Active Recombinant Human Selectin E
| Cat.No. : | SELE-2638H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant human Selectin E consisting of 535 amino acids is expressed inCHO cells. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | CHO |
| Tag : | Non |
| Description : | E-selectin, also known as CD62E, is a cell adhesion molecule expressed only on endothelial cells activated by cytokines. Like other selectins, it plays an important part in inflammation. In humans, E-selectin is encoded by the SELE gene. E-selectin recognizes and binds to sialylated carbohydrates present on the surface proteins of certain leukocytes. These carbohydrates include members of the Lewis X and Lewis A families found on monocytes, granulocytes, and T-lymphocytes. |
| Form : | Lyophilized. |
| Formulation : | Lyophilized from Dulbecco"s PBS with stabilizer. |
| Molar Mass : | 58800 Da. |
| Biological Activity : | Shown to bind to E-selectin ligands on U937 cells. |
| Purity : | ≥95% by SDS-PAGE. |
| Storage : | ≤ -20oC. Ship: Dry Ice Only. |
| Publications : |
A computational and experimental study to develop E-selectin targeted peptides for molecular imaging applications (2018)
|
| Gene Name | SELE selectin E [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Synonyms | SELE; selectin E; CD62 antigen-like family member E; E-selectin; ELAM-1; OTTHUMP00000032746; OTTHUMP00000032747; OTTHUMP00000032748; OTTHUMP00000032749; endothelial adhesion molecule 1; endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1; leukocyte endothelial cell adhesion molecule 2; leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion molecule 2; ELAM; ESEL; CD62E; ELAM1; LECAM2 |
| Gene ID | 6401 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000450 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000441 |
| MIM | 131210 |
| UniProt ID | P16581 |
| Chromosome Location | 1q22-q25 |
| Pathway | Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs); Malaria |
| Function | binding; oligosaccharide binding; phospholipase binding; sialic acid binding; sugar binding; transmembrane receptor activity |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| Sele-6390R | Recombinant Rat Sele Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Sele-860M | Recombinant Mouse Sele protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| SELE-2242H | Recombinant Human SELE protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| SELE-5083H | Recombinant Human SELE Protein (Met1-Pro556), C-His tagged | +Inquiry |
| SELE-1106H | Recombinant Human SELE Protein (Trp22-Ser371), N-His tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| SELE-2992HCL | Recombinant Human SELE cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| SELE-960RCL | Recombinant Rat SELE cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| SELE-845MCL | Recombinant Mouse SELE cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| SELE-1099CCL | Recombinant Cynomolgus SELE cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Fernandes AC, et al. Future Med Chem. 2018
E-selectin is overexpressed on angiogenic and inflamed endothelium. Molecules binding to E-selectin with high affinity and specificity enable its use as a molecular imaging biomarker. To test this hypothesis, the interactions of four different peptides with E-selectin were analyzed by computational methodologies, surface plasmon resonance and in vitro using activated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Poly(butyl cyanoacrylate) microbubbles were functionalized with the best candidates and evaluated as molecular ultrasound probes in cultured cells and explanted carotid arteries. The results showed that H2N-P3A5 and Ac-P4 peptides bound stronger to E-selectin than Ac-P1 and H2N-P2, but with lower specificity. H2N-P2 bound with higher specificity and affinity than Ac-P1.
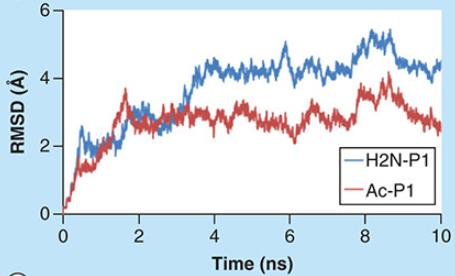
Fig1. Molecular docking simulation trajectories of the complex.
