CD5
-
Official Full Name
CD5 molecule -
Overview
CD5 is a 67kDa single-chain transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on mature T lymphocytes, most thymocytes and B lymphocytes subset (B-1a lymphocytes) and on many T-cell leukemias and lymphomas. It is a type I membrane glycoprotein whose extracellular region contains three scavenger receptor cysteine-rich (SRCR) domains. The CD5 is a signal transducing molecule whose cytoplasmic tail is devoid of any intrinsic catalytic activity. CD5 modulates signaling through the antigen-specific receptor complex (TCR and BCR). CD5 may serve as a dual receptor, giving either stimulatory or inhibitory signals depending both on the cell type and development stage. In thymocytes and B1a cells seems to provide inhibitory signals, in peripheral mature T lymhocytes it acts as a costimulatory signal receptor. CD19 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and has two Ig like domains. The CD19 molecule is expressed on 100% of the peripheral B cells as defined by expression of kappa or lamda light chains. It is expressed on approximately 10% of normal human peripheral blood cells and approximately 60% of splenic lymphocytes. It is not expressed on granulocytes, monocytes or T cells as defined by CD3 expression. CD19 defines a pan B antigen which is expressed from the earliest stages of B progenitor development, but is lost on terminal differentiation to plasma cells. It may also be present on some early myeloid progenitors, particularly those of the monoblastic type. The CD19 antigen is expressed on approximately 12% of peripheral blood lymphocytes. It appears to be expressed on myeloid leukemia cells, particularly those of monocytic lineage. Leukemia phenotype studies have demonstrated that the earliest and broadest B cell restricted antigen is the CD19 antigen. -
Synonyms
CD5;CD5 molecule;CD5 antigen (p56 62) , LEU1;T-cell surface glycoprotein CD5;T1;CD5 antigen (p56-62);lymphocyte antigen T1/Leu-1;LEU1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Bovine
- Mus musculus
- Human Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- C-His
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- Strep II
- Non
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is CD5 Protein?
CD5, also called lymphocyte surface antigen 5 (Ly-5), is a glycoprotein found mainly on T and B cells. It's important for the immune system, guiding how cells signal, interact, and react to immune responses. CD5 helps regulate immune cell activation, growth, and differentiation, keeping the immune system balanced and preventing improper reactions. Its expression levels can change in certain diseases; for instance, it