PSAP
-
Official Full Name
prosaposin -
Overview
Anti-PSAP reacts with prostatic acid phosphatase in the glandular epithelium of normal and hyperplastic prostate, carcinoma of the prostate, and metastatic cells of prostatic carcinoma. This marker may be helpful in pinpointing the site of origin in cases -
Synonyms
PSAP;prosaposin;GLBA, SAP1, sphingolipid activator protein 1;proactivator polypeptide;variant Gaucher disease and variant metachromatic leukodystrophy;sphingolipid activator protein-1;GLBA;SAP1;FLJ00245;MGC110993
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Guinea pig
- Pig
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Nicotiana Benthamiana
- Yeast
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His&T7
- His
- Non
- His&Fc&Avi
- His&Flag
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSAP-18H | Recombinant Human PSAP protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 196-274 a.a. | |
| PSAP-19H | Recombinant Human PSAP protein, His/T7-tagged | E.coli | Human | His&T7 | 17-524 a.a. | |
| Psap-1013M | Recombinant Mouse Psap Protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His | 1-557 a.a. |
|
| Psap-1125R | Recombinant Rat Psap protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | His | Met1-Asn554 |
|
| PSAP-13538M | Recombinant Mouse PSAP Protein | Mammalian Cell | Mouse | His |
|
|
| PSAP-20H | Recombinant Human PSAP protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | 1-524 a.a. |
|
| PSAP-21H | Recombinant Human PSAP protein, His-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His | 17-524 a.a. |
|
| PSAP-256H | Recombinant Human PSAP protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | 18-524 a.a. |
|
| PSAP-257H | Recombinant Human PSAP protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | Human | GST | 1-524 a.a. |
|
| PSAP-30347TH | Recombinant Human PSAP, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | 255-526 a.a. |
|
| PSAP-4756R | Recombinant Rat PSAP Protein | Mammalian Cell | Rat | His |
|
|
| PSAP-6374C | Recombinant Chicken PSAP | Mammalian Cell | Chicken | His |
|
|
| PSAP-9387Z | Recombinant Zebrafish PSAP | Mammalian Cell | Zebrafish | His |
|
|
| PSAP-2792HCL | Recombinant Human PSAP 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| PSAP-2793HCL | Recombinant Human PSAP 293 Cell Lysate | HEK293 | Human | Non |
|
|
| PSAP-01H | Recombinant Human PSAP Protein, His-tagged | Nicotiana Benthamiana | Human | His |
|
|
| PSAP-189H | Recombinant Human PSAP protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 406-487 aa |
|
| PSAP-30115H | Recombinant Human PSAP protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | Asp196-Val274 |
|
| PSAP-3377H | Recombinant Human PSAP protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 311-391aa |
|
| PSAP-4415R | Recombinant Rat PSAP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Rat | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| PSAP-4415R-B | Recombinant Rat PSAP Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Rat |
|
||
| PSAP-5503G | Recombinant Guinea pig PSAP protein, His-tagged | Yeast | Guinea pig | His | 1-81aa |
|
| PSAP-5504H | Recombinant Human PSAP protein, His-tagged | Yeast | Human | His | 311-391aa |
|
| PSAP-5505P | Recombinant Pig PSAP protein, His-Flag-tagged | Yeast | Pig | His&Flag | 1-80aa |
|
| PSAP-6022H | Recombinant Human PSAP Protein (Gly17-Asn524), N-His tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Gly17-Asn524 |
|
| PSAP-611HF | Recombinant Full Length Human PSAP Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 524 amino acids |
|
| PSAP-614HF | Recombinant Full Length Human PSAP Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | Human | GST | Full L. 524 amino acids |
|
| PSAP-7197M | Recombinant Mouse PSAP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Mouse | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| PSAP-7197M-B | Recombinant Mouse PSAP Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Mouse |
|
Background
What is PSAP Protein?