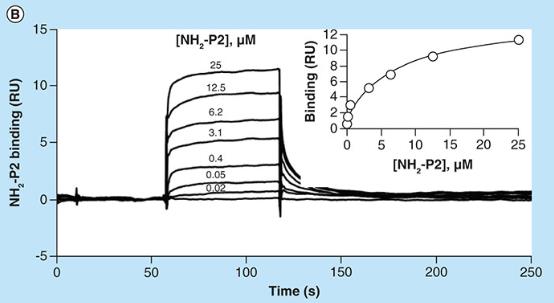
Fig2. Typical superposed sensorgrams obtained over E-selectin are displayed.
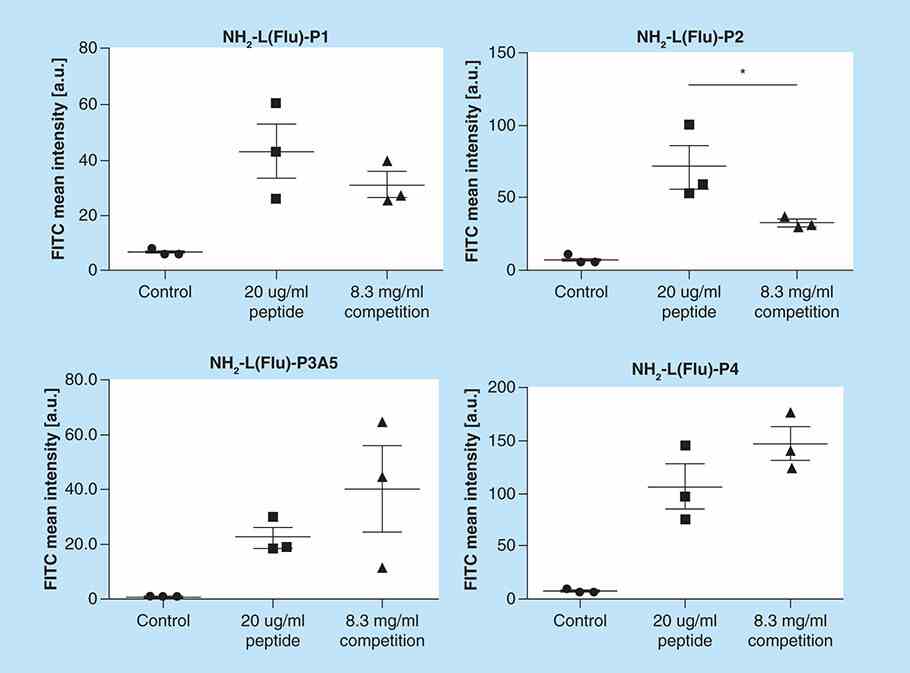
Fig3. In vitro binding studies.
Case 2: Zhou F, et al. J Cell Sci. 2021
Selectins and integrins are key players in the adhesion and signaling cascade that recruits leukocytes to inflamed tissues. Selectin binding induces β2 integrin binding to slow leukocyte rolling. Here, a micropipette was used to characterize neutrophil adhesion to E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) at room temperature. The αLβ2 activation required more than 5 s contact to E-selectin and spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) activity. A multi-zone channel was used to analyze αLβ2 activation by P-selectin in separate zones of receptors or antibodies, finding an inverse relationship between the rolling velocity on ICAM-1 and P-selectin dose, and a P-selectin dose-dependent change from bent to extended conformations with a closed headpiece that was faster at 37°C than at room temperature. Activation of αLβ2 exhibited different levels of cooperativity and persistent times depending on the strength and duration of selectin stimulation. These results define the precise timing and kinetics of intermediate activation of αLβ2 by E- and P-selectins.
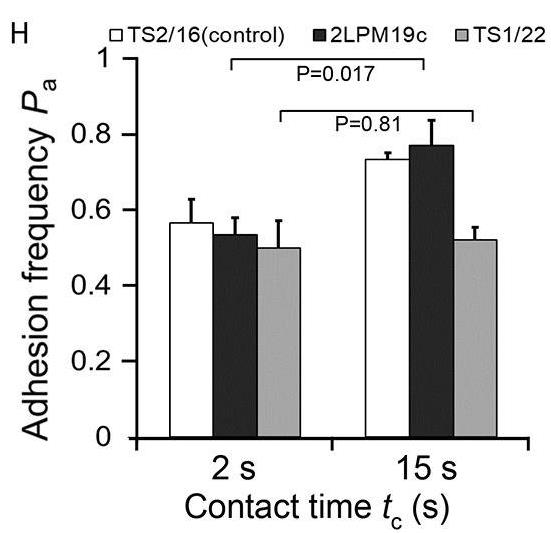
Fig1. Adhesion frequencies between neutrophils and RBCs coated with E-selectin–Ig and ICAM-1–Ig.
