DHODH
-
Official Full Name
dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone) -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the fourth enzymatic step, the ubiquinone-mediated oxidation of dihydroorotate to orotate, in de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis. This protein is a mitochondrial protein located on the outer surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane. -
Synonyms
DHODH;dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone);dihydroorotate dehydrogenase;dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (quinone), mitochondrial;dihydroorotate oxidase;human complement of yeast URA1;URA1;POADS;DHOdehase
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Pongo Abelii
- Bovine
- Mus musculus
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is DHODH Protein?
DHODH, or dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, is an enzyme hanging out in the mitochondria, which you can think of as the cell's power stations. Its main gig is helping make pyrimidines, a critical piece of RNA and DNA. This enzyme acts like a traffic cop, controlling the flow of this building block, so cells can grow and split. Without it, the whole process slows down, making it super important for cell growth. Because of its crucial role, scientists are really interested in DHODH when it comes to fighting viruses and even cancer. Some drugs target this enzyme to hinder the growth of harmful cells or viruses by essentially starving them of the ingredients they need to make new genetic material. So, in short, DHODH is pretty important for cell growth and a hot target for therapeutic research.What is the Function of DHODH Protein?
DHODH, or dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, plays a vital role inside cells. Found in the mitochondria—the cell’s power centers—it helps crank out pyrimidines, which are necessary for making RNA and DNA. Imagine DHODH as a cog in a machine; without it, creating these genetic building blocks would stop, halting cell growth and division. This function is critical not just for routine cell maintenance but also for quick cell growth, like in cancer or viral infections. Researchers are keen on DHODH because targeting it could help manage cell growth in various diseases, making it a big focus in developing new treatments.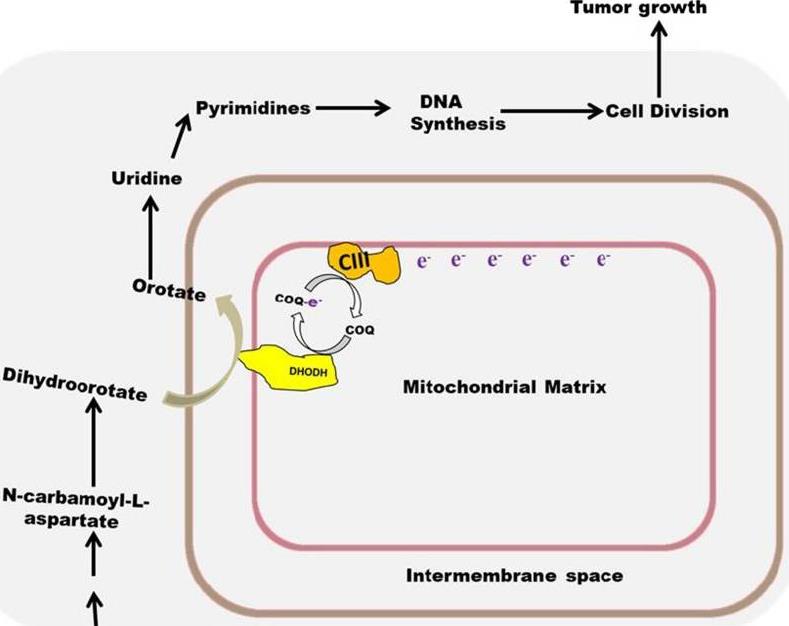
Fig1. Role of DHODH and complex III in tumor growth. (Alvan Amos, 2023)
DHODH Related Signaling Pathway
The pathways involving DHODH (dihydroorotate dehydrogenase) are pretty interesting because they're key to a lot of cellular activity. DHODH helps produce pyrimidines, essential components for DNA and RNA, tying it to various cell processes. One major area is the immune system; DHODH activity can affect immune signaling, helping the body tackle viruses and bacteria. It also impacts decisions on cell growth, which is crucial for normal function and development. In some diseases, like cancer, these pathways might get overly active, leading to uncontrolled cell growth. That's why there's a lot of interest in targeting DHODH pathways for new treatments, particularly in cancer and immune-related conditions. Researchers are exploring these pathways to find ways to adjust them for better health solutions.DHODH Related Diseases