The PSAP protein, or Prosaposin, is a versatile glycoprotein with various roles within cells. It’s the precursor for saposins A, B, C, and D, which are crucial for breaking down certain sphingolipids in lysosomes. In the lysosome, PSAP is processed into these four saposins, aiding lysosomal enzymes in hydrolyzing specific sphingolipids. Beyond its intracellular function, PSAP can be secreted into body fluids like plasma, milk, or cerebrospinal fluid, where it shows neurotrophic and myelin-supporting activity. A lack of PSAP in mice is fatal, causing severe leukoencephalopathy and sphingolipid accumulation. Furthermore, PSAP is involved in various cellular processes, including the action of neurotrophic factors and roles in nervous system development. Thus, PSAP plays a significant role in sphingolipid metabolism, neuroprotection, and more across different cellular functions.What is the Function of PSAP Protein?
PSAP, known as prosaposin, is a versatile protein with a range of roles inside cells. For starters, it’s a lysosome-related protein that gets processed to activate enzymes crucial for sphingolipid metabolism. When broken down, PSAP forms four bioactive peptides: saposins A, B, C, and D. These peptides help enzymes break down sphingolipids, which is vital for keeping lysosomes functioning well and maintaining lipid balance. Beyond that, PSAP acts as a neurotrophic factor, working alongside another lysosomal protein, PGRN, to influence its functionality. It’s also involved in maintaining lipid balance in dopamine neurons and shows protective effects in Parkinson’s disease models. In developing dorsal root ganglia, the presence of PSAP and its receptors, GRP37 and GPR37L1, hint at a role in activating both satellite and neuronal cells. Thus, PSAP is key in sphingolipid metabolism, neuroprotection, and various cellular activities.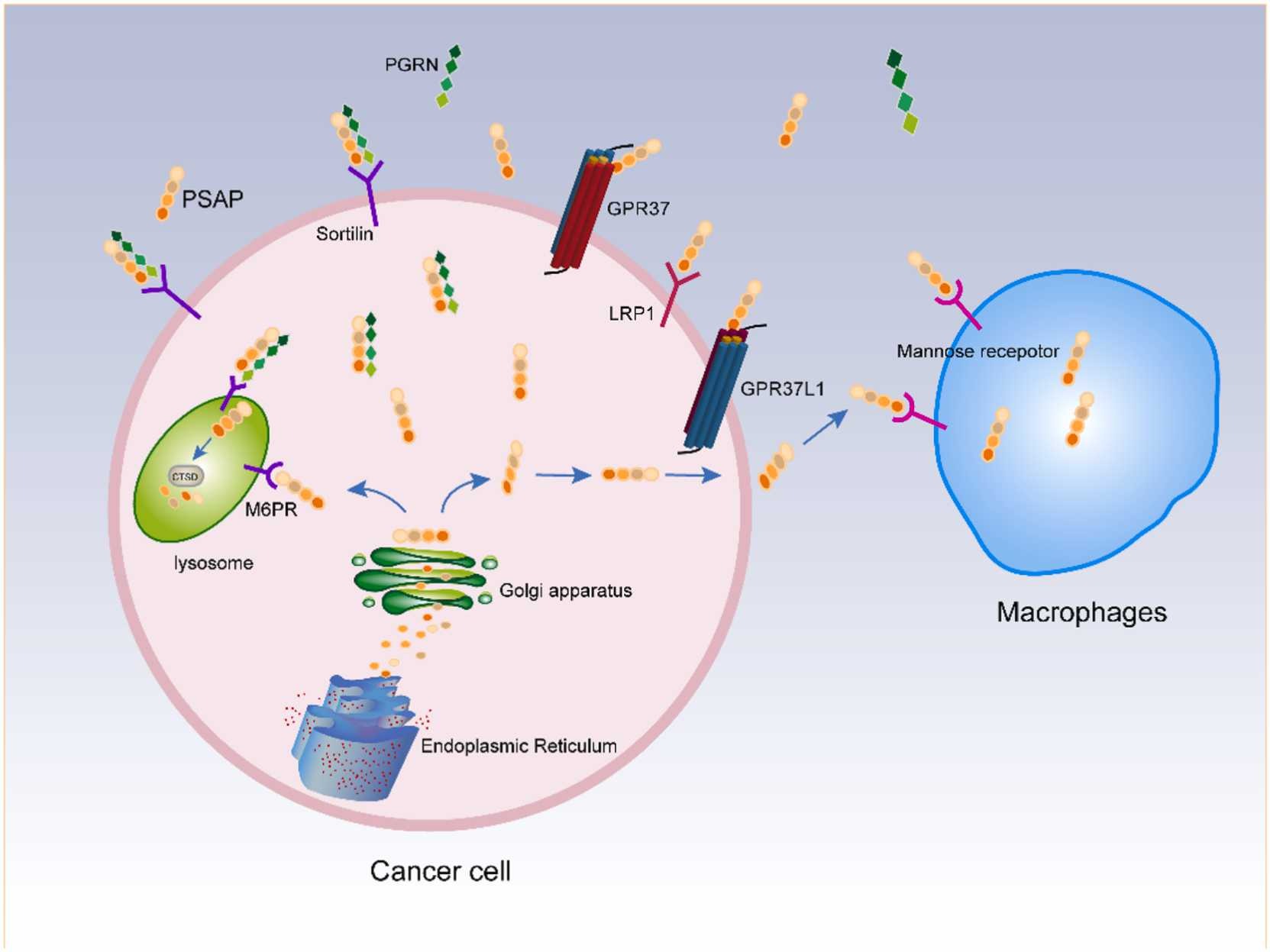
Fig1. Processing of PSAP. (Lirong Yan, 2024)
PSAP Related Signaling Pathway
