CDK6
-
Official Full Name
cyclin-dependent kinase 6 -
Overview
The cyclin-dependent kinases form complexes with their cyclin partners and with CDK inhibitors. CDK6 and CDK4 associate with the D-type cyclins and target the retinoblastoma protein, allowing passage through the G1/S phase restriction point (1). CDK6/cycl -
Synonyms
CDK6;cyclin-dependent kinase 6;PLSTIRE;cell division protein kinase 6;serine/threonine-protein kinase PLSTIRE;MGC59692
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- Sf9 Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- E.coli
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Sf21 Cells
- GST
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is CDK6 protein?
CDK6 gene (cyclin dependent kinase 6) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 7 at locus 7q21. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the CMGC family of serine/threonine protein kinases. This kinase is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression and G1/S transition. The activity of this kinase first appears in mid-G1 phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits including D-type cyclins and members of INK4 family of CDK inhibitors. This kinase, as well as CDK4, has been shown to phosphorylate, and thus regulate the activity of, tumor suppressor protein Rb. Altered expression of this gene has been observed in multiple human cancers. The CDK6 protein is consisted of 326 amino acids and CDK6 molecular weight is approximately 36.9 kDa.
What is the function of CDK6 protein?
CDK6 protein is a protein belonging to the cell cycle dependent kinase (CDK) family, which plays an important role in the cell cycle. CDK6 is mainly expressed in the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and plays a role in DNA replication and microtubule assembly. It participates in DNA replication by binding to DNA polymerase and binds to tubulin to provide the components required for the assembly of microtubules. In addition, CDK6 also interacts with various proteins such as CTD4, p21 and p53, which enable CDK6 to perform important biological functions in the cell cycle. In tumor cells, the activity of CDK6 is related to the metabolism and anti-tumor immune response of tumor cells. Inhibition of CDK6 activity can affect the metabolism of tumor cells and enhance the anti-tumor immune response.
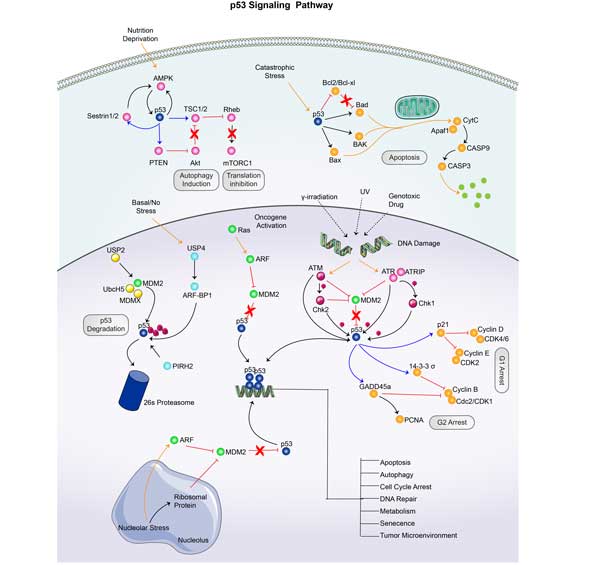
CDK6 Related Signaling Pathway
CDK6 forms a complex with cyclin D, which promotes cell progression from G1 phase to S phase by phosphorylating retinoblastoma protein (Rb). The use of CDK6 inhibitors affected the metabolism of tumor cells, including the number of mitochondria and lysosomes and the oxidative phosphorylation process. CDK6 inhibitors may enhance the anti-tumor immune response by affecting the expression of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) in tumor cells. CDK6 is associated with the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, and activation of this pathway is associated with resistance to CDK6 inhibitors.
CDK6 Related Diseases
The CDK6 protein has been implicated in the development of a variety of cancers, including but not limited to breast cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, ovarian cancer, multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukemia, some types of lymphoma, and glioblastoma. It plays a key role in the proliferation of tumor cells by regulating the progression of the cell cycle, in particular by facilitating the transition of cells from the G1 phase to the S phase through the formation of complexes with cyclin D. In addition, abnormal expression or dysfunction of CDK6 may lead to uncontrolled proliferation of cells, which in turn promotes tumor development.
