Recombinant Mouse Nanp Protein, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | Nanp-1813M |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Mouse Nanp Protein (Met1-Val248) with N-His tag was expressed in E. coli. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Mouse |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | Met1-Val248 |
| Description : | Predicted to enable asparagine-tRNA ligase activity. Predicted to be involved in asparaginyl-tRNA aminoacylation. Predicted to act upstream of or within translation. Located in mitochondrion. Is expressed in embryo; extraembryonic component; and primitive endoderm. Human ortholog(s) of this gene implicated in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness 94 and combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 24. Orthologous to human NARS2 (asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase 2, mitochondrial). |
| Form : | Freeze-dried powder |
| Molecular Mass : | Predicted Molecular Mass: 31.5 kDa Accurate Molecular Mass: 33 kDa |
| Purity : | > 90% |
| Applications : | Positive Control; Immunogen; SDS-PAGE; WB. |
| Stability : | The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37 centigrade for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition. |
| Storage : | Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8 centigrade for one month. Aliquot and store at -80 centigrade for 12 months. |
| Storage Buffer : | PBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 1mM DTT, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300. |
| Reconstitution : | Reconstitute in PBS or others. |
| Gene Name | Nanp N-acetylneuraminic acid phosphatase [ Mus musculus (house mouse) ] |
| Official Symbol | Nanp |
| Synonyms | NANP; N-acetylneuraminic acid phosphatase; N-acylneuraminate-9-phosphatase; neu5Ac-9-Pase; haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain containing 4; haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain-containing protein 4; Hdhd4; 1600031M04Rik; MGC103377; |
| Gene ID | 67311 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_026086 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_080362 |
| UniProt ID | Q9CPT3 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| NANP-1010H | Recombinant Human NANP | +Inquiry |
| NANP-2763R | Recombinant Rhesus Macaque NANP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Nanp-4287M | Recombinant Mouse Nanp Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| NANP-2825H | Recombinant Human N-acetylneuraminic Acid Phosphatase, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| NANP-3555R | Recombinant Rat NANP Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| NANP-3980HCL | Recombinant Human NANP 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Willems AP, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019
Biosynthesis of CMP-sialic acid, the essential substrate, comprises five enzymatic steps, involving ManNAc and sialic acid and their phosphorylated forms as intermediates. Genetic diseases in this pathway result in different and tissue-restricted phenotypes, which is poorly understood.
Researchers aimed to study the mechanisms of sialic acid metabolism in knockouts (KO) of the sialic acid pathway in two independent cell lines. Sialylation of cell surface glycans was reduced by KO of GNE (UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase), NANS (sialic acid synthase) and CMAS (N-acylneuraminate cytidylyltransferase) genes, but was largely unaffected in NANP (N-acylneuraminate-9-phosphatase) KO, as studied by MAA and PNA lectin binding. LC-MS analysis of sialic acid metabolites showed that CMP-sialic acid was dramatically reduced in GNE and NANS KO cells and undetectable in CMAS KO. In agreement with normal cell surface sialylation, CMP-sialic acid levels in NANP KO were comparable to WT cells, even though sialic acid 9-phosphate, the substrate of NANP accumulated.
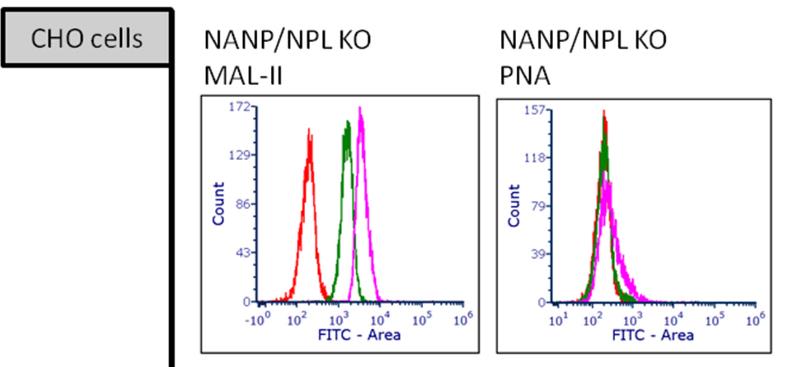
Fig1. Flow cytometry analysis of MAL-II and PNA lectin binding in CHO KO clones.