DHODH, which stands for dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, is tied to a range of diseases because of its key role in how cells grow and function. Take cancer, for instance: cancer cells divide rapidly and need lots of DNA and RNA, which rely on DHODH. Blocking DHODH can starve these cells and slow tumor growth, making it a target for cancer therapies. In autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, where the immune system goes into overdrive and attacks healthy tissues, DHODH inhibitors can help tone down this response. Some viruses also latch onto DHODH to help them multiply. By targeting DHODH, we could potentially cut off the resources they need to spread, giving us a new angle for antiviral treatments. Because DHODH is at the heart of these vital processes, it’s a big focus in creating innovative medical therapies.Bioapplications of DHODH
DHODH (dihydroorotate dehydrogenase) is important in medicine due to its role in key body processes. In cancer, blocking DHODH can help slow down tumor growth by cutting off the supply of DNA and RNA that cancer cells require to keep multiplying. For autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, DHODH inhibitors can calm down an overactive immune system. Plus, since some viruses use DHODH to replicate, stopping this enzyme could be helpful in fighting viral infections. Because of its involvement in these critical areas, DHODH is a significant target for developing new treatments across different health challenges.Case Study
Case Study 1: Xiang H. et al. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is challenging to treat, with ferroptosis playing a key role. Researchers studied PACS2's impact on this process. Lowering PACS2 in heart cells treated with high glucose and palmitic acid (HGPA) reduced signs of ferroptosis—like iron and ROS increases—by adjusting CPT1A and DHODH levels. However, further PACS2 reduction with a CPT1A agonist worsened cell death. In diabetic mice, removing PACS2 improved heart function and reduced ferroptosis, suggesting a potential treatment avenue.-
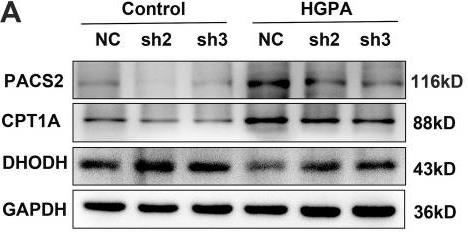 Fig1. After HGPA intervention and PACS2 silencing, protein blotting was used to detect the expression of PACS2, CPT1A and DHODH.
Fig1. After HGPA intervention and PACS2 silencing, protein blotting was used to detect the expression of PACS2, CPT1A and DHODH. -
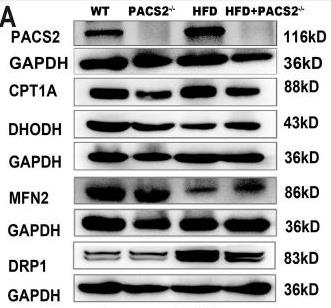 Fig2. Protein blotting was used to detect the expression of PACS2, CPT1A, DHODH and the mitochondrial proteins.
Fig2. Protein blotting was used to detect the expression of PACS2, CPT1A, DHODH and the mitochondrial proteins.
Case Study 2: Zhao B-q. et al. J Virol. 2024
Mitochondria help control viral replication through immune pathways. DHODH inhibitors, targeting mitochondria, that effectively fight classical swine fever virus (CSFV) by blocking pyrimidine synthesis and enhancing immune responses. DHODH is crucial for CSFV replication, and the virus's NS4A protein interacts with DHODH to aid replication. Specific amino acid regions in both proteins are key to this interaction.-
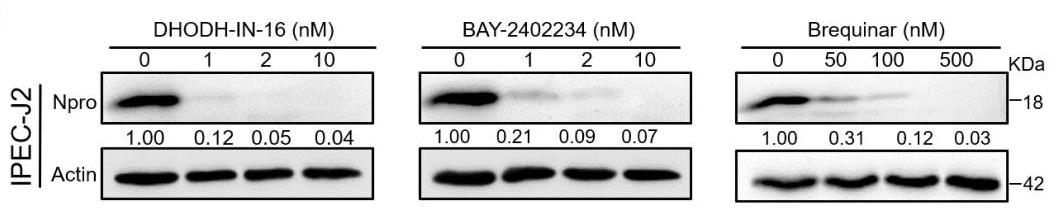 Fig3. IPEC cells were treated with either DMSO or different concentrations of DHODH-IN-16, BAY-2402234, and Brequinar.
