ETF1
-
Official Full Name
eukaryotic translation termination factor 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a class-1 polypeptide chain release factor. The encoded protein plays an essential role in directing termination of mRNA translation from the termination codons UAA, UAG and UGA. This protein is a component of the SURF complex which promotes degradation of prematurely terminated mRNAs via the mechanism of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Pseudogenes of this gene are found on chromosomes 6, 7, and X. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2013] -
Synonyms
ETF1;eukaryotic translation termination factor 1;ERF;RF1;ERF1;TB3-1;D5S1995;SUP45L1;eukaryotic peptide chain release factor subunit 1;protein Cl1;polypeptide chain release factor 1;sup45 (yeast omnipotent suppressor 45) homolog-like 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Mamanlian cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His&T7
- His
- Non
- Myc&DDK
- His&Fc&Avi
- Flag
Background
What is ETF1 protein?
ETF1 gene (eukaryotic translation termination factor 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 5 at locus 5q31. This gene encodes a class-1 polypeptide chain release factor. The encoded protein plays an essential role in directing termination of mRNA translation from the termination codons UAA, UAG and UGA. This protein is a component of the SURF complex which promotes degradation of prematurely terminated mRNAs via the mechanism of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). The ETF1 protein is consisted of 437 amino acids and ETF1 molecular weight is approximately 49.0 kDa.
What is the function of ETF1 protein?
ETF1 or eRF1 protein plays a critical role in the termination of protein synthesis. It recognizes the stop codons UAA, UAG, and UGA during mRNA translation and facilitates the release of the completed polypeptide chain from the ribosome. The protein is a component of the SURF complex, which is involved in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), a process that degrades mRNAs containing premature stop codons. ETF1 is essential for maintaining the fidelity of protein synthesis and is conserved across eukaryotes, highlighting its importance in cellular function.
ETF1 related signaling pathway
The ETF1-related signaling pathway is primarily involved in the regulation of energy metabolism and mitochondrial function. ETF1, also known as electron-transfer-flavoprotein subunit alpha, plays a crucial role in the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system by transferring electrons from fatty acid beta-oxidation and amino acid degradation to the electron transport chain. Dysregulation of this pathway can lead to impaired energy production, accumulation of toxic metabolic intermediates, and development of metabolic disorders such as multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) or glutaric aciduria type I. Understanding the mechanisms underlying ETF1-mediated signaling is essential for developing therapeutic strategies targeting mitochondrial dysfunction and metabolic diseases.
ETF1 related diseases
The ETF1-related diseases primarily involve conditions associated with mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation defects and impaired energy metabolism. Mutations in the ETF1 gene, which encodes electron-transfer flavoprotein subunit alpha, can lead to multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) or glutaric aciduria type I. These disorders result from dysfunctional fatty acid beta-oxidation and amino acid degradation pathways, causing accumulation of toxic metabolites and leading to symptoms such as metabolic acidosis, hypoglycemia, and neurological impairments. Understanding the role of ETF1 in these diseases is crucial for developing targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes.
Bioapplications of ETF1
The ETF1-related diseases primarily involve conditions associated with mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation defects and impaired energy metabolism. Mutations in the ETF1 gene, which encodes electron-transfer flavoprotein subunit alpha, can lead to multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) or glutaric aciduria type I. These disorders result from dysfunctional fatty acid beta-oxidation and amino acid degradation pathways, causing accumulation of toxic metabolites and leading to symptoms such as metabolic acidosis, hypoglycemia, and neurological impairments. Understanding the role of ETF1 in these diseases is crucial for developing targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Alexey Shuvalov, 2024
The eRF1 protein, encoded by ETF1, terminates translation by recognizing stop codons. ETF1 produces two isoforms: the well-studied eRF1 and a shorter, less studied isoform 2. This research using a mammalian in vitro translation system revealed that eRF1 isoform 2 is involved in translation, interacts with ribosomal subunits, and has reduced activity in codon recognition and peptide release. It specifically interacts with eRF3a but less effectively stimulates its GTPase activity. Here eRF1 isoform 2 suppresses readthrough of upstream open reading frames and reduces the translation efficiency of long coding sequences, suggesting a role in regulating translation termination.

Fig1. eRF1iso2 bound to different ribosomes.
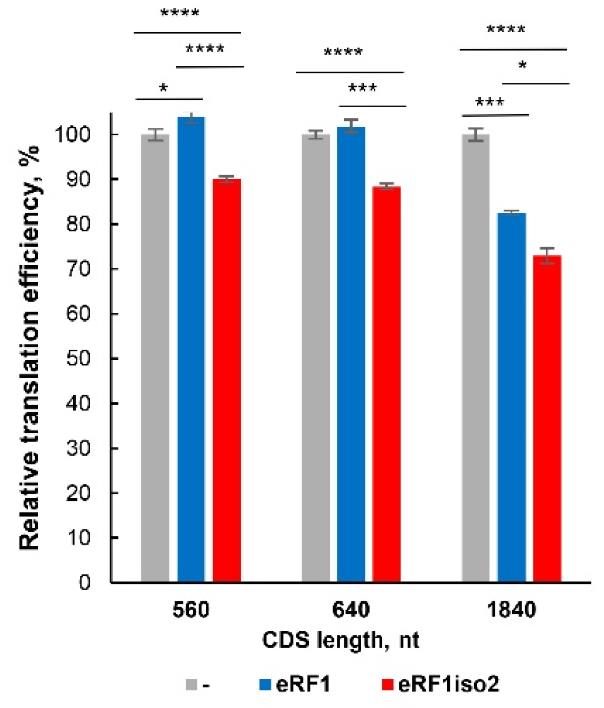
Fig2. Translation of Nluc mRNAs with various CDS lengths in the presence of eRF1 isoforms in HeLa lysate.