Prosaposin (PSAP) plays various roles across multiple signaling pathways. As a trophic factor for both myelin and neurons, it interacts with G protein-coupled receptors, GPR37 and GPR37L1, triggering receptor-mediated internalization and ERK phosphorylation signaling. In sphingolipid metabolism, PSAP regulates enzymatic hydrolysis, with Saposin-A and Saposin-C enhancing the breakdown by specific ceramidases, highlighting their intricate role in cellular processes. Furthermore, PSAP is implicated in neuronal ferroptosis; its absence disrupts lysosomal lipid metabolism, leading to lipofuscin formation and Fe2+ accumulation, which generates ROS via the Fenton reaction, causing oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation. Additionally, PSAP interacts with mTOR signaling in atherosclerosis by affecting glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation. In the realm of tumor immunity, highly glycosylated PSAP facilitates immune evasion, impacting dendritic cell function. Thus, PSAP is pivotal in neurotrophic support, lipid metabolism, oxidative stress responses, and tumor immune pathways.PSAP Related Diseases
The PSAP protein is linked to a bunch of diseases, mainly neurological degenerative ones and certain metabolic disorders. When we talk about neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD), PSAP plays a crucial role. For instance, increased PSAP expression is associated with neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s, which are made up of overly phosphorylated tau proteins. Variations in the PSAP gene may also trigger neuronal death pathways in AD, possibly because of apoptosis. In Parkinson’s, a decrease in PSAP ties to the loss of dopamine neurons, while increased α-synuclein is a classic PD marker. Some genetic changes in PSAP could raise Parkinson’s risk, notably seen in Japanese patients. Moving on to metabolic diseases, PSAP is involved with conditions like Krabbe disease, metachromatic leukodystrophy, and Gaucher disease, all caused by deficiencies in different saposins. Changes in the PSAP gene can impair its function, affecting lipid degradation in lysosomes and thereby leading to these metabolic disorders. Hence, PSAP protein is a key player in both neurological and metabolic diseases, making it a vital target for research and treatment.Bioapplications of PSAP
