PPIA
-
Official Full Name
peptidylprolyl isomerase A (cyclophilin A) -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) family. PPIases catalyze the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides and accelerate the folding of proteins. The encoded protein is a cyclosporin binding-protein and may play a role in cyclosporin A-mediated immunosuppression. The protein can also interact with several HIV proteins, including p55 gag, Vpr, and capsid protein, and has been shown to be necessary for the formation of infectious HIV virions. Multiple pseudogenes that map to different chromosomes have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
PPIA;peptidylprolyl isomerase A (cyclophilin A);CYPA;CYPH;HEL-S-69p;peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A;PPIase A;rotamase A;cyclophilin;T cell cyclophilin;cyclosporin A-binding protein;epididymis secretory sperm binding protein Li 69p
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Rat
- Cattle
- Pig
- E.coli
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- HEK293
- Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
- HEK293T
- Mammalian cells
- E. coli
- His
- GST
- Non
- Myc&DDK
- His&Strep
- His&Fc&Avi
- His&SUMO
- His&Myc
- His&Myc&SUMO
- Flag
Background
What is PPIA protein?
PPIA gene (peptidylprolyl isomerase A) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 7 at locus 7p13. This gene encodes a member of the peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) family. PPIases catalyze the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides and accelerate the folding of proteins. The encoded protein is a cyclosporin binding-protein and may play a role in cyclosporin A-mediated immunosuppression. The protein can also interact with several HIV proteins, including p55 gag, Vpr, and capsid protein, and has been shown to be necessary for the formation of infectious HIV virions. The PPIA protein is consisted of 165 amino acids and PPIA molecular weight is approximately 18.0 kDa.
What is the function of PPIA protein?
The PPIA protein, also known as cyclophilin A, is a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) that plays a crucial role in protein folding and assembly. It is involved in the regulation of gene expression, particularly through its interaction with the RNA-binding protein TARDBP (TDP-43), which is implicated in neurodegenerative diseases such as ALS. PPIA's PPIase activity and its ability to bind RNA are key to its function in mRNA processing and transport, as well as in cellular responses to stress. Moreover, PPIA has been identified as a potential therapeutic target due to its role in various diseases, including its involvement in the pathogenesis of cancer and neurodegeneration.

Fig1. CypA facilitates or inhibits the replication of viruses. (Farman Ullah Dawar, 2017)
PPIA related signaling pathway
PPIA, also known as peptidylprolyl isomerase A or cyclophilin A, plays a significant role in the signaling pathways involving protein folding and immune response. It acts as a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, aiding in the proper folding of proteins by facilitating the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic bonds. PPIA is crucial in the unfolded protein response and interacts with the immunosuppressant drug cyclosporine A, inhibiting its activity. Additionally, PPIA is involved in T-cell activation and cytokine production, playing a pivotal role in the immune system's regulation. Its involvement in various signaling pathways highlights its importance in cellular processes, immune responses, and disease pathogenesis.
PPIA related diseases
The PPIA protein, also known as peptidylprolyl isomerase A or cyclophilin A, is involved in protein folding and immune responses. It plays a role in various diseases including cardiovascular diseases, viral infections, neurodegeneration, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, sepsis, asthma, and periodontitis. Mutations in PPIA have been associated with increased risk of diseases like cancer and can impact protein stability and function, contributing to disease progression.
Bioapplications of PPIA
PPIA has several bioapplications due to its roles in protein folding and immune response. It is widely used as a target for immunosuppressive therapies, particularly in organ transplantation, where inhibitors like cyclosporine A bind to PPIA to prevent T-cell activation. Additionally, PPIA is involved in the development of diagnostic assays for various diseases, including cancer and neurodegenerative disorders, due to its upregulation in these conditions. Its role in protein folding and cellular signaling pathways also makes it a potential target for therapeutic interventions in diseases associated with protein misfolding and aggregation, such as Alzheimer's disease and prion diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Laure Maneix, 2024
Here peptidyl-prolyl isomerase A (PPIA) is crucial for maintaining hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, as its loss speeds up cellular aging. PPIA targets proteins with intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs), which are important for protein-protein and protein-nucleic acid interactions and phase separation. PPIA influences the formation of stress granules, P-bodies, and nucleoli, enhancing cells' stress resistance. A decrease in PPIA expression and the translation of IDR-rich proteins is linked to hematopoietic stem cell aging, suggesting that disrupted protein interaction networks might play a role in this process.

Fig1. PPIA levels in the PB are elevated in animals receiving Ppia-transduced BM.