often rises in some lymphomas, making it a marker for these cancers. In autoimmune diseases, CD5 is involved in several conditions, offering new insights for targeted treatments. In cancer therapy, CD5's role in dendritic cells is linked to strong anti-tumor immune responses, highlighting its potential in immunotherapy. Thus, CD5 is crucial for immune regulation and has promising applications in disease treatment.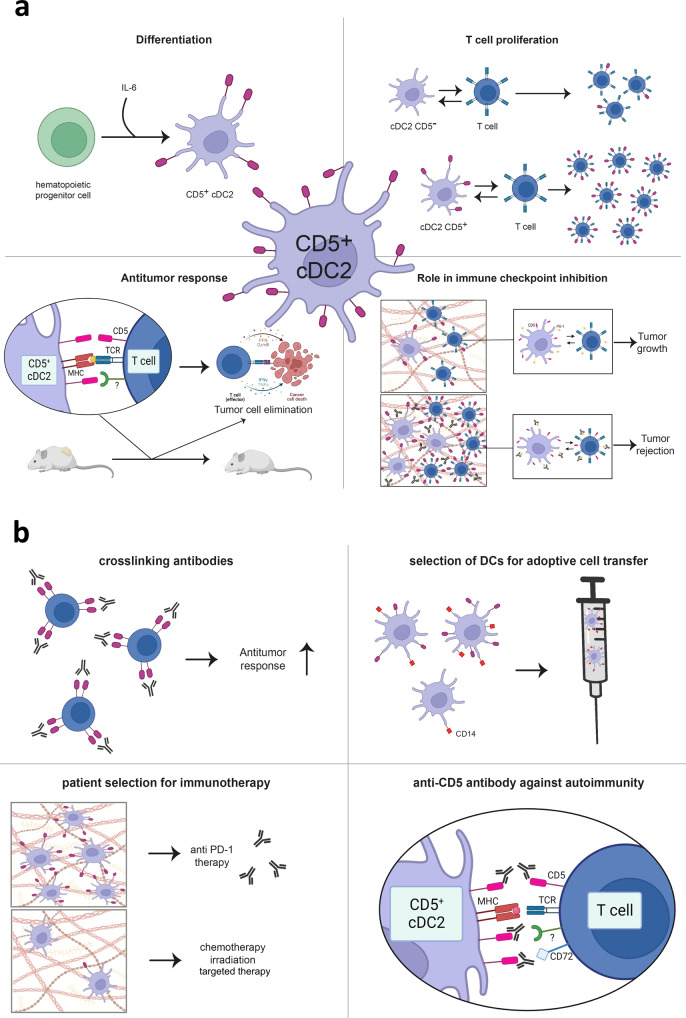
Fig1. The role of CD5 in tumor immunology and therapeutic chances. (Sandra Schwarz, 2023)
What is the Function of CD5 Protein?
CD5 is a glycoprotein found on T and B cells, playing a regulatory role in the immune system. It acts as a co-stimulatory molecule on resting T cells, boosting CD3 signaling. In mature peripheral T cells, CD5 enhances the redistribution of CD3 into lipid rafts, increasing ZAP-70 and LAT activation and Ca2+ influx. CD5 associates with SHP-1 to negatively regulate TCR activation post-TCR engagement. Its regulatory nature varies based on lymphocyte subtype and differentiation stage. In B cells, CD5's role isn't fully clear, but it's thought to influence apoptosis and block proliferation. CD5 is also on dendritic cells (DCs), crucial for strong anti-tumor responses. Mice lacking CD5+ DCs struggle to mount effective CD4+ and CD8+ T cell immune reactions, unlike those with intact DCs, which can reject tumors. These findings highlight CD5's acknowledged role in T cell signaling and tolerance, with its function on DCs becoming clearer, particularly in DC-mediated responses. Overall, CD5 influences TCR and BCR signaling, thymocyte selection, T cell differentiation, and immune tolerance.CD5 Related Signaling Pathway
CD5 plays a key regulatory role in several signaling pathways, especially in T and B cell immune responses. In T cells, CD5 interacts with CBL protein at the immune synapse to downregulate TCR signaling. This involves phosphorylation that allows CD5 to engage with inhibitory molecules like CBL and UBASH3, leading to modifications of positive effectors like ZAP70 and PI3K. CD5 also links with CSK to control LCK, where LCK phosphorylates CD5 following TCR activation, and CSK connects with phosphorylated CD5 to inhibit LCK, reducing TCR signaling intensity. In B cells, CD5 binds with CD79a in the BCR complex, affecting B1a cell growth and survival by altering gene expression through pathways like STAT3 or NFAT2. CD5 also interacts with PI3K/mTOR, Ca2+/NFAT, and other pathways, impacting B cell function and tolerance. These interactions underline CD5's complex role in managing immune cell behavior.CD5 Related Diseases
