CR1
-
Official Full Name
CR1 complement component (3b/4b) receptor 1 (Knops blood group) -
Synonyms
CR1;complement component (3b/4b) receptor 1 (Knops blood group);complement component (3b/4b) receptor 1, including Knops blood group system;complement receptor type 1;CD35;KN;CD35 antigen;C3b/C4b receptor;C3-binding protein;Knops blood group antigen;complement component receptor 1;C3BR;C4BR
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mammalian cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- His&Fc&Avi
- Non
| Cat.# | Product name | Source (Host) | Species | Tag | Protein Length | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR1-506H |
Active Recombinant Human CR1 protein, His-tagged
|
Mammalian cells | Human | His | 42-1971 a.a. |
|
| CR1-507H | Recombinant Human CR1 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | Human | His | Ile1780~Pro2039 |
|
| CR1-2726H | Recombinant Human CR1 protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | Human | GST | 41-234aa |
|
| CR1-2727H | Recombinant Human CR1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | Human | His&Fc&Avi |
|
|
| CR1-2727H-B | Recombinant Human CR1 Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads | HEK293 | Human |
|
||
| CR1-4018H | Recombinant Human CR1 Protein (Met1-Asp1971), C-His tagged | Mammalian cells | Human | His | Met1-Asp1971 |
|
| CR1-P016H | Recombinant Human CR1 therapeutic protein(Mirococept) | Human | Non |
|
Background
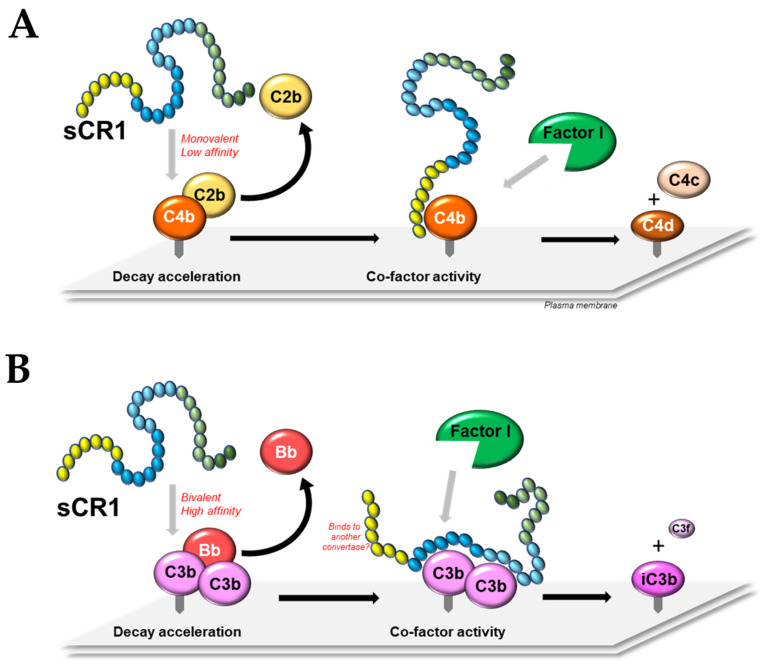
Fig1. A model of the molecular mechanisms of soluble CR1. (Matthew P Hardy, 2023)
What is CR1 protein?
CR1 gene (complement C3b/C4b receptor 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q32. The gene encodes a monomeric single-pass type I membrane glycoprotein found on erythrocytes, leukocytes, glomerular podocytes, and splenic follicular dendritic cells. The protein mediates cellular binding to particles and immune complexes that have activated complement. Decreases in expression of this protein and/or mutations in this gene have been associated with gallbladder carcinomas, mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, sarcoidosis and Alzheimer's disease. The CR1 protein is consisted of 2039 amino acids and CR1 molecular weight is approximately 223.7 kDa.
What is the function of CR1 protein?
CR1 protein is a multifunctional glycoprotein expressed on a variety of cell types, including red blood cells, monocytes, macrophages, B lymphocytes, etc. CR1 plays a key role in regulating complement system activation, promoting phagocytosis, and regulating immune complex clearance. Through its multiple domains, CR1 binds to C3b and C4b to promote the regulation of the complement system and prevent excessive attack by its own tissues. In addition, CR1 is also involved in the control of proliferation of B cells and immune regulation of T cells.
CR1 related signaling pathway
The CR1 receptor recognizes and binds to its ligands, chemokines such as CCL15, as well as C3b on bacteria or viruses. This binding is highly specific, ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of signal transduction. CR1 binds to the ligand and increases intracellular calcium concentration via the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) pathway. This process is a classical pathway of signal transduction, with calcium ions acting as a second messenger, initiating a downstream signal cascade. These signaling molecules are modulated through interactions and feedback that amplify the initial signal, allowing the cell to make a stronger and more durable response. At the same time, CR1 can also act as a cofactor of factor I, promote the inactivation of C3b and C4b, and prevent tissue damage caused by excessive complement activation.