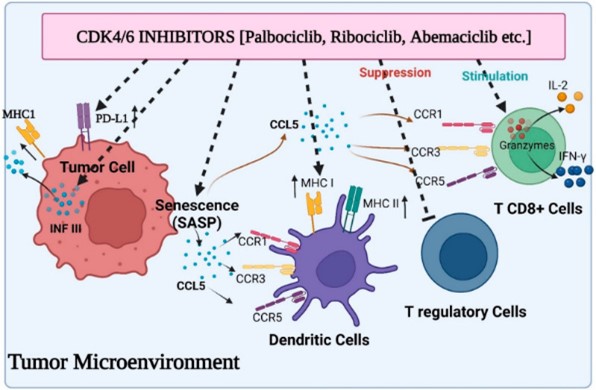
Fig1. Various aspects of immunomodulation via CDK4/6 inhibitors on the tumor microenvironment. (Pratibha Pandey, 2023)
Bioapplications of CDK6
First, as a target for drug development, CDK6 inhibitors have become a first-line drug for the treatment of some types of cancer, particularly in advanced hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Second, the research and development of CDK6 inhibitors is expanding to other cancer types, such as non-small cell lung cancer and pancreatic cancer. In addition, CDK6 activity and expression levels are also used as biomarkers to assess tumor aggressiveness and monitor treatment effects.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Zhixuan Xiong, 2024
While the function of CDK proteins in regulating mammalian innate immune responses and virus replication is well-documented, their role in chickens remains unclear. To address this, researchers cloned several chicken CDKs, specifically CDK6 through CDK10. They observed that CDK6 is widely expressed across various chicken tissues, with localization in the cytoplasm, nucleus, or both in DF-1 cells. In addition, they also found that multiple chicken CDKs negatively regulate IFN-β signaling induced by chicken MAVS or chicken STING by targeting different steps. Moreover, during infection with infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV), various chicken CDKs, except CDK10, were recruited and co-localized with viral protein VP1. Interestingly, overexpression of CDK6 in chickens significantly enhanced IBDV replication. Conversely, knocking down CDK6 led to a marked increase in IFN-β production, triggered by chMDA5. Furthermore, targeting endogenous CDK6 with RNA interference substantially reduced IBDV replication.
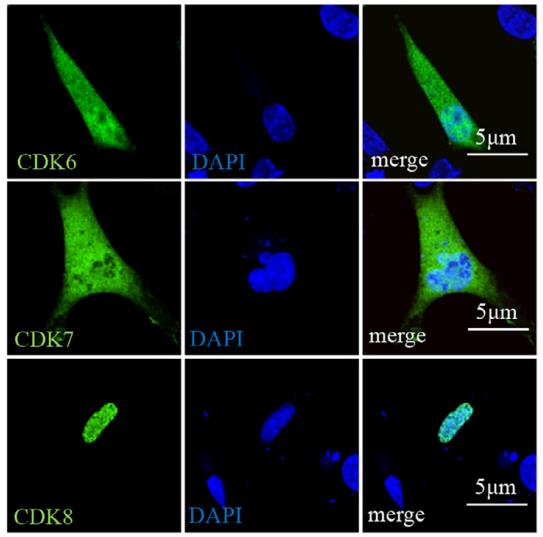
Fig1. DF-1 cells were transfected with chicken Myc-CDKs for 24 h.
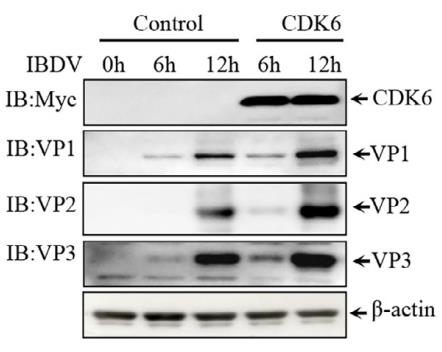
Fig2. Fresh DF-1 cells transfected with Myc-chCDK6 plasmids for 24 h were infected with IBDV.