Prosaposin (PSAP) is a pretty big deal when it comes to a bunch of areas like research, industry, and medicine. In the research world, it’s being closely looked at because it helps keep dopamine neurons healthy and plays a role in experimental Parkinson’s disease. People are also exploring its impact on Alzheimer’s, especially how it affects amyloid-beta (Aβ) and cell death. When it comes to industrial uses, recombinant PSAP is key for creating new bio-products and medicines. It’s used to make antibodies for different science techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, immunocytochemistry, ELISA, and flow cytometry. In the medical field, PSAP is connected to diseases like Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and some cancers. For example, it’s being studied in cancer to see how changes in tumor cells can lead to immune escape, giving new ideas for cancer treatments. Plus, its potential role in atherosclerosis makes it a target for research in that area too. So, PSAP is really important in studying disease mechanisms, checking drug targets, and developing new treatments.Case Study
Case Study 1: Xu X. et al. J Biol Chem. 2002
New research hints that presenilin proteins might play a role in cell death associated with Alzheimer’s. While the exact mechanism is still a mystery, we’ve identified a protein called presenilin-associated protein (PSAP) that binds to one type of presenilin (PS1) but not another (PS2). Interestingly, PSAP hangs out in mitochondria, fitting in with carrier proteins found there. We’ve spotted it in enriched mitochondrial samples and its presence aligns with mitochondrial markers. When there’s too much PSAP, it seems to trigger cell death through apoptosis, with signs like membrane changes, DNA fragmentation, and activation of certain molecules like caspase-3. Even though a specific inhibitor can stop the cell death cascade, it doesn’t prevent PSAP from causing cytochrome c release, showing this process might bypass usual pathways. Overall, PSAP seems to be a key player in promoting apoptosis.-
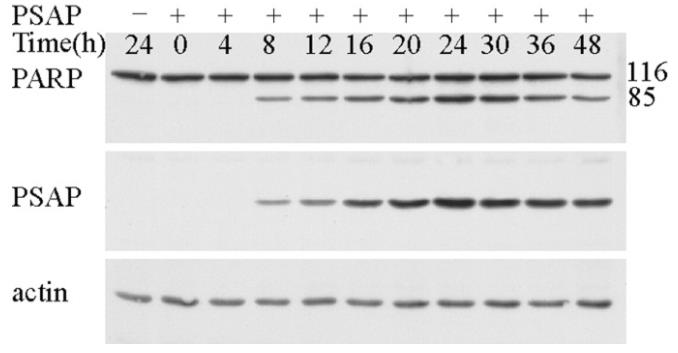 Fig1. Time course of PSAP-induced cleavage of PARP.
Fig1. Time course of PSAP-induced cleavage of PARP. -
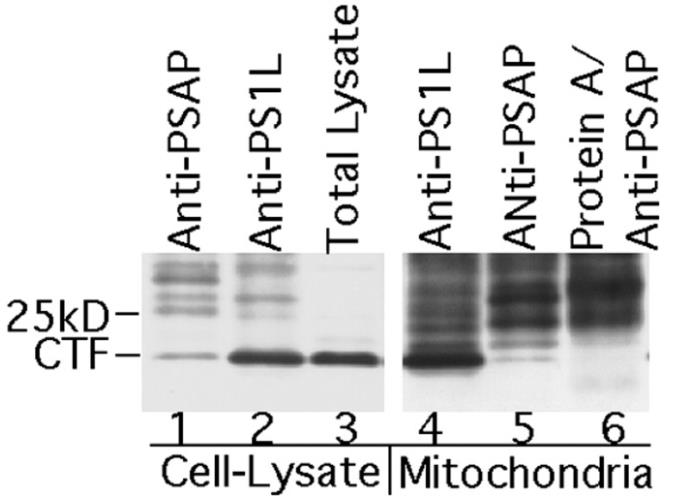 Fig2. Co-immunoprecipitation of PSAP and PS1 from mitochondria.
