A2M
-
Official Full Name
alpha-2-macroglobulin -
Overview
Alpha-2-macroglobulin is a protease inhibitor and cytokine transporter. It inhibits many proteases, including trypsin, thrombin and collagenase. A2M is implicated in Alzheimer disease (AD) due to its ability to mediate the clearance and degradation of A-beta, the major component of beta-amyloid deposits. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
A2M;alpha-2-macroglobulin;A2MD;CPAMD5;FWP007;S863-7;alpha-2-M;C3 and PZP-like alpha-2-macroglobulin domain-containing protein 5
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Pig
- Rat
- Insect Cells
- Mouse Serum
- Human Plasma
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cell
- Human
- Insect Cell
- Mammalian cells
- HEK293
- HEK293T
- Yeast
- Rat serum
- Mouse
- His
- Non
- GST
- Flag
- His&Fc&Avi
- Myc&DDK
Background
What is A2M Protein?
A2M gene (alpha-2-macroglobulin) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12p13. A2M protein is a high molecular weight glycoprotein widely present in plasma and synovial fluid, which has extensive protease inhibition. Through its unique "trapping" mechanism, A2M is able to inhibit a variety of proteases, including serine, carboxyl, mercaptan, and metalloproteinases. The main function of A2M is as a non-specific protease inhibitor, which can bind to a variety of immune inflammatory factors and cytokines, affect the balance of these factors in the body, and play a wide range of physiological functions. Genetic polymorphisms of A2M may affect its function and are associated with susceptibility to certain diseases. The A2M protein is consisted of 1474 amino acids and A2M molecular weight is approximately 163.3 kDa.
What is the Function of A2M Protein?
Through its unique "trapping" mechanism, A2M is able to inhibit many types of proteases, including serine, carboxyl, mercaptan, and metalloproteinases. When the protease recognizes and hydrolyzes the "trap region" of A2M, the A2M undergoes a conformational change, forming a cage structure that wraps the protease and prevents it from interacting with the substrate. A2M can bind and regulate immune inflammatory factors and cytokines, affect the balance of these factors in the body, and play an anti-inflammatory role. In neurological diseases, A2M binds to amyloid beta (Aβ) and promotes the breakdown and clearance of Aβ through cellular endocytosis mediated by low density lipoprotein receptor-associated protein (LRP), alleviating its neurotoxicity. A2M is involved in the regulation of extracellular matrix proteins and influences the process of tissue remodeling and repair.
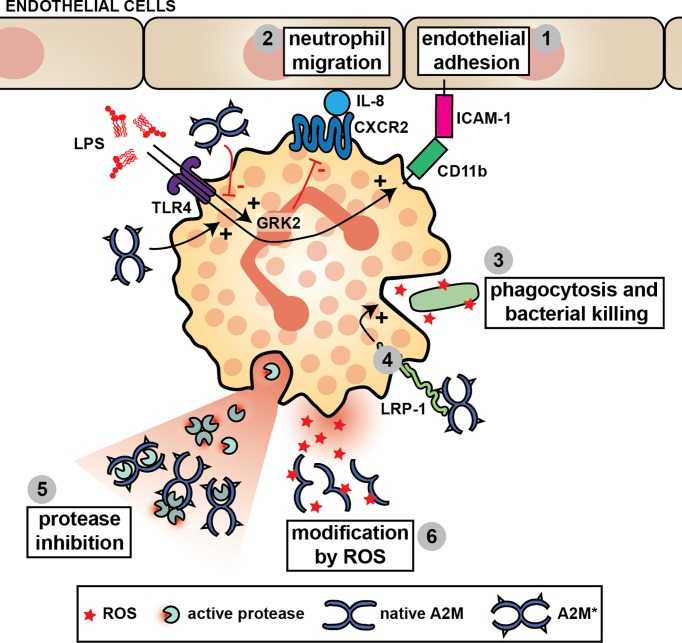
Fig1. A2M and neutrophil function. (Jennifer Vandooren, 2021)
A2M Related Signaling Pathway
A2M proteins play key roles in a variety of biological processes, including protease inhibition, regulation of inflammatory responses, extracellular matrix remodeling, regulation of FGF signaling pathways, promotion of tumor cell proliferation and invasion, and protection in neurological diseases. Through its unique "trapping" mechanism, A2M inhibits the activity of various proteases, and affects the balance of immune cytokines and cytokines, thus participating in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and apoptosis. In the development of tumor, the abnormal expression of A2M may be related to the enhancement of the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells, and its role in the tumor microenvironment is also involved in the formation of intercellular communication and tumor treatment resistance.
