CDK2
-
Official Full Name
cyclin-dependent kinase 2 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of a family of serine/threonine protein kinases that participate in cell cycle regulation. The encoded protein is the catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent protein kinase complex, which regulates progression through the cell cycle. Activity of this protein is especially critical during the G1 to S phase transition. This protein associates with and regulated by other subunits of the complex including cyclin A or E, CDK inhibitor p21Cip1 (CDKN1A), and p27Kip1 (CDKN1B). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2014] -
Synonyms
CDK2;cyclin-dependent kinase 2;CDKN2;p33(CDK2);p33 protein kinase;cdc2-related protein kinase;cell division protein kinase 2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Insect Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Human
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Sf21 Cells
- His
- GST
- MBP
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is CDK2 protein?
CDK2 gene (cyclin dependent kinase 2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12q13. This gene encodes a member of a family of serine/threonine protein kinases that participate in cell cycle regulation. The encoded protein is the catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent protein kinase complex, which regulates progression through the cell cycle. Activity of this protein is especially critical during the G1 to S phase transition. This protein associates with and regulated by other subunits of the complex including cyclin A or E, CDK inhibitor p21Cip1 (CDKN1A), and p27Kip1 (CDKN1B). The CDK2 protein is consisted of 298 amino acids and CDK2 molecular weight is approximately 33.9 kDa.
What is the function of CDK2 protein?
It is particularly important for the transition from the G1 phase to the S phase, where it helps initiate DNA synthesis and duplication of centrosomes. CDK2 is activated by binding with cyclins, particularly cyclin E and cyclin A, and its activity is tightly regulated by various mechanisms including phosphorylation and interaction with CDK inhibitors such as p21 and p27. It is also involved in other cellular processes such as DNA repair, transcription, and apoptosis. Drug-targeted inhibition of CDK2 is an area of interest in cancer therapy, and understanding its regulatory mechanisms and substrates is crucial for developing targeted treatments.

Fig1. Dual roles of CDK2 in DNA damage and DDR. (Qi Liu, 2020)
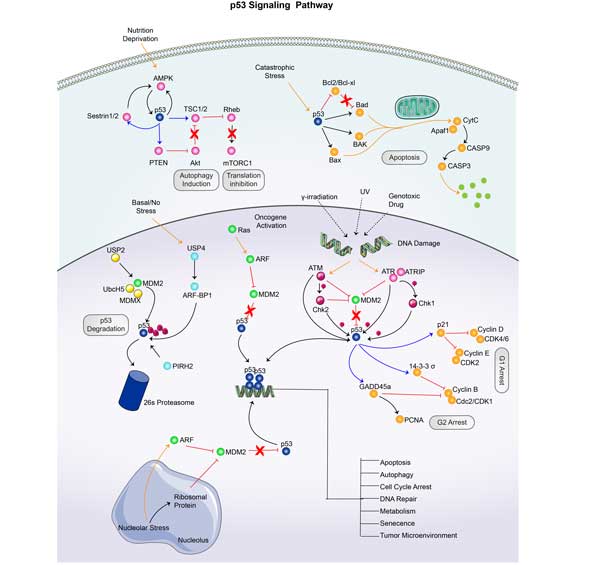
CDK2 Related Signaling Pathway
In cell cycle regulation, CDK2 regulates G1-S and S-G2 transitions by binding to cyclin E and cyclin A, phosphorylation of CAK complexes (CDK7, MAT1, cyclin H) and dephosphorylation of CDC25A. During apoptosis regulation, CDK2 regulates the core regulatory and functional components of the apoptosis pathway through phosphorylation of pro-survival factors and transcription factors, such as FOXO1 and myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein (MCL-1). In tumors, the non-cell cycle functions of CDK2 include participating in cell differentiation, promoting tumor occurrence and malignant process, and associated with chromosomal instability (CIN), participating in a variety of carcinogenic signaling pathways, and the imbalance of its content or activity may lead to the uncontrolled proliferation of tumor cells. It also affects many biological functions such as tumor cell differentiation, senescence, apoptosis and chromosome instability.
CDK2 Related Diseases
The abnormal activity of CDK2 is closely related to the occurrence and development of many diseases, especially tumors. Its imbalance may lead to uncontrolled cell cycle and disorderly proliferation of tumor cells. The abnormal signaling pathway involved in CDK2 is also related to the differentiation, senescence, apoptosis and chromosome stability of tumor cells, thus affecting the malignant process of tumor. In addition, abnormal functioning of CDK2 has been associated with certain non-neoplastic diseases, such as certain hereditary cancer syndromes.
Bioapplications of CDK2
Because of its key role in cell cycle regulation and the development of multiple tumors, CDK2 has become an important target for drug development, and its related applications are mainly focused on the discovery and development of anticancer drugs, including the design and application of selective CDK2 inhibitors, which have shown potential to treat cancer by interfering with tumor cell proliferation and survival signaling pathways. In addition, CDK2 inhibitors are also being studied to enhance the sensitivity of tumor cells to other anti-cancer treatments, such as radiation and chemotherapy, as well as as part of a combination treatment strategy.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Zhengchao Shen, 2021
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are hyperactive in many cancers and have served as cancer therapeutic targets for decades. Palbociclib (Palb) is the first approved CDK4/6 inhibitor to treat hormone receptor (HR)-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer. CDK2 compensation of CDK4/6 loss is one of the causes that cancer cells are resistant to Palb. Hence, targeting multiple CDKs could be a novel strategy to prevent the drug resistance of cancer cells and expand the application of Palb in other cancer. In this study, researchers initially indicated Polyphyllin I (PPI) significantly inhibits non-small lung cancer cell (NSCLC) proliferation, promotes cell apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, PPI can inhibit Rb through the p21/CDK2/Rb signaling pathway in NSCLC. A combination of PPI and Palb exerts a significant synergistic anti-cancer ability on NSCLC.