Fig2. Co-immunoprecipitation of PSAP and PS1 from mitochondria.
Case Study 2: Li T. et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013
PSAP, short for presenilin-associated protein, is known to be a mitochondrial protein that nudges cells toward apoptosis, though exactly how remains unclear. To unravel this, we’ve created a system to tweak its expression and looked at how it mingles with proteins like B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) family proteins, cytochrome c, Smac, and Apaf-1. Our research revealed that reducing Apaf-1 halted the caspase activation and PARP cleavage triggered by PSAP, underscoring the importance of the apoptosome formation initiated by cytochrome c. We also found that Smac is crucial since its reduction stopped the PSAP-induced apoptosis as well. Interestingly, even when Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL were overexpressed, PSAP-induced cell death wasn’t prevented, and removing Bid, Bax, and Bak didn’t affect the release of cytochrome c and Smac, suggesting that the Bcl-2 family proteins aren’t involved in PSAP-induced apoptosis regulation.-
 Fig3. Knockdown of caspase-9 abolished PSAP-induced apoptosis.
Fig3. Knockdown of caspase-9 abolished PSAP-induced apoptosis. -
 Fig4. Overexpression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL proteins had no effect on PSAP-induced apoptosis.
Fig4. Overexpression of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL proteins had no effect on PSAP-induced apoptosis.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PSAP-01H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PSAP-01H)
-
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PSAP-6022H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PSAP-6022H)
Involved Pathway
PSAP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PSAP participated on our site, such as Lysosome, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PSAP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Lysosome | PLA2G15,GALC,ATP6AP1,M6PR,GGA1,PPT1,ATP6V0D2,ARSB,GM2A,GNS |