CD5 protein is linked to various diseases and is important in immune regulation. It's highly expressed in regulatory T and B cells, playing a role in autoimmune diseases by maintaining immune tolerance. In conditions like T-ALL and certain CLL types, CD5 is a potential target due to its high presence. Elevated soluble CD5 levels in some inflammatory diseases might dampen immune modulation. CD5 is also connected to conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, liver injury, fibrosis, and tumors. Overall, CD5's involvement in disease progression and immune responses highlights its potential as a target for autoimmune and blood cancer treatments.Bioapplications of CD5
CD5 protein is crucial in biomedical fields, particularly in immune and blood cancer treatments. It's a target for CAR-T therapy against T cell malignancies like T-ALL, allowing effective cancer cell elimination with minimal impact on normal cells. CD5L aids immune regulation by impacting macrophages and T cell responses. In biomarker research, CD5+ R/R DLBCL is studied for potential treatment targets. It also influences autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and type 1 diabetes by affecting Treg cells and cytokines. Moreover, CD5+ B cells are key in immune-related blood disorders, indicating disease activity and potential treatment strategies. These insights into CD5's functions support the development of innovative therapies.Case Study
Case Study 1: Xu Y. et al. J Hematol Oncol. 2019
Researchers are investigating CAR-modified cells to treat cancer, focusing on how CAR-T and CAR-NK-92 cells differ. CAR-T cells are great for B cell cancers, but using them for T cell cancers is tricky since they share antigens with normal T cells. Researchers identified CD5 as a key marker for targeting T cell malignancies and developed two anti-CD5 CAR constructs with differing costimulatory domains: BB.z and 2B4.z. These led to BB.z-NK and 2B4.z-NK cells. In studies, both cell types effectively attacked CD5+ cancerous cells and improved survival in a mouse model of T-ALL. Remarkably, 2B4.z-NK cells outperformed BB.z-NK cells in anti-cancer activity and lytic effects.-
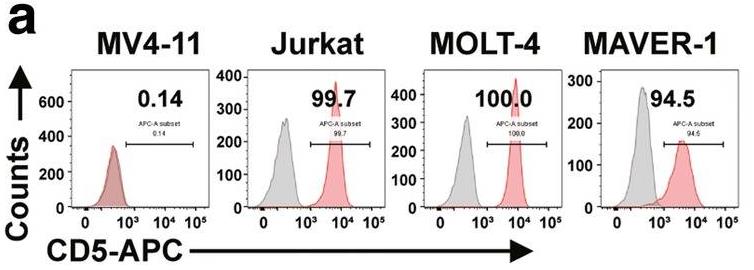 Fig1. Representative flow cytometry analysis showing the expression of CD5 on MV4-11, Jurkat, MOLT-4, and MAVER-1 cells.
Fig1. Representative flow cytometry analysis showing the expression of CD5 on MV4-11, Jurkat, MOLT-4, and MAVER-1 cells. -
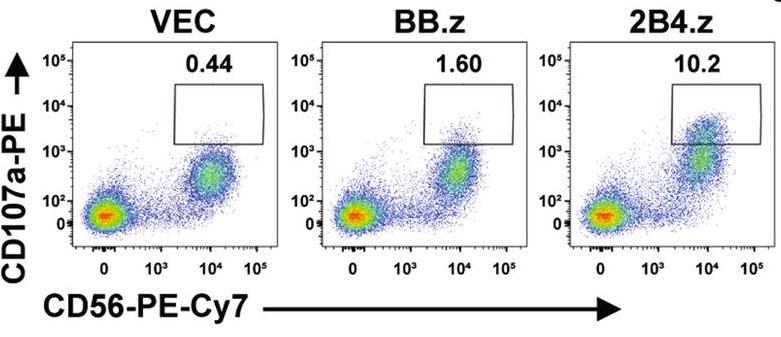 Fig2. Representative flow cytometry analysis showing the proportion of CD107a+CD56+ cells after co-incubation with target cells.
Fig2. Representative flow cytometry analysis showing the proportion of CD107a+CD56+ cells after co-incubation with target cells.
