DNASE1L3
-
Official Full Name
deoxyribonuclease I-like 3 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the DNase family. The protein hydrolyzes DNA, is not inhibited by actin, and mediates the breakdown of DNA during apoptosis. Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene have been observed but have not been thoroughly characterized. -
Synonyms
DNASE1L3;deoxyribonuclease I-like 3;deoxyribonuclease gamma;DNAS1L3;DNase gamma;LSD;LS-DNase;DNase I-like 3;Liver and spleen DNase;DNase I homolog protein 2;DNase I homolog protein DHP2;deoxyribonuclease I-like III;DHP2;SLEB16
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- E. coli
- Insect Cell
- GST
- His
- Non
- N-GST, C-His
- His&Fc&Avi
- His&Myc
Background
What is DNASE1L3 protein?
DNASE1L3 gene (deoxyribonuclease 1L3) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3p14. DNASE1L3 is an enzyme belonging to the deoxyribonuclease I family, whose primary function is to hydrolyze DNA. It is not inhibited by actin, which means it can remain active in the presence of actin. During apoptosis, DNASE1L3 mediates the breakdown of DNA. This process is essential for clearing DNA fragments from dead cells and helps maintain the body's normal physiological state. The DNASE1L3 protein is consisted of 305 amino acids and DNASE1L3 molecular weight is approximately 35.5 kDa.
What is the function of DNASE1L3 protein?
DNASE1L3 is an enzyme with DNA hydrolysis activity that plays a role in a variety of cellular processes. DNASE1L3 is highly expressed in dendritic cells and is essential for regulating the immune response of their own DNA and chromatin. It helps maintain immune tolerance and prevent the development of autoimmune diseases by degrading DNA produced during apoptosis and necrosis. In addition, DNASE1L3 is also associated with the stability of the cell cycle regulatory protein P21, which regulates the cell cycle by affecting the ubiquitination degradation of P21. Therefore, DNASE1L3 plays an important role in maintaining immune balance, anti-tumor immunity, and cell cycle regulation.
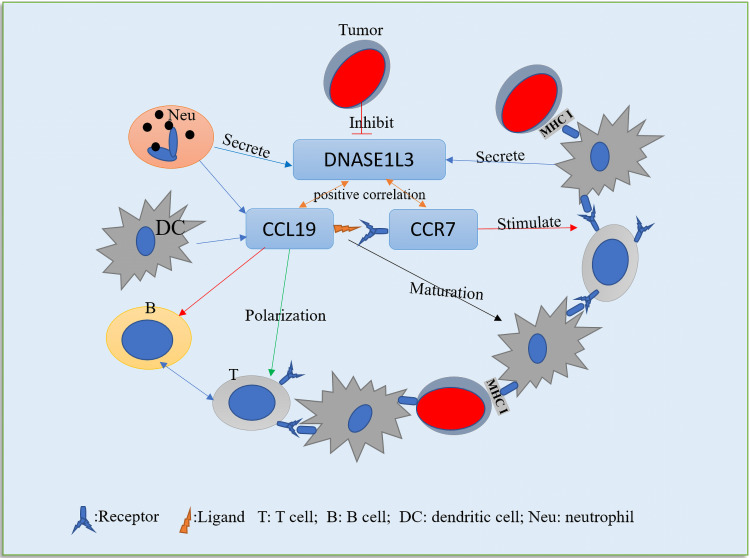
Fig1. One probable underlying mechanism in the correlation among DNASE1L3, tumor cells and tumor immune microenvironment. (Zenghua Deng, 2021)
DNASE1L3 related signaling pathway
DNASE1L3 may act by regulating cytokines and chemokines in the inflammatory response. For example, it can affect the production and release of inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). DNASE1L3 plays an important role in the process of apoptosis, and it may affect the process of apoptosis by regulating the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins. DNASE1L3 can also influence tumor growth and spread by regulating cytokines and chemokines in the tumor microenvironment. DNASE1L3 can also influence the process of DNA repair by regulating DNA damage-induced signaling pathways.
DNASE1L3 related diseases
DNASE1L3 protein plays a role in various diseases, especially in tumor immunity and autoimmune diseases. In the context of tumor immunity, DNASE1L3 regulates the function of dendritic cells (DCs) to enhance anti-tumor immune responses and inhibit tumor progression. For example, in colorectal cancer, the downregulation of DNASE1L3 expression is associated with poor prognosis and reduced immune cell infiltration. In autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), the reduction of DNASE1L3 activity may lead to an immune dysregulation of self-DNA and chromatin, thereby promoting the progression of the disease. Additionally, DNASE1L3 also plays a role in hepatocellular carcinoma by interacting with β-catenin to promote its ubiquitin degradation pathway, inhibiting the proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of tumor cells.
Bioapplications of DNASE1L3
The biological applications of rhDNASE1L3 are mainly related to inflammation regulation, tumor therapy and reproductive biology research. In autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, the application of rhDNASE1L3 may help regulate abnormal immune responses and inflammatory states. In the tumor microenvironment, rhDNASE1L3 can regulate the expression of cytokines and chemokines, affecting tumor growth and spread. The specific mechanisms of action of rhDNASE1L3 during spermatogenesis and maturation are being studied and may be critical for male fertility.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Deliang Guo, 2021
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a difficult cancer to treat due to its aggressive nature and lack of effective therapies. DNASE1L3, a DNA damage response enzyme, plays a role in HCC progression and angiogenesis. This study showed that DNASE1L3 is downregulated in HCC and associated with poorer patient outcomes. Researchers discovered that DNASE1L3 reduces cytoplasmic DNA accumulation under DNA damage stress, which inhibits cell senescence and the associated pro-angiogenic secretory phenotype through the p53 and NF-κB pathways. Additionally, DNASE1L3 translocates to the nucleus and interacts with H2BE to regulate these effects, suggesting it as a potential therapeutic target for HCC.