A2M Related Diseases
Abnormal expression of A2M protein (α2-macroglobulin) is associated with a variety of diseases, including but not limited to Alzheimer's disease, in which A2M is involved in the clearance of beta-amyloid and affects the progression of the disease; In tumor development, such as high-grade serous ovarian cancer, A2M gene expansion is associated with tumor cell proliferation and aggressiveness; In metabolic diseases, such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, the expression level of A2M is related to the disease state; As well as in inflammatory and immune responses, A2M influences the onset and progression of disease by regulating the activity of cytokines. In addition, mutations in the A2M gene can also lead to rare genetic disorders, such as α2-macroglobulin deficiency.
Bioapplications of A2M
Due to its key role in disease development, A2M protein shows potential for a wide range of applications in medical research and clinical treatment, including as a biomarker for early diagnosis and disease surveillance, and as a therapeutic target for the development of novel therapeutic strategies, particularly in Alzheimer's disease, tumor therapy, inflammatory diseases and metabolic diseases. The regulatory role of A2M also makes it a candidate molecule for drug development, potentially helping to develop interventions that target specific pathological processes, such as controlling disease progression by inhibiting or activating the function of A2M. In addition, functional studies of A2M will also help to understand its complex mechanisms in cell signaling and extracellular matrix interactions, providing new perspectives and methods for precision medicine.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Changqi Sun, 2023
Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and subsequent upregulation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is implicated as an important player in the development of posttraumatic osteoarthritis (PTOA). Alpha 2-macroglobulin (A2M) can inhibit this inflammatory pathway, making it a promising therapy for PTOA. Herein, researchers demonstrate that A2M binds and neutralizes IL-1β, blocking downstream NF-κB-induced catabolism seen in in vitro. Human chondrocytes (cell line C28) were incubated with A2M protein and then treated with IL-1β. The degree of binding between A2M and IL-1β was evaluated through immunoprecipitation (IP). Catabolic proteins, including IL-1β and NF-kB, were detected by Western blot. Pro-inflammatory and chondrocyte-related gene expression was examined by qRT-PCR. IP experiments demonstrated that A2M could bind IL-1β. Additionally, western blot analysis revealed that A2M neutralized IL-1β and NF-κB in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, A2M decreased levels of MMPs and TNF-α and increased the expression of cartilage protective genes Col2, Type2, Smad4, and aggrecan. Mostly importantly, A2M was shown to directly neutralize IL-1β to downregulate the pro-inflammatory responses mediated by the NF-kB pathway.
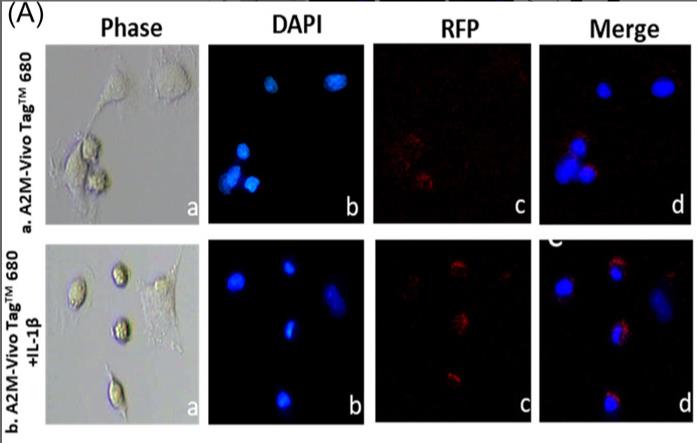
Fig1. A2M was labeled with Vivo Tag™ 680 (red one) and was identified within the chondrocytes.
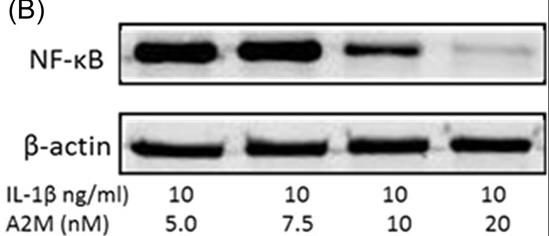
Fig2. Effects of IL-1β or A2M on NF-κB expression in human C28 chondrocyte.
Case Study 2: Pablo F Barcelona, 2015
Previously, the research team showed that the soluble protein α2-macroglobulin (α2M) is neurotoxic. Toxicity is due in part to α2M binding to NGF and inhibiting trophic activity, presumably by preventing NGF binding to TrkA. However, the mechanisms remained unclear. Here, they show ex vivo and in vivo three mechanisms for α2M neurotoxicity. First, unexpectedly the α2M-NGF complexes do bind TrkA receptors but do not induce TrkA dimerization or activation, resulting in deficient trophic support. Second, α2M makes stable complexes with proNGF, conveying resistance to proteolysis that results in more proNGF and less NGF. Third, α2M-proNGF complexes bind p75(NTR) and are more potent agonists than free proNGF, inducing tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) production. Hence, α2M regulates proNGF/p75(NTR) positively and mature NGF/TrkA negatively, causing neuronal death ex vivo.