Case Study 2: Rai AK. et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017
So far, the role of CD5 in acute T cell lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) hasn't been thoroughly examined. Researchers found that leukemic T cells show much lower surface CD5 (sCD5) compared to their non-leukemic counterparts. This study uncovers how CD5 expression and function are controlled in these cancerous cells. Out of 250 leukemia and lymphoma patients who were tested, 39 had T-ALL. They noticed that amplification of CD5's E1A and E1B transcripts aligns with how much CD5 protein appears on the cell surface and inside the cells. When blocked CD5, it impacted interleukin IL-2 production and affected the survival of both cancerous and non-cancerous cells. Lack of sCD5 on T-ALL cells was tied to more E1B transcription and less E1A, important for CD5's presence on lymphocytes. High E1B levels meant more cytoplasmic CD5 (cCD5) in leukemic cells. Blocking CD5 boosted IL-2 production in non-leukemic T cells, potentially improving their survival after 48 hours.-
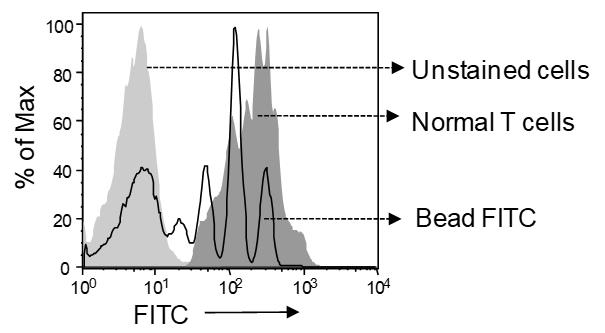 Fig3. Overlaid histogram showed expression of CD5.
Fig3. Overlaid histogram showed expression of CD5. -
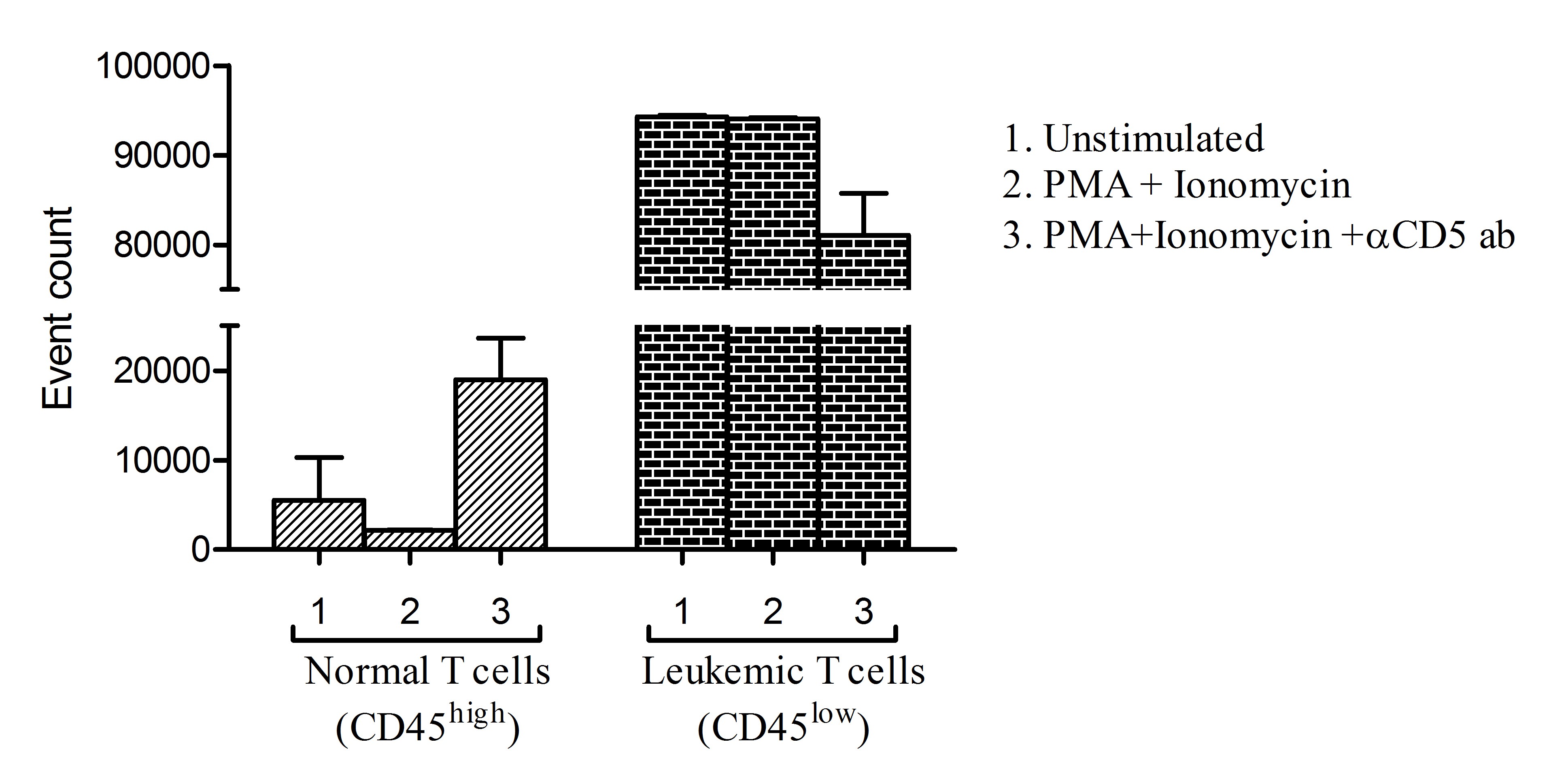 Fig4. Cells from T-ALL patients cultured under different conditions and 3. polyclonal stimulation.