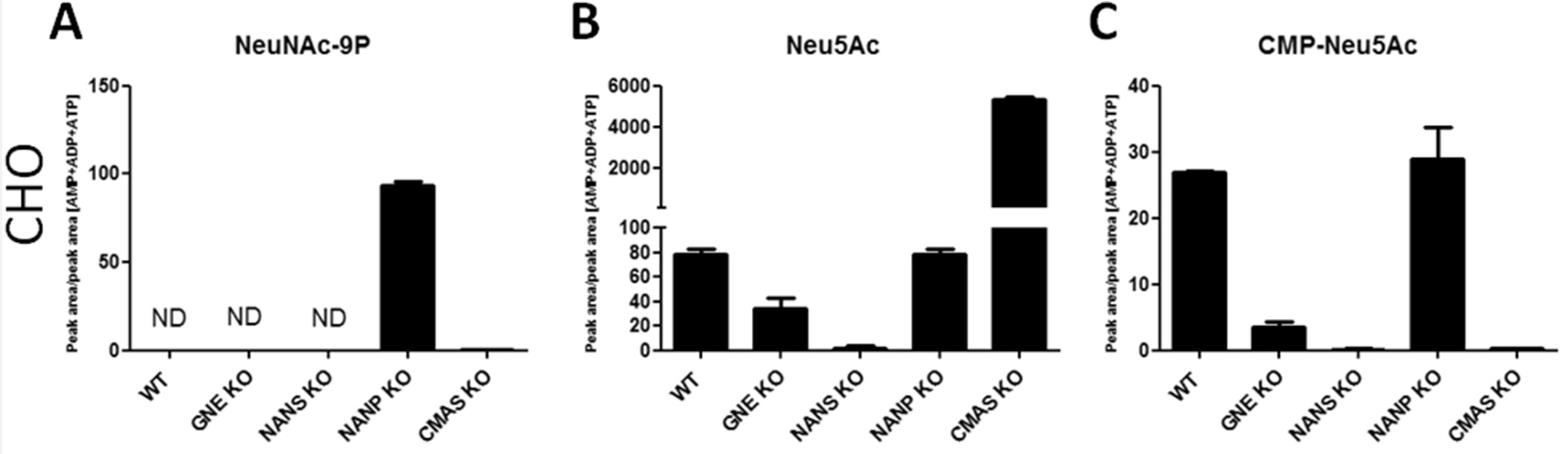
Fig2. LC/MS analysis of sialic acid metabolites in CHO KO clones.
Case 2: Maliekal P, et al. Glycobiology. 2006
The synthesis of N-acetylneuraminate (Neu5Ac), the main form of sialic acid, proceeds in vertebrates through the condensation of N-acetylmannosamine 6-phosphate and phosphoenolpyruvate to Neu5Ac-9-phosphate, followed by the dephosphorylation of the latter by a specific phosphatase. In this work, researchers have purified Neu5Ac-9-Pase more than 1000-fold from rat liver. Its dependency on Mg2+ and the fact that it was inhibited by vanadate and Ca2+ suggested that it belonged to the haloacid dehalogenase family of phosphatases. Trypsin digestion and mass spectrometry analysis of a polypeptide of about 30 kDa that co-eluted with the activity in the last purification step indicated the presence of a protein designated "haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain containing 4." The recombinant enzyme displayed a >230-fold higher catalytic efficiency on Neu5Ac-9-phosphate than on its second best substrate. Its properties were similar to those of the enzyme purified from rat liver. Neu5Ac inhibited the enzymatic activity by 50% at 15 mM, indicating that no significant inhibition is exerted at physiological concentrations of Neu5Ac.