Fig1. WB of A549 and H460 cells were infected by lentiviruses with control or p21 shRNA.

Fig2. The harvested tumors were subsequently lysed and western blot analysis was performed.
Case Study 2: Jing Feng, 2020
Hormone receptor-positive breast cancer accounts for around 75% of breast cancers. The estrogen receptor pathway promotes tumor progression and endocrine resistance. Recently, the cross-talk between the ER signaling pathway and cell cycle regulation has been identified. It is necessary to determine the underlying molecular mechanisms involved in the ER signaling pathway and find new target genes for prognosis and drug resistance in ER+ breast cancer. In this study, lncRNA MAFG-AS1 was shown to be up-regulated and associated with poor prognosis in ER+ breast cancer. Functionally, down-regulation of MAFG-AS1 could inhibit cell proliferation and promote apoptosis. In addition, MAFG-AS1 which contained an estrogen-responsive element could promote CDK2 expression by sponging miR-339-5p. Subsequently, MAFG-AS1 and CDK2 were found to be up-regulated in tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 cells. Cross-talk between the ER signaling pathway and cell cycle conducted by MAFG-AS1 and CDK2 could promote tamoxifen resistance.

Fig3. Expression of CDK2 in 50 breast tumors compared with para-carcinoma tissues.

Fig4. Western blot was performed to detect CDK2 expression in T47D and MCF-7 with MAFG-AS1 and miR-339-5p over expression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CDK2-1933H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CDK2-1000H)
Involved Pathway
CDK2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CDK2 participated on our site, such as APC/C-mediated degradation of cell cycle proteins,Activation of ATR in response to replication stress,Activation of the pre-replicative complex, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CDK2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell Cycle Checkpoints | BARD1,RNF168,KAT5,CHEK1,THRSP,CDK5RAP2,FAM175A,UIMC1,RAD9A,RAD50 |
| Activation of ATR in response to replication stress | MCM8,RAD9,HUS1,DBF4,RAD9A,CLSPN,RAD17,MCM10,CHEK1,RAD9B |
| BARD1 signaling events | RAD50,CSTF1,BARD1,NPM1,RBBP8 |
| Cell cycle | ORC6L,CDC20,ORC4,ORC3L,DCTN1A,VRK2,CDC7,BLZF1,GADD45A,CCNB2 |
| APC/C-mediated degradation of cell cycle proteins | PSMD14,UBE2C,ANAPC10,PSMD5,PSME3,PSMD9,PSMD10,NEK2,PSMA8,AURKB |
| Activation of the pre-replicative complex | DBF4,MCM10,MCM8,CDT1 |
| B Cell Receptor Signaling Pathway | PIK3CA,ITK,VAV2,DOK1,BCL10,LIME1,LILRB3,SOS1,TTC6,PILRB |
Protein Function
CDK2 has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,cyclin binding,cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CDK2 itself. We selected most functions CDK2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CDK2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity | CCNK,CDK4,CDK7,CDK20,STK30,CDK15,NAT1,CDKL3,CDK12,CDK3 |
| ATP binding | HSPD1,KCNJ11,SMC1AL,MCM6,PIKFYVE,GLUL,ACVR1C,UCKL1,DARS2,DDX5 |
| metal ion binding | RBM4.1,PKM,PARP12A,GFI1B,CHN2,HDAC8,GALNT5,NUBP2,ZNF606,PRDM13 |
| cyclin binding | CDK12,PFTK1,CDK6,CDKN1A,USP2,CDK5RAP3,MDFIC,CUL3,FBXW7,HDAC3 |
| protein complex binding | PPP1R9B,YWHAB,PAFAH1B1,SLC25A3,INS2,ITGB1BP1,UQCRC1,AKAP5,ADRB2,UGT1A6A |
| protein binding | SPARC,AGPS,NUAK1,SH2D1A,ASGR2,ADRA2C,ARNTL,TNNI2,SYNJ2BP,LRRC6 |
Interacting Protein
CDK2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CDK2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CDK2.
CCNA2
CDK2 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Histone PhosphorylationIntracellular Kinases in the Akt Pathway
Cyclin-Dependent Protein Kinases (CDKs)
Glomerulonephritis Therapeutic Targets
G1 (Restriction) Checkpoints
CDKs (Cyclin Dependent Kinases)
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Shi, HL; Fu, CL; et al. The FGF-1-specific single-chain antibody scFv1C9 effectively inhibits breast cancer tumour growth and metastasis. JOURNAL OF CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR MEDICINE 18:2061-2070(2014).
- Wang, B; Li, DP; et al. Ionizing Radiation-Inducible miR-27b Suppresses Leukemia Proliferation via Targeting Cyclin A2. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY BIOLOGY PHYSICS 90:53-62(2014).