Fig4. Cells from T-ALL patients cultured under different conditions and 3. polyclonal stimulation.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD5-6713H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD5-6713H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD5-135H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD5-135H)
Involved Pathway
CD5 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD5 participated on our site, such as Hematopoietic cell lineage, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD5 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | IL2RA,KITLG, B2M,CD8B1,EPOR,HLA-DRB3,ITGB3,GM-CSF,CD33,TFRC |
-
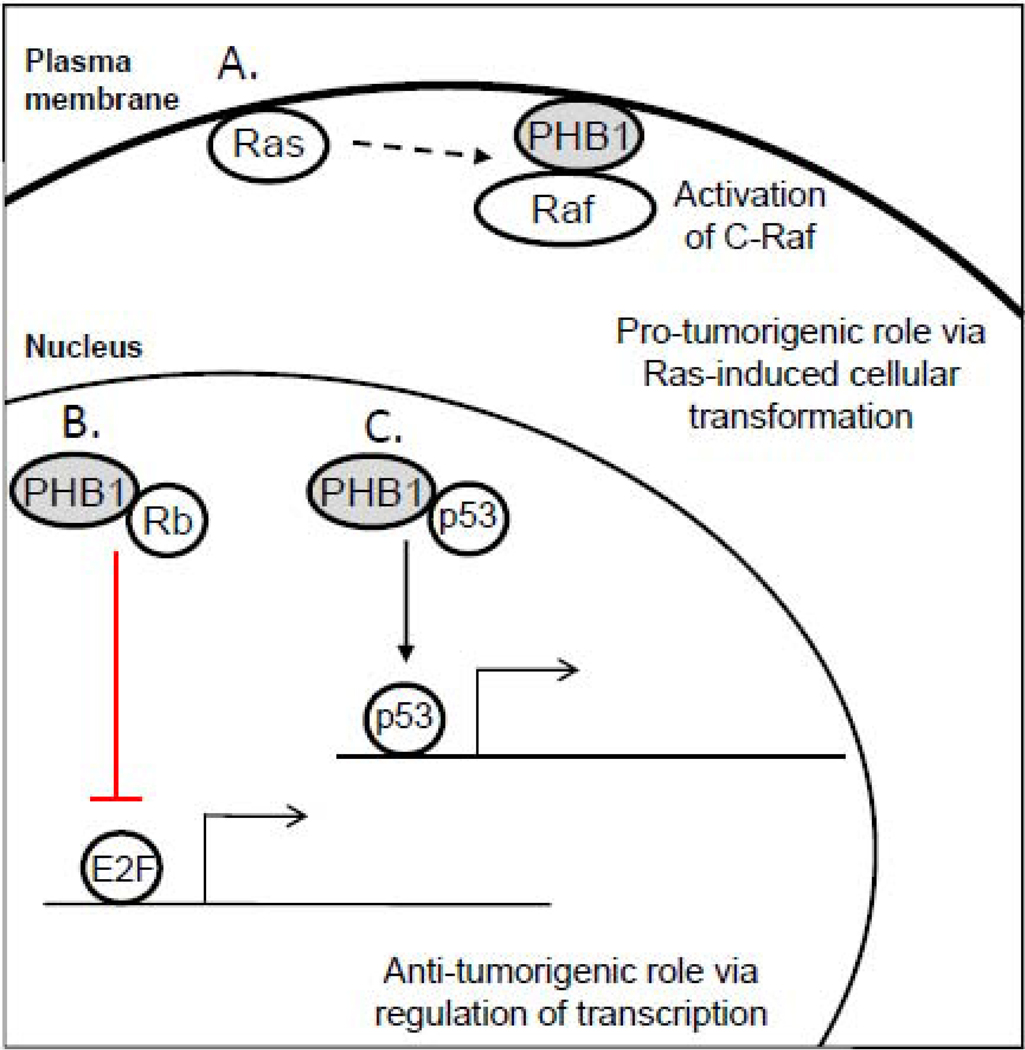 Fig1. Simplified model of the opposing roles of CD51 in tumorigenesis. (Arianne L Theiss, 2011)
Fig1. Simplified model of the opposing roles of CD51 in tumorigenesis. (Arianne L Theiss, 2011) -
 Fig2. Hypothetical model illustrating in the regulation of mitochondrial fragmentation, apoptosis, and chemosensitivity in gynecologic cancer cells. (Bao Kong, 2022)
Fig2. Hypothetical model illustrating in the regulation of mitochondrial fragmentation, apoptosis, and chemosensitivity in gynecologic cancer cells. (Bao Kong, 2022)
Protein Function