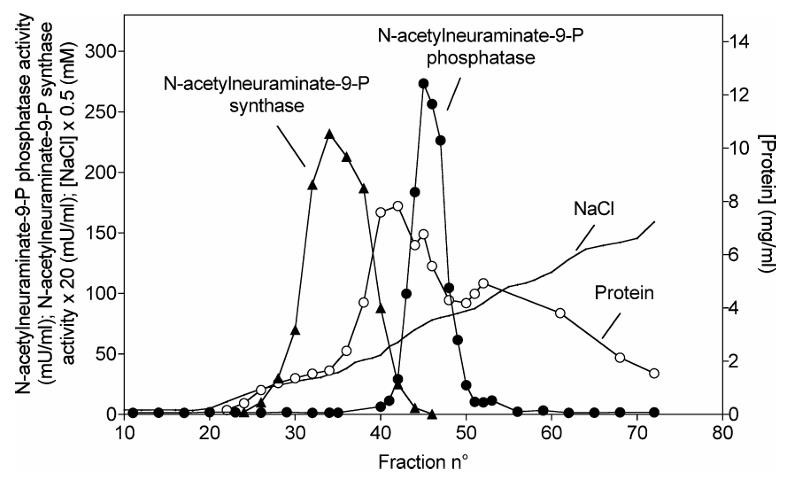
Fig1. Purification of Neu5Ac-9-Pase by chromatography on DEAE Sepharose.
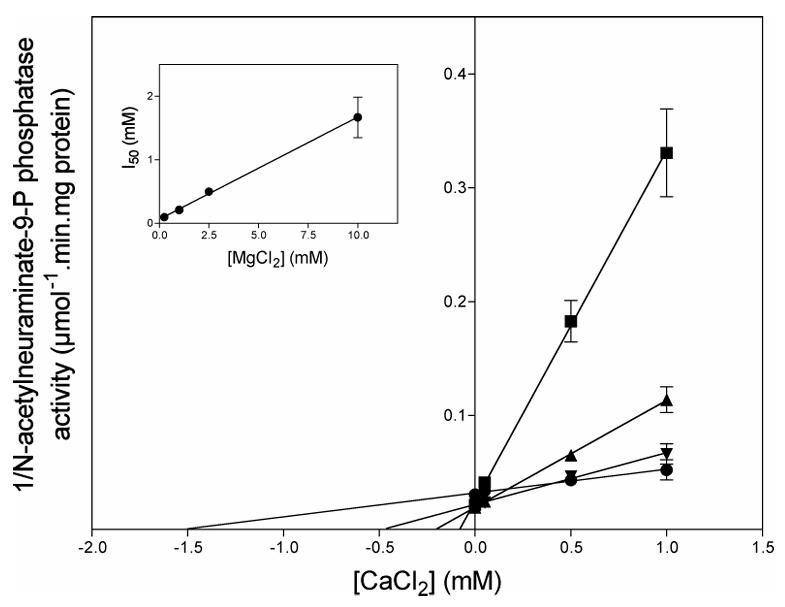
Fig2. Inhibition of human recombinant Neu5Ac-9-Pase by Ca2+.
N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) phosphatase is an important biological enzyme, Nanp for short, that plays a key role in the metabolism of organisms.
Bioengineering applications: Neu5Ac is an important compound with wide applications in the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries, and mouse-derived N-acetylneuraminic phosphatase can be used for biosynthesis of Neu5Ac. By means of metabolic engineering, optimizing the biosynthetic pathway of Neu5Ac and reducing the accumulation of intermediate products can increase the yield of Neu5Ac.
Basic research: The rat Nanp gene has a high degree of homology with the human NANP gene, so the rat can serve as an important animal model for the study of human diseases and drug development. Studying the Nanp gene in rats will help to understand the Neu5Ac biosynthesis process and develop related therapies. Studies have shown that Neu5Ac can reduce hypercoagulability in rats with hyperlipidemia induced by a high fat diet, suggesting that Neu5Ac may help prevent clotting related cardiovascular events.
Drug development: Neu5Ac phosphatase is a key enzyme in the Neu5Ac biosynthetic pathway, and its research contributes to the development of drugs that regulate the level of Neu5Ac, which may have important significance for the treatment of related diseases.
Food and cosmetics industry: Neu5Ac has application potential in food and cosmetics industry due to its various physiological functions. Mouse-derived Neu5Ac phosphatase can promote the synthesis of Neu5Ac, which may have an impact on these industries.