-
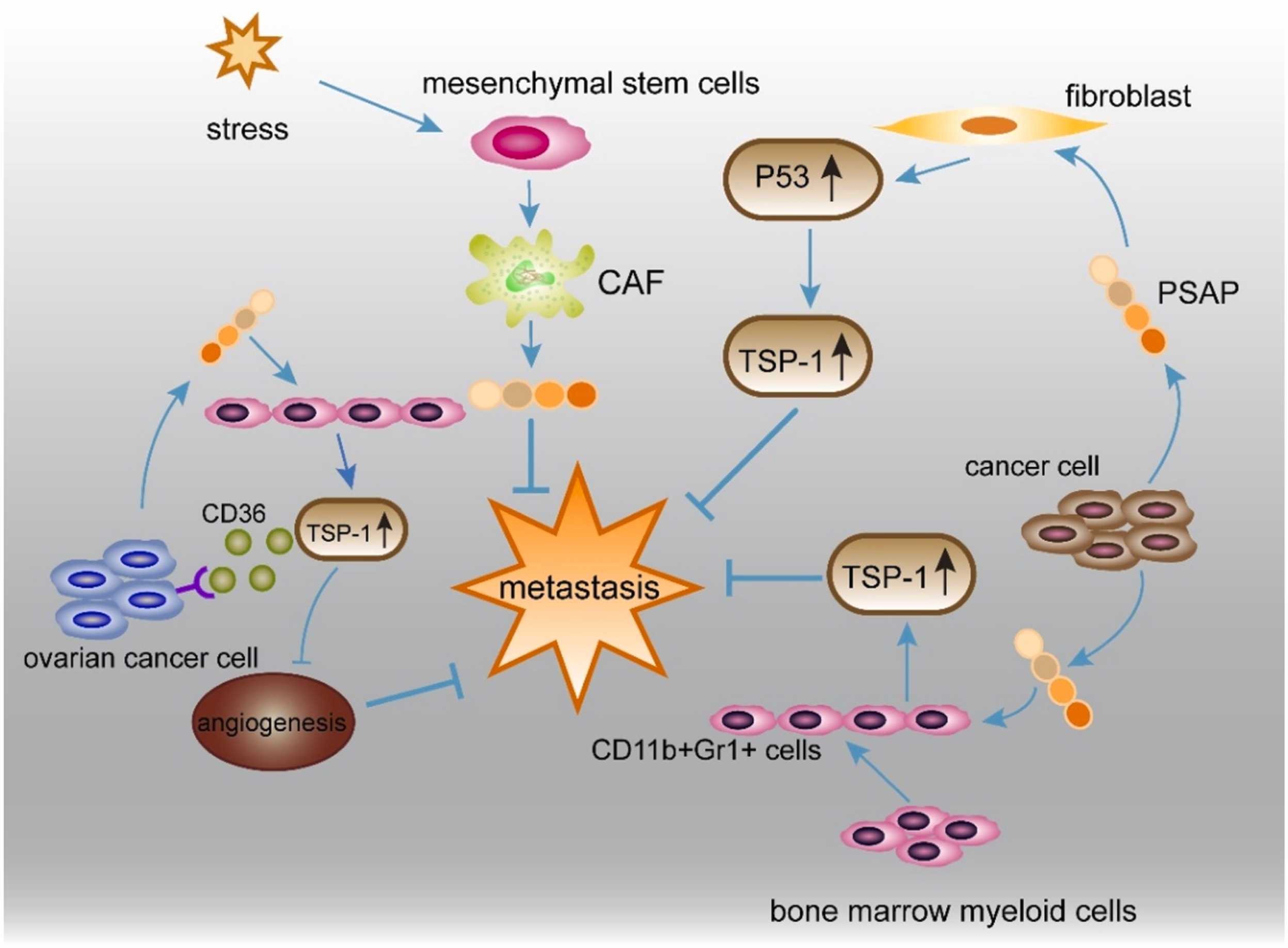 Fig1. Crosstalk of cancer cells and the tumor environment via PSAP. (Lirong Yan, 2024)
Fig1. Crosstalk of cancer cells and the tumor environment via PSAP. (Lirong Yan, 2024) -
 Fig2. Pro-CTSD, PSAP, and PGRN Network (PPPN) Proteins Interact with and Help Activate Each Other within the Lysosome. (Nahid Tayebi, 2020)
Fig2. Pro-CTSD, PSAP, and PGRN Network (PPPN) Proteins Interact with and Help Activate Each Other within the Lysosome. (Nahid Tayebi, 2020)
Protein Function
PSAP has several biochemical functions, for example, G-protein coupled receptor binding,enzyme activator activity,lipid binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PSAP itself. We selected most functions PSAP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PSAP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| lipid binding | TRIP10,S1PR4,Alb,SH3GL2,AP2A2,FFAR2,APOA5,RASGRP2,APOA1B,STARD10 |
| protein binding | DRD4,Fzd4,NAA38,PLEKHG2,PPP2R5D,MON1B,THAP10,GTF2F2,RAB26,TNFRSF12A |
| G-protein coupled receptor binding | RSPO3,RSPO2,GPRC5B,NMS,GNA13A,ADORA1,ARRB2,HSPA8,ITGB4,GNAI2 |
| enzyme activator activity | OGT,LTC4S,SAE1,TIMP2,MMP24,TAB1,CLPSL1,ALDH1A2,HSPB2,TRIM23 |
Interacting Protein
PSAP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PSAP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PSAP.
CASP14;PRSS3;SMAD9;ZBED1;ERBB2;UBE3A;SGCG;SMAD2;COPS6;q81pd4_bacan;SGK223;uvrD;CELSR1;MAFF;pi3p;cona_canen;CFTR
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Shimokawa, T; Nabeka, H; et al. Distribution of prosaposin in rat lymphatic tissues. CELL AND TISSUE RESEARCH 352:685-693(2013).
- Downes, MR; Torlakovic, EE; et al. Diagnostic utility of androgen receptor expression in discriminating poorly differentiated urothelial and prostate carcinoma. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY 66:779-786(2013).