CD5 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,receptor activity,scavenger receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD5 itself. We selected most functions CD5 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD5. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transmembrane signaling receptor activity | KLRB1,LILRB3,CLEC4A,CD3G,LEPR,CD3E,GHRHRA,LAG3,TLR2-2,KLRC1 |
| protein binding | ZNF567,PAX6,HDC,TAC1,TMCO6,ORC3L,RPS3,SPG21,PNRC2,ITGB3 |
| receptor activity | TNFRSF11B,CD86,NLGN4X,CXCR3,LYVE1,CADM2A,RAMP1,KLRG1,XPR1,ITGB4 |
| scavenger receptor activity | SUSD2,HHIPL1,PRSS7,TINAGL1,ABHD1,TMPRSS13B,CD163,TMPRSS4B,LOXL2,CXCR7 |
Interacting Protein
CD5 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD5 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD5.
PIK3R1;CD72;RASA1
Resources
Research Area
ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related MoleculesB Cell CD Antigen
B Cell Markers
CD Antigen (Regulatory T Cells)
Scavenger Receptors
Lymphoid Lineage Markers
B Cell Receptor-Associated Proteins
Mediators in B Cell Development
CAR-T Cell Therapy Targets
Tumor Antigens
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Kostopoulos, IV; Paterakis, G; et al. Immunophenotypic Analysis Reveals Heterogeneity and Common Biologic Aspects in Monoclonal B-Cell Lymphocytosis. GENES CHROMOSOMES & CANCER 54:210-221(2015).
- Antosz, H; Wojciechowska, K; et al. IL-6, IL-10, c-Jun and STAT3 expression in B-CLL. BLOOD CELLS MOLECULES AND DISEASES 54:258-265(2015).