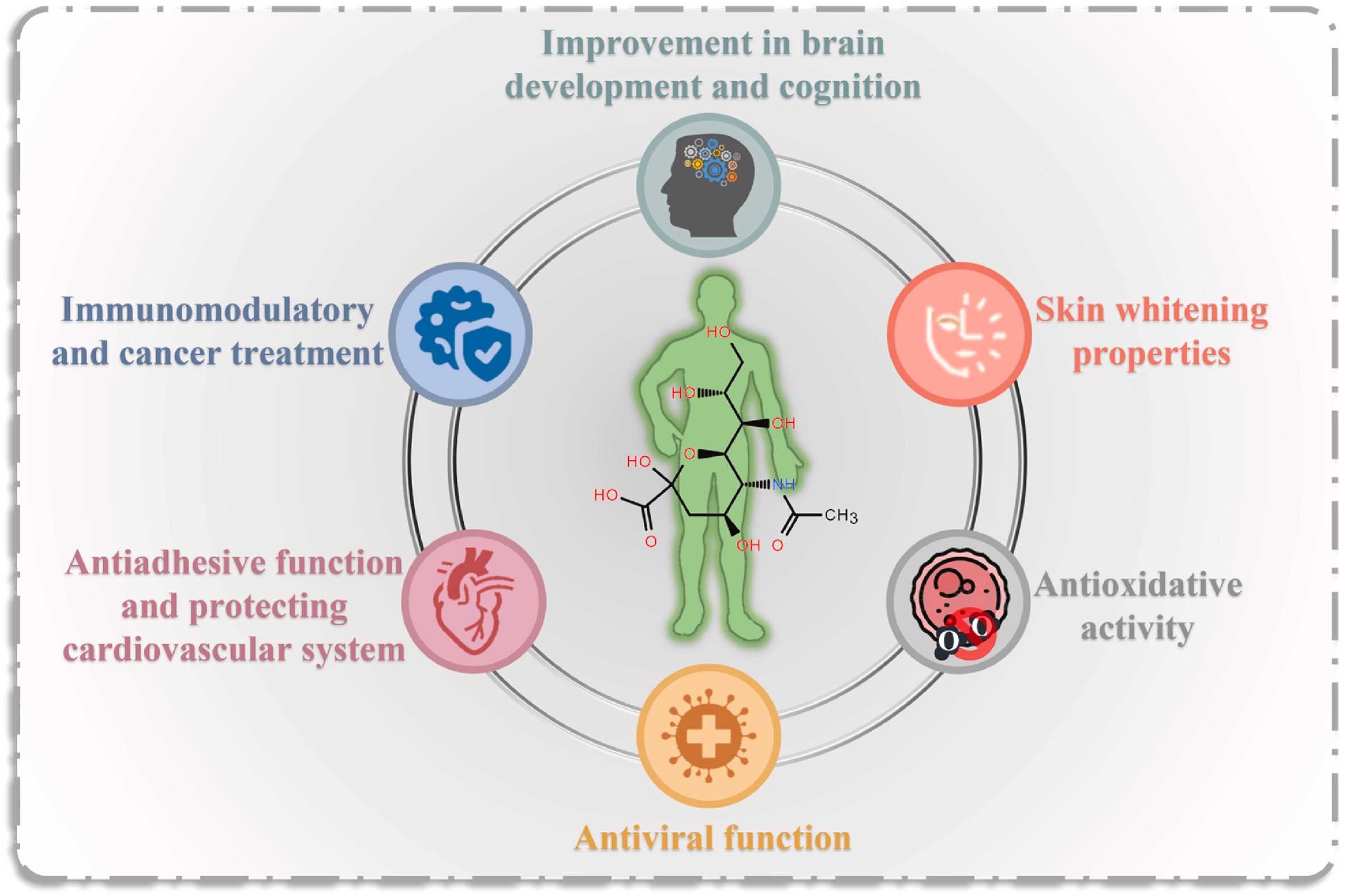
Fig1. Physiological roles of Neu5Ac. (Mingli Zhao, 2023)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All Nanp Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All Nanp Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