Case Study 2: Tingting Jiang, 2024
Cisplatin resistance is ubiquitous among patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC). The present study assessed the role of fisetin in regulating cisplatin sensitivity and increasing the efficacy of chemotherapy for patients with RCC. Cell Counting Kit-8 and colony formation assays were used to assess the proliferation of RCC cells after fisetin and cisplatin treatment. The mRNA expression levels of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)6 were evaluated using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. The expression levels of CDK6 and key proteins of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway were assessed using western blotting. The present study demonstrated that fisetin regulated the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway through CDK6 inhibition, which enhanced cisplatin sensitivity. Overexpression of CDK6 neutralized the positive effects of fisetin on the improvement of cisplatin sensitivity in RCC cells.
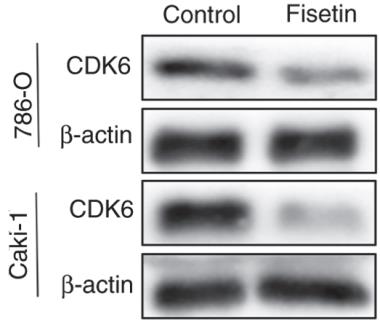
Fig3. Expression levels of CDK6 protein.
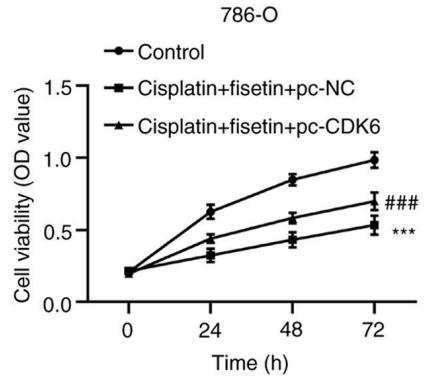
Fig4. RCC cell proliferation after CDK6 overexpression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CDK6-1032H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CDK6-1028H)
Involved Pathway
CDK6 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CDK6 participated on our site, such as B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway,C-MYB transcription factor network,Cell Cycle, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CDK6 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| C-MYB transcription factor network | MYB,MYF6,ADORA2B,MYC,CDKN1B,LECT2,CEBPB,CEBPA,CLTA,CREBBP |
| Cellular Senescence | LMNB1,TERF2IP,CDK4,SUZ12B,CEBPB,HIST1H1E,CDKN2A,HIST4H4,PHC2,EP400 |
| B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway | PIK3CB,PPP3R2,BCL2L11,AKT2,CARD11,CDK2,LILRB3,PIK3R2,NFATC1,BLK |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | TP53,TGFBR2,MECOM,TGFB3,CCND1,HDAC2,MAPK1,TGFB1,SHC4,GRB2 |
| Cell cycle | YWHAZ,ARPP19A,CLASP1A,ACD,CDK11B,ENSA,TTK,CSNK2A2,DHFR,ESPL1 |
| Cell Cycle, Mitotic | CENPL,CEP76,CP110,NCAPH2,CDK11A,CSNK2A2,ARPP19B,NIPBL,SMC2,INCENP |
| Cellular responses to stress | RNF2,WIPI1,HIST2H3C,CDKN2A,MOV10,TERF2,BMI1A,SUZ12A,MAP1LC3B,MAPKAPK2B |
Protein Function
CDK6 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,cyclin binding,cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CDK6 itself. We selected most functions CDK6 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CDK6. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity | CDK7,NAT1,CDKL1,CDK12,CDKL4,CDKL2,CDK20,CDK2,MAK,CDKL3 |
| protein binding | NUAK1,POC1B,SDCBP2,RNF111,RSPH3,CDKN2AIP,CLK3,IL12B,DEPDC6,KIAA1274 |
| ATP binding | MYLK3,SUCLG2,ABCF3,YRK,BMPR2A,MARK4,ACVR1,BCS1L,MYHZ1.1,IGF1RB |
| cyclin binding | CDKN1A,CDK5RAP3,USP2,HDAC3,INCA1,CDK12,PTCH1,CUL3,FBXW7,CDK2 |
Interacting Protein
CDK6 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CDK6 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CDK6.
CDKN2A;CCND3
CDK6 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Caro-Astorga, J; Fajardo, I; et al. Nascent histamine induces alpha-synuclein and caspase-3 on human cells. BIOCHEMICAL AND BIOPHYSICAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS 451:580-586(2014).
- Xu, F; Liu, J; et al. LSECtin Expressed on Melanoma Cells Promotes Tumor Progression by Inhibiting Antitumor T-cell Responses. CANCER RESEARCH 74:3418-3428(2014).