Case Study 2: Polina Kryuchkova, 2013
eRF1, a critical protein synthesis termination factor in eukaryotes, is composed of three functional domains. This study investigates the role of 41 conserved residues in the N-domain of human eRF1 in stop codon recognition. Through mutations and in vitro translation assays, we identified 15 key residues for stop codon decoding. Our data also suggest a ribosomal complex conformational change during eRF1 binding to mRNA, leading to a proposed two-step model for stop codon decoding by eukaryotic ribosomes.
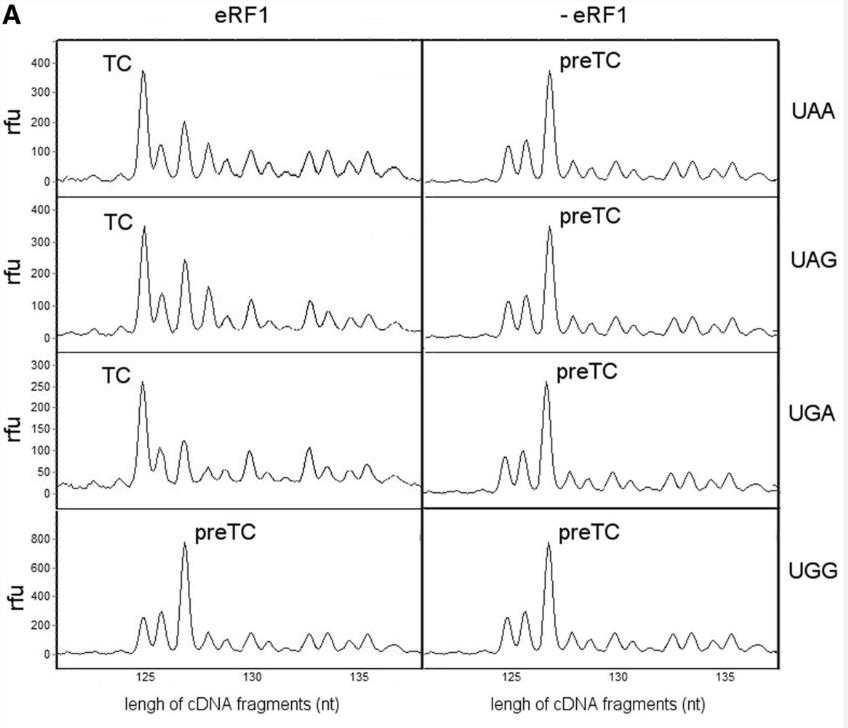
Fig3. Toe-prints with the human wt eRF1 at different stop codons and UGG codon.
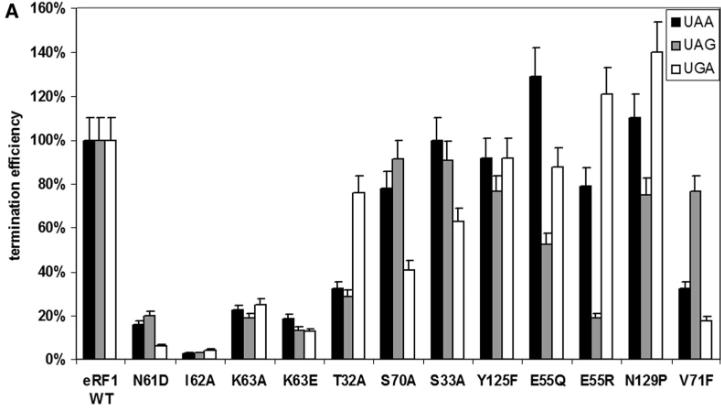
Fig4. Termination efficiencies of the wt eRF1 and mutant eRF1s at different stop codons in the absence of eRF3-GTP.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (ETF1-1397H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (ETF1-3514H)
Involved Pathway
ETF1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways ETF1 participated on our site, such as mRNA surveillance pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with ETF1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| mRNA surveillance pathway | CPSF1,CPSF2,UPF1,PPP1CAA,ETF1A,PELO,PNN,PABPC1,PABPC4,SMG1 |
Protein Function
ETF1 has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA binding,poly(A) RNA binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by ETF1 itself. We selected most functions ETF1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with ETF1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ribosome binding | EFTUD1,BAG6,ETF1A,EIF2S1A,CPEB4,HSPA5,NARG1,EIF3K,ETF1B,ERI1 |
| protein binding | NCKIPSD,RRAS2,NDEL1,NDP,NUTF2,QKI,DDIT4L,ICAM1,RASSF7,AP1B1 |
| translation release factor activity | MTRF1,GSPT1L,GSPT2 |
| RNA binding | TDRKH,RPL21,SPI1,EXOSC1,EIF4E2RS1,CELF3A,UPF1,ATXN2,MPHOSPH6,EIF5A |
| translation release factor activity, codon specific | ETF1A,MTRF1L,ETF1B,MTRF1 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | CNBP,TDRD9,MRPS12,MEX3C,FAM98A,DDX23,HIST2H4,HIST1H4K,PTRF,ZYX |
Interacting Protein
ETF1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with ETF1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of ETF1.
KEAP1;GSPT1;a8k1f4_human;MLF1;PSMD2;IKBKE;TRMT10C;GSPT2;FKBPL;TRAF6;Mphosph9;FGFR1OP;ALB;VCAM1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