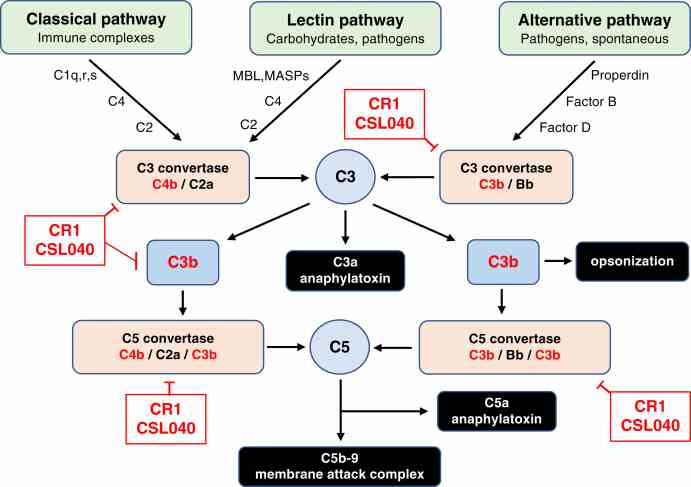
Fig2. Involvement of CR1/CSL040 in complement pathway inhibition. (Sandra Wymann, 2021)
CR1 related diseases
The CR1 protein, or complement receptor 1, is an important immunomodulatory protein that plays a role in a variety of diseases. CR1 is mainly expressed on red blood cells, white blood cells and endothelial cells in certain tissues, and is involved in regulating the activity of the complement system, promoting the clearance of immune complexes, and playing a role in inflammatory responses and autoimmune diseases. Genetic polymorphisms of CR1 are associated with risk and prognosis for a variety of diseases, including cardiovascular, infectious, and autoimmune diseases. For example, CR1 has been reported in chronic Chagas disease, Alzheimer's disease, diabetes-related diseases, and certain eye diseases such as age-related macular degeneration. In addition, CR1 also plays a role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, possibly influencing the disease process by regulating amyloid metabolism.
Bioapplications of CR1
CR1 is an important immunomodulatory protein that plays a central role in the activation and regulation of the complement system. rhCR1 can be used to study the regulatory mechanisms of the complement system and its function in the immune response. In addition, because CR1 expression and function can change in a variety of diseases, rhCR1 can also be used to develop and test new therapies for these diseases, including autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and certain types of cancer. For example, by studying rhCR1's interaction with the complement system, its role in disease can be better understood and new strategies for targeted therapy of the complement system can be provided.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Sandra Wymann, 2021
Human complement receptor 1 (HuCR1) regulates the complement system by binding to C3b/C4b and accelerating their decay. Researchers created a truncated version of HuCR1, CSL040, which is a potent inhibitor of complement activation. CSL040 maintains its binding to C3b and C4b and its decay acceleration activity, and it is stable under various conditions. It has a better pharmacokinetic profile than the full HuCR1, and its effect on acute complement-mediated kidney injury was tested in a glomerulonephritis model, showing potential for complement-related disease treatment.

Fig1. Biosensor data of plasma-derived human C3b binding to HuCR1(1971).
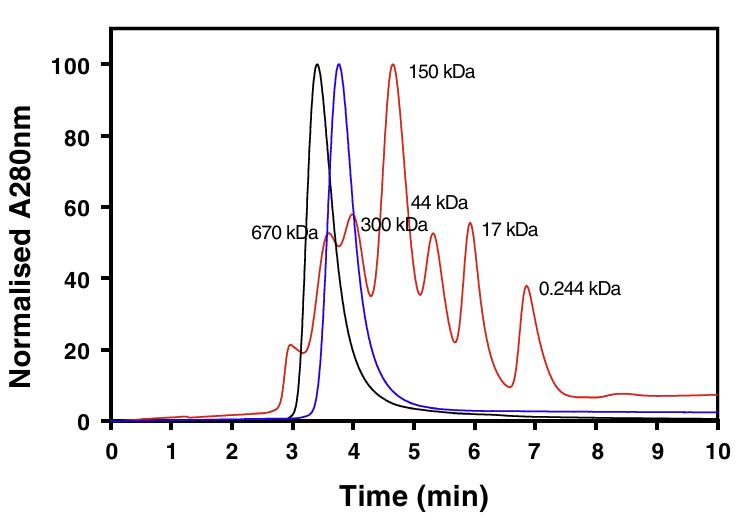
Fig2. The analytical SEC of HuCR1 variants.