Fig3. IPEC cells were treated with either DMSO or different concentrations of DHODH-IN-16, BAY-2402234, and Brequinar. -
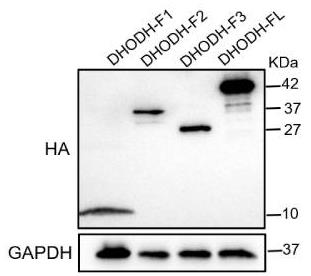 Fig4. Cells transfected with pHA-DHODH or its truncated mutant plasmids or control vector for 24 h were harvested and subjected to Western blotting.
Fig4. Cells transfected with pHA-DHODH or its truncated mutant plasmids or control vector for 24 h were harvested and subjected to Western blotting.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DHODH-1859R)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DHODH-1859R) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (DHODH-01H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (DHODH-01H)
Involved Pathway
DHODH involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DHODH participated on our site, such as Metabolic pathways,Metabolism,Metabolism of nucleotides, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DHODH were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolic pathways | ABP1,B3GAT3,LSS,DBH,ATP5A1,CEPT1B,SRM,RPE,DHFRL1,PLCD3 |
| Pyrimidine biosynthesis | DUT |
| Metabolism | CYB5A,ABHD3,CYP2K19,CYP3A7,PCBD1,GLYATL2,GLYAT,NAALAD2,NUDT4B,NHLRC1 |
| Pyrimidine metabolism | PRIM1,UCKL1,NME5,UCK2,ZNRD1,NT5C2B,DPYDB,NT5C3L,POLA1,POLD2 |
| Metabolism of nucleotides | ADSL,PNP5B,DTYMK,NUDT15,ADSS,GLRX,ADK,GRX2,ADSSL1,PAICS |
-
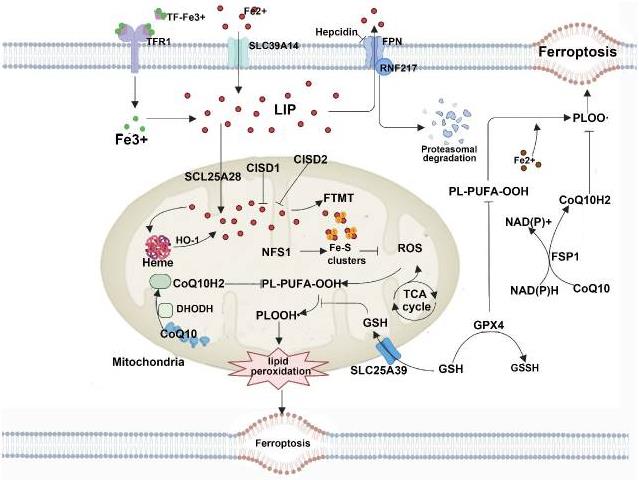 Fig1. Mitochondria host a wide range of key metabolic processes and are a major source of reactive oxygen species (ROS). (Zhiyong Long, 2024)
Fig1. Mitochondria host a wide range of key metabolic processes and are a major source of reactive oxygen species (ROS). (Zhiyong Long, 2024) -