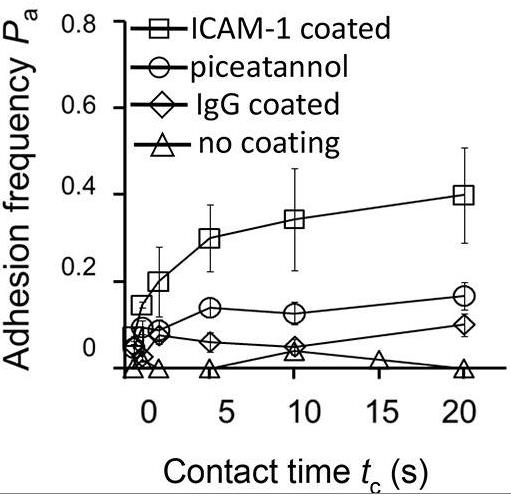
Fig2. Binding of neutrophils to RBCs bearing ICAM-1–Ig with 1μg/ml E-selectin–Ig in the medium.
Recombinant human (rh) SELE (selectin E) is a cell adhesion molecule that plays a key role in inflammation and immune responses. Some potential applications of rhSELE include:
Research and drug development: rhSELE can be used in in vitro studies to investigate the mechanisms underlying leukocyte-endothelial interactions and inflammatory processes. This can help in the development of novel anti-inflammatory therapeutics.
Diagnostic tools: rhSELE can be utilized in diagnostic assays to detect and quantify levels of SELE expression in patient samples. Elevated levels of SELE are associated with various inflammatory conditions, making it a potential biomarker for disease diagnosis and monitoring.
Target for therapeutic intervention: Targeting SELE with specific inhibitors or antibodies may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of inflammatory disorders. By blocking the interaction of SELE with its ligands, such as leukocytes, it may be possible to reduce inflammation and tissue damage.
Vaccine development: SELE is involved in the recruitment of immune cells to sites of inflammation, and its modulation can impact immune responses. Utilizing rhSELE in vaccine development research may help in enhancing immune responses and improving vaccine efficacy.
Tissue engineering: Incorporating rhSELE in tissue engineering approaches can help in promoting cell adhesion and migration, leading to enhanced tissue regeneration and repair. This may have applications in regenerative medicine and wound healing.
Overall, the applications of rhSELE span various fields, including research, diagnostics, therapeutics, and tissue engineering, with the potential to advance our understanding and treatment of inflammatory and immune-related conditions.
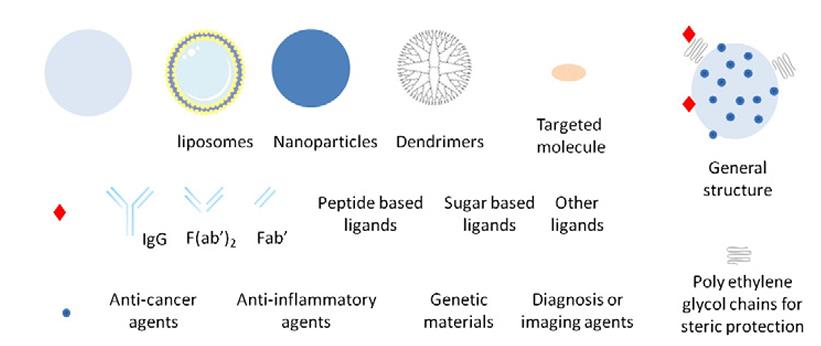
Fig1. Schematic representation of the different concepts used to target E-selectin. (Emile Jubeli, 2012)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All SELE Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All SELE Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