Fig1. estern blot analysis of DNASE1L3 protein expression in HCC cell lines and a normal liver cell line.

Fig2. FRET assay for DNASE1L3-H2BE interactions in living cells.
Case Study 2: Bo Li, 2022
DNASE1L3, part of the deoxyribonuclease 1 family, is implicated in both intracellular and extracellular processes, including its role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This research indicates that DNASE1L3 is underexpressed in HCC and associated with clinical features of the disease. Both in vivo and in vitro, DNASE1L3 was found to suppress HCC cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Mechanistically, DNASE1L3 facilitates the degradation of β-catenin by enhancing its ubiquitination and preventing its nuclear translocation, which leads to the downregulation of c-Myc, P21, and P27, thereby inhibiting cell cycle progression and EMT signaling.

Fig3. Silver staining of SDS-PAGE gel.

Fig4. Western blot showing the effect of DNASE1L3 on β-catenin stability in Huh7 cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DNASE1L3-12097H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (DNASE1L3-1535H)
Involved Pathway
DNASE1L3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DNASE1L3 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DNASE1L3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
DNASE1L3 has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,calcium ion binding,deoxyribonuclease activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DNASE1L3 itself. We selected most functions DNASE1L3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DNASE1L3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| endodeoxyribonuclease activity | DNASE1L3L,DNASE1L2,ZRANB3,MBD4,DNASE2A,MRE11A,DNASE1,APLF,DNASE1L1,ERCC4 |
| endodeoxyribonuclease activity, producing 5-phosphomonoesters | TATDN2,DNASE1L1,DNASE1L2,TATDN3,ENDOV,TATDN1 |
| calcium ion binding | S100P,FBN1,PCDH10B,CLGN,RHOT1B,NOTCH2NL,MYO5A,SMOC2,PCDHB1,EGFL8 |
| DNA binding | ZFAND5,ENG1A,RREB1,IRF2A,HJURP,HOXA13,ORC3,MCM2,ADNP,NKX3-1 |
| deoxyribonuclease activity | NME1,TATDN2,DNASE1L1,TATDN1,DNASE1L2,DNASE1L3L,TATDN3,ENDOG |
Interacting Protein
DNASE1L3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DNASE1L3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DNASE1L3.
CD247
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References