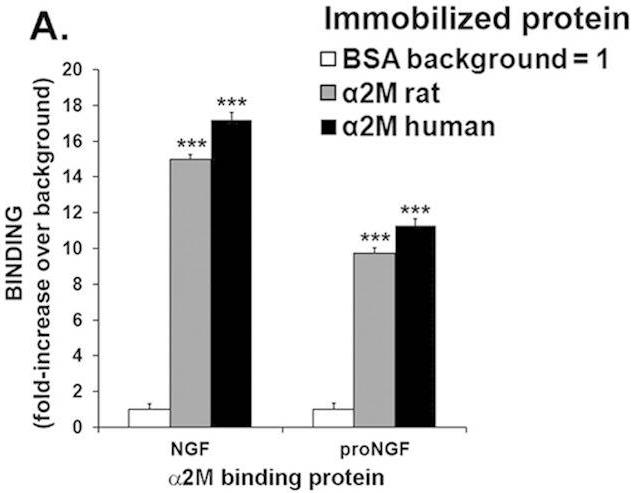
Fig3. Soluble NGF and soluble proNGF bind to immobilized α2M.
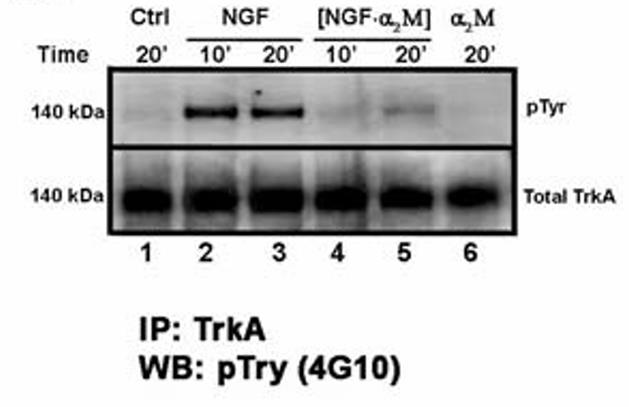
Fig4. The effects of mature NGF and α2M-NGF complexes were tested for biochemical activation of TrkA and p-Tyr.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (A2M-003H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (A2M-5731H)
Involved Pathway
A2M involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways A2M participated on our site, such as Complement and coagulation cascades, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with A2M were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | MBL2,CFB,CFH,BDKRB1,FGA,BDKRB2,CD46,F10,CR1,FGG |
Protein Function
A2M has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium-dependent protein binding,enzyme binding,growth factor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by A2M itself. We selected most functions A2M had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with A2M. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| interleukin-1 binding | HAX1,TRIM16 |
| calcium-dependent protein binding | SYT1,S100A6,ANXA11,CCDC167,RBM22,PDCD6,MASP2,ANXA2,PDCD6IP,VPS37C |
| enzyme binding | ARPC4,ATG3,TP53,KIAA1967,PDE4DIP,BCL10,CCND1,HIST1H2AG,AXIN1,PTEN |
| protease binding | SERPINF2,CCDC71L,FLOT1,SERPINB9,CSTA,DERL1,ADAM8A,ALPI,ITGB3,SERPINB6 |
| protein binding | STRADA,PTPN4,ZC3H15,LMO4,SIRPB1,NUS1,ARMC2,SREK1,SGOL1,CUEDC2 |
| receptor binding | PANX1,FZD8,SRMS,INSL3,TYROBP,DECR2,PLAUR,BMP2,HCK,PVRL1 |
| interleukin-8 binding | CXCR1,CXCR2 |
| tumor necrosis factor binding | TNFRSF1A,Tnfrsf26 |
| growth factor binding | ACVR1C,RHBDF2,LTBP4,NRP2,ACVR2A,REG3B,LIFR,SDCBP,TEK,ACVR2B |
Interacting Protein
A2M has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with A2M here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of A2M.
SMAP;ADAMTS12;ADAMTS7;IL1B;KLK3;MMP2;IL10;SPACA3;IFIT3;NUDT21;MGEA5;CDK2AP2;RPP14;APOE;TTR;TK1;APP;CYP2C8;UMPS
Resources
Research Area
Serine Proteases and RegulatorsCoagulation Cascade Protease Inhibitors
FGF Family
Acute Phase Proteins
Metalloproteases and Regulators
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Lee, JH; Cho, CH; et al. Semi-quantitative Measurement of a Specific Glycoform Using a DNA-tagged Antibody and Lectin Affinity Chromatography for Glyco-biomarker Development. MOLECULAR & CELLULAR PROTEOMICS 14:782-795(2015).
- Vissers, LELM; Bonetti, M; et al. Heterozygous germline mutations in A2ML1 are associated with a disorder clinically related to Noonan syndrome. EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF HUMAN GENETICS 23:317-324(2015).



