Recombinant Human USP40
| Cat.No. : | USP40-1000H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human USP40 full length or partial length protein was expressed. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Mammalian Cells |
| Tag : | His |
| Form : | Liquid or lyophilized powder |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 eu per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Purity : | >80% |
| Notes : | This item requires custom production and lead time is between 5-9 weeks. We can custom produce according to your specifications. |
| Storage : | Store it at +4 oC for short term. For long term storage, store it at -20 oC~-80 oC. |
| Storage Buffer : | PBS buffer |
| Gene Name | USP40 ubiquitin specific peptidase 40 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | USP40 |
| Gene ID | 55230 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_018218.2 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_060688.1 |
| MIM | 610570 |
| UniProt ID | Q9NVE5 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| USP40-17929M | Recombinant Mouse USP40 Protein | +Inquiry |
| USP40-0634H | Recombinant Human USP40 Protein (F2-R1235), Tag Free | +Inquiry |
| USP40-0635H | Recombinant Human USP40 Protein (F2-R1235), His/Flag tagged | +Inquiry |
| USP40-9966M | Recombinant Mouse USP40 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| USP40-4624C | Recombinant Chicken USP40 | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Mo H, et al. Cancer Lett. 2024
The protein known as Yes-associated protein (YAP) plays a crucial role in driving the advancement of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and its levels are regulated by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Despite this, the specific part played by the ubiquitin-specific protease 40 (USP40) in maintaining YAP's stability had not been well defined. In this study, USP40 was newly recognized as a key controller of YAP levels and its downstream target genes within HCC cells. USP40 was found to bind with YAP, eliminating the polyubiquitin chains linked at lysine 48 (K48) at the K252 and K315 positions on YAP, which helps to preserve YAP's stability. The presence of USP40 was linked to increased HCC cell proliferation, the ability to form colonies, migration, and the formation of spheroids in laboratory settings, and it also enhanced tumor growth in living organisms in a manner that relied on YAP. YAP, in a reciprocal action, boosted the transcription of the USP40 gene within HCC cells. An RNA sequencing study revealed a significant overlap, with approximately 37% of genes regulated by USP40 also being under the influence of YAP. It was also observed that the upregulation of USP40 caused by environmental stiffness was negated when YAP was suppressed, and reducing USP40 levels lessened the accumulation of YAP triggered by stiffness in HCC cells.
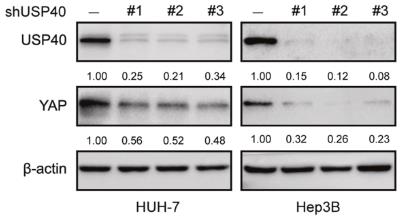
Fig1. WB results showed the levels of USP40 and YAP in HUH7 and Hep3B cells transfected with three independent USP40 shRNAs.
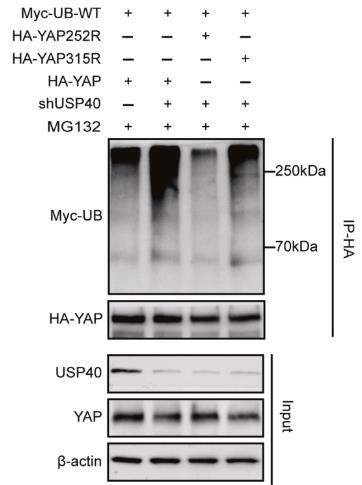
Fig2. K252 mutation markedly reduced and K315 mutation partially decreased USP40 knockdown-induced YAP ubiquitination.
Case 2: Wu Q, et al. Biol Direct. 2024
The purpose of this work was to elucidate the function and mechanism of the deubiquitinating enzyme USP40 in HCC progression. The presence and levels of USP40 in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues and cell lines were examined using reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), western blot analysis, and immunohistochemistry (IHC). A series of both in vitro and in vivo tests were performed to ascertain the significant role USP40 plays in the progression of HCC. The relationship between USP40 and Claudin1 was uncovered through immunofluorescence imaging, co-immunoprecipitation, and ubiquitination assays. The findings indicate that USP40 is overexpressed in HCC tissues and is indicative of an unfavorable prognosis for HCC patients. Decreasing USP40 levels in cells was found to impede the proliferation, migration, and stem-like properties of HCC cells, while increasing USP40 levels had the reverse effect. Additionally, Claudin1 was verified as a gene downstream of USP40. On a molecular level, USP40 was shown to bind with Claudin1, preventing its polyubiquitination and thus stabilizing the Claudin1 protein.