Fig2. PLA to quantify PPIA protein levels in mouse HSCs.
Case Study 2: Weiqiang Lu, 2024
NRF2 overactivation is a known driver of various cancers, including NSCLC, but targeting it has been challenging. This research reveals that PPIA is essential for NRF2 protein stability, and without PPIA, NRF2 degrades, inhibiting cancer cell growth. PPIA binds directly to NRF2, shielding it from KEAP1-mediated degradation. An FDA-approved drug, CsA, can disrupt this NRF2-PPIA interaction, promoting NRF2 degradation and impairing NRF2-driven glutamine metabolism, thus suppressing tumor growth. A combination of CsA and a glutaminase inhibitor shows promise in treating NRF2-hyperactivated NSCLC in patient-derived models.
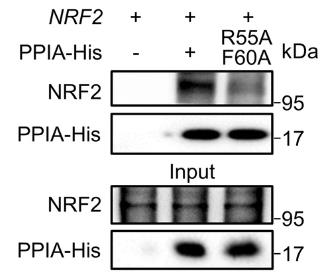
Fig3. Pull-down assay of PPIA WT/NRF2 and PPIAR55A&F60A/NRF2.
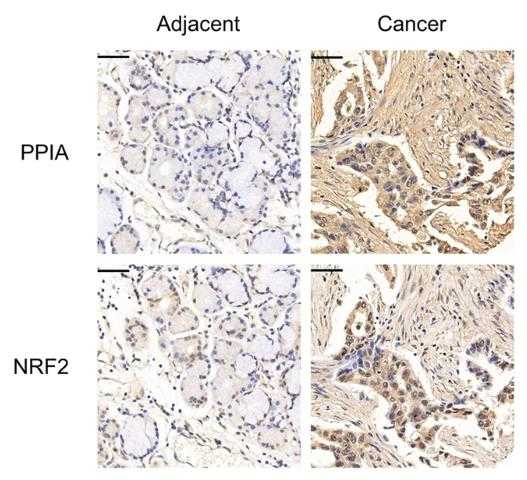
Fig4. Representative immunohistochemical analysis of PPIA in human LUAD tissue microarray.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (PPIA-187H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (PPIA-001H)
Involved Pathway
PPIA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways PPIA participated on our site, such as APOBEC3G mediated resistance to HIV-1 infection,Assembly Of The HIV Virion,Basigin interactions, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with PPIA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall | CEACAM6,GRB7,PROCR,CEACAM8,DOK2,SLC7A8A,GAS6,F11R.2,MERTK,SLC16A8 |
| Assembly Of The HIV Virion | gag,VPS37A,NMT2 |
| Early Phase of HIV Life Cycle | CCR5,PSIP1,BANF1,gag |
| Basigin interactions | SLC16A1,SLC16A8,SLC7A10,SLC7A8A,SLC3A2A,NADL1.1,ITGB1B.1,SLC7A6,BSG,SLC3A2B |
| Binding and entry of HIV virion | CCR5,gag |
| APOBEC3G mediated resistance to HIV-1 infection | PSIP1,gag,HMGA1,BANF1,APOBEC3G |
| Budding and maturation of HIV virion | VPS37A,gag,PDCD6IP,CHMP4B,CHMP4C |
| Disease | DPF1,RBP1,SUPT4H1,PRELP,ARF1,AP2A1,CDK9,MMADHC,EEF2,HEY2 |
Protein Function
PPIA has several biochemical functions, for example, peptide binding,peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity,poly(A) RNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by PPIA itself. We selected most functions PPIA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with PPIA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| poly(A) RNA binding | LRRC47,DDX55,HDAC2,ZC3H10,PES1,SRSF11,TSFM,PCBP4,RAVER2,NMD3 |
| peptide binding | Ctsl,Npepo,LTA4H,ADNP,ERAP2,CRIP1,GPR37L1,ENPEP,MAS1,MME |
| virion binding | HIPK2,APCS,TSG101,CD209,CLEC4M,PVRL1,PTX3,HSP90B1 |
| protein binding | PNKP,GNE,CD40,CRYBB3,ITGB1BP2,C4orf46,RHOH,C1GALT1C1,GCET2,NFATC2 |
| unfolded protein binding | SYVN1,LRPAP1,AIP,DNAJB8,DNAJA2L,HSP90AA1,PFDN4,LMAN1,HSP90AA1.2,HSPD1 |
| peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity | FKBP3,PIN4,PPIL3,FKBP14,FKBP1B,PPIAB,FKBP7,PPIE,FKBP1AB,PPIL4 |
Interacting Protein
PPIA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with PPIA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of PPIA.
gag;q99ib8-pro_0000045602;LNX1;SUPT5H;PTPRN;AIFM1;gag-pol
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Lacombe, J; Mange, A; et al. A Multiparametric Serum Marker Panel as a Complementary Test to Mammography for the Diagnosis of Node-Negative Early-Stage Breast Cancer and DCIS in Young Women. CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY BIOMARKERS & PREVENTION 23:1834-1842(2014).
- Garibo, D; Flores, C; et al. Inhibition equivalency factors for microcystin variants in recombinant and wild-type protein phosphatase 1 and 2A assays. ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE AND POLLUTION RESEARCH 21:10652-10660(2014).