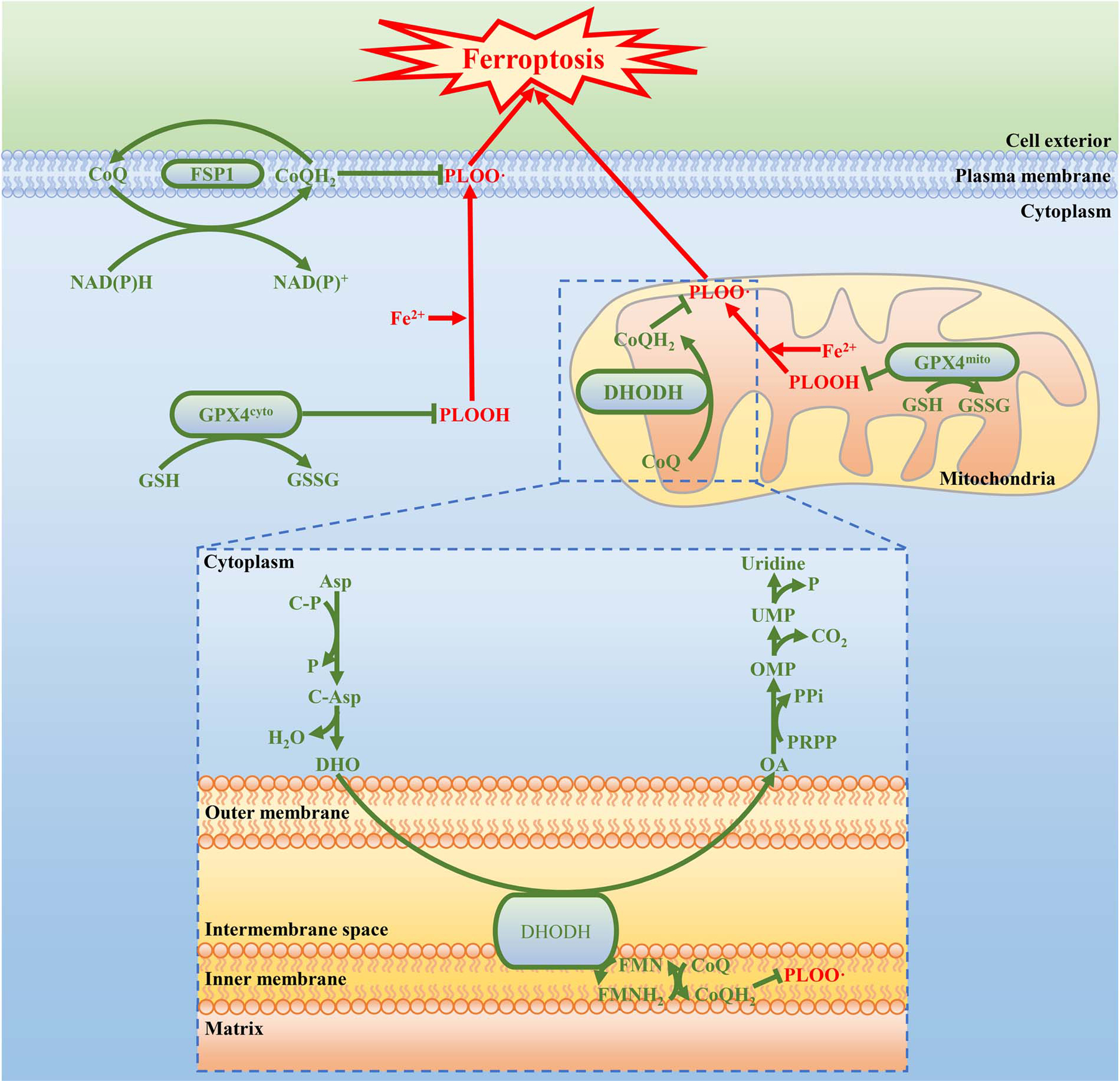 Fig2. The working model depicting how GPX4, FSP1, and DHODH suppress ferroptosis at different subcellular compartments. (Chao Mao, 2021)
Fig2. The working model depicting how GPX4, FSP1, and DHODH suppress ferroptosis at different subcellular compartments. (Chao Mao, 2021)
Protein Function
DHODH has several biochemical functions, for example, FMN binding,dihydroorotate dehydrogenase activity,drug binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DHODH itself. We selected most functions DHODH had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DHODH. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ubiquinone binding | ETFDH,SDHDB,SDHDA,SDHD,SDHB |
| FMN binding | NDOR1,TYW1B,TYW1,CREG2,NOS3,MTRR,CREG1,HAO2,POR,HAO1 |
| drug binding | RARB,GLRB,SLC6A4A,TLR8,MTOR,CHRM3,ABP1,PPARA,DRD3,PPP3CB |
Interacting Protein
DHODH has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DHODH here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DHODH.
MT2A;TMED10
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Schaefer, CM; Schafer, MKH; et al. Region-Specific Distribution of Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase in the Rat Central Nervous System Points to Pyrimidine De Novo Synthesis in Neurons. NUCLEOSIDES NUCLEOTIDES & NUCLEIC ACIDS 29:476-481(2010).
- Thomson, TA; Spinella-Jaegle, S; et al. In vitro and In vivo inhibition of immunoglobulin secretion by the immunosuppressive compound HR325 is reversed by exogenous uridine. SCANDINAVIAN JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY 56:35-42(2002).