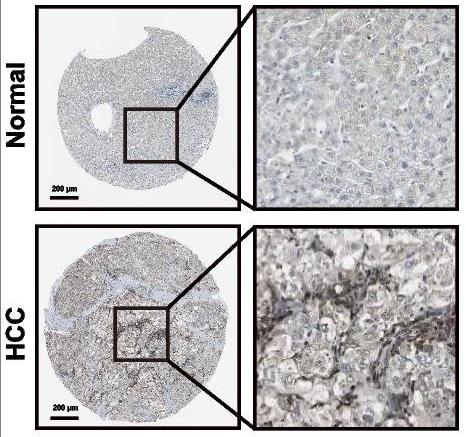

Fig1. IHC images of USP40 expression in liver normal tissues and HCC samples were gained from the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) database.
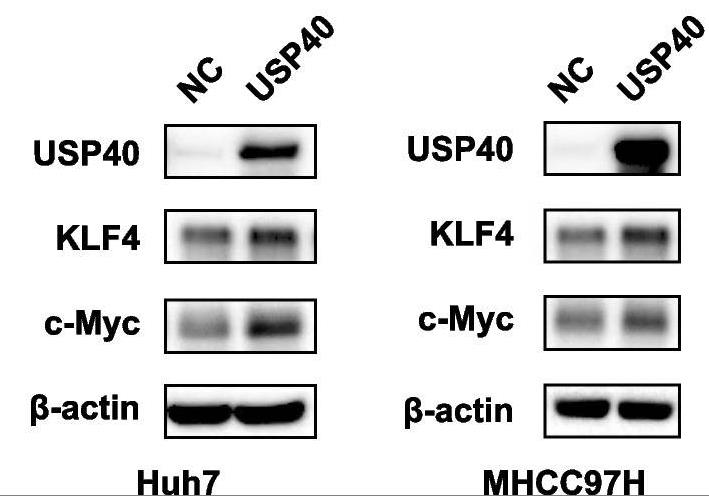
Fig2. Overexpression of USP40 increased the expression of tumor stem cell indicators c-Myc and KLF4.
The USP40 protein is a deubiquitinating enzyme that removes ubiquitin chains from proteins. Within the cell, the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) is an important protein degradation pathway in which the ubiquitin enzyme E3 connects ubiquitin molecules to target proteins so that they are labeled as proteins to be degraded. Deubiquitinating enzymes reverse this process by removing ubiquitin molecules from the target protein, preventing it from being degraded.
Antibodies to the USP40 protein can be used for a variety of scientific research applications, including Western Blot, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunocytochemistry (ICC/IF) techniques, which are widely used to detect USP40 expression in human, mouse, and rat samples. In addition, the key protective role of USP40 in vascular injury was revealed, particularly in endothelial cell barrier breakdown and inflammatory responses, where USP40 maintains endothelial integrity by targeting the heat shock protein HSP90β, suggesting that USP40 may have potential applications in the treatment of vascular diseases and acute infectious diseases. In studies of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), USP40 has been found to promote the progression of liver cancer by forming a positive feedback loop with YAP protein, which provides new targets and therapeutic approaches for liver cancer treatment.
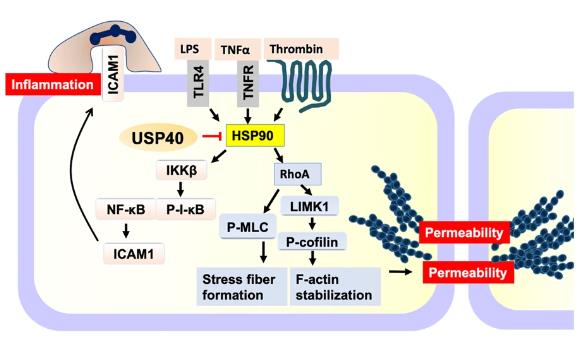
Fig1. USP40 preserves EC integrity by deubiquitinating and inactivating HSP90β, resulting in reductions in inflammatory stimulus-induced EC inflammation and hyperpermeability. (Jiaxing Miao, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All USP40 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All USP40 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