Case Study 2: Anuja Java, 2015
The complement regulator gene cluster, including Complement receptor 1 (CR1), controls the complement system's amplification at the C3 activation step. CR1, expressed on podocytes in the kidney, has a significant role in regulating complement activation on epithelial cells. Using a Chinese hamster ovary cell model, researchers found CR1 to be a powerful regulator of both classical and alternative complement pathways, reducing C3b deposition by approximately 80% and over 95%, respectively, mainly through decay acceleration. CR1 also cleaved deposited C4b and C3b to C4d and C3d. It acted intrinsically, binding but not internalizing immune complexes. These findings highlight CR1's potential as a complement regulator and immune receptor in epithelial cells.
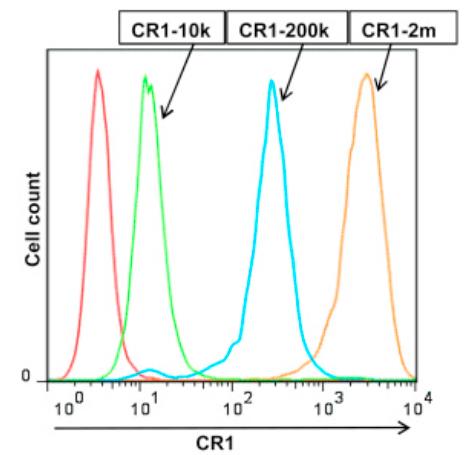
Fig3. Flow cytometry to compare expression of CR1 on transfected CHO cells.
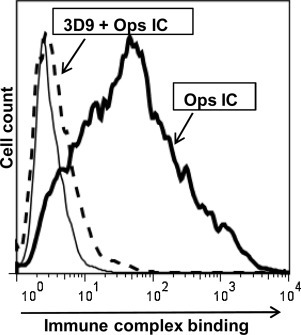
Fig4. CR1 binds opsonized immune complexes.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CR1-507H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CR1-4018H)
Involved Pathway
CR1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CR1 participated on our site, such as Complement and Coagulation Cascades,Complement cascade,Hematopoietic cell lineage, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CR1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | TNF,ITGA1,CD14,CR2,CD3E; CD3D,GM2002,IL3RA,ITGA6,ITGA5,ITGA3 |
| Complement and coagulation cascades | PLAT,F7,CFH,F10,C8G,Serpina1b,LOC100514666,F12,KNG1,MASP2 |
| Immune System | KIF2B,UBE2E3,KIF5B,LAIR1,DDOST,GHRB,TCIRG1,OSCAR,KPNA4,AGER |
| Leishmaniasis | HLA-DRA,IL1A,MARCKSL1,HLA-DRB3,ITGA4,FCGR2A,Itgam&Itgb2,IFNGR2,PRKCB,PTGS2 |
| Innate Immune System | DEFA1,CD300E,PANX1,POLR3F,MASP2,TNRC5,DUSP3B,LAT2,SUGT1,BTR06 |
| Complement cascade | CFHL4,CRP,HBL3,FCN2,CFHL3,CFHL2,IGKC,CFHL1,FCN1,FCN3 |
| Legionellosis | TLR5,EEF1A2,MYD88,CASP9,EEF1G,RELA,TNF,HSPA1B,NFKB2,HBS1L |
Protein Function
CR1 has several biochemical functions, for example, complement component C3b binding,complement component C3b receptor activity,complement component C4b binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CR1 itself. We selected most functions CR1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CR1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| complement component C4b binding | MASP2 |
| virus receptor activity | EFNB3,CD46,RPSA,LAMP1,NCAM1,HSPA1B,PVR,LDLR,CD209,SELPLG |
| complement component C3b binding | PHB |
Interacting Protein
CR1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CR1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CR1.
purL;q7ara8_yerpe;ubiF;bioB;ypvA;pgl;lexA
Resources
Research Area
B Cell CD AntigenOther Proteins Involved in Regulating B Cell Activation
T Follicular Helper (Tfh) Cells
MDSC Phenotyping - Negative Markers
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Koechli, V; Klaeser, B; et al. Consolidation of first remission using radioimmunotherapy with yttrium-90-ibritumomab-tiuxetan in adult patients with Burkitt lymphoma. LEUKEMIA RESEARCH 39:307-310(2015).
- Ogembo, JG; Muraswki, MR; et al. A chimeric EBV gp350/220-based VLP replicates the virion B-cell attachment mechanism and elicits long-lasting neutralizing antibodies in mice. JOURNAL OF TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE 13:-(2015).


