITED2,HIF1A |
| protein heterodimerization activity | MAFG,LIMK1,H2AFB1,HIST1H3G,H2-AB1,KCNB1,HIST1H2AG,ERBB3,UGT1A3,IRAK1 |
| RNA polymerase II regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | KAT2B,AASS,STOX1,SP1,ZFP39,PHOX2A,MYOG,LMO2,LYL1,ZNF773 |
| glucocorticoid receptor binding | GRIP1,ETS2,NRIP1,STAT3,NR4A2,YWHAH,EP300,STAT5B,FKBP4 |
| RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | MYC,TCF3A,NDN,NKX2,CDX4,BCL11B,FOSB,POU4F3,SMAD3,GLI2 |
| kinase binding | PTPN22,CAB39,UBQLN1,ABI2,HPCA,TRIP6,PRKCD,DLG4,RPS3,SNAI1 |
Interacting Protein
CEBPB has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CEBPB here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CEBPB.
SMAD4;E2;TP53;E2;E2;E2;HMGA1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



