Recombinant Human CDC42 protein(Met1-Cys188), GST-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CDC42-1806H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CDC42 isoform 2 (P60953-2) (Met 1-Cys 188) was expressed in E. coli, fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | GST |
| Protein Length : | Met1-Cys188 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 0.15M NaCl, 0.5mM GSH, pH 8.0. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human CDC42/GST chimera consists of 423 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 48.1 kDa. It migrates as an approxiamtely 44 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Purity : | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | CDC42 cell division cycle 42 (GTP binding protein, 25kDa) [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CDC42 |
| Synonyms | CDC42; cell division cycle 42 (GTP binding protein, 25kDa); cell division cycle 42 (GTP binding protein, 25kD); cell division control protein 42 homolog; CDC42Hs; G25K; G25K GTP-binding protein; GTP-binding protein, 25kD; growth-regulating protein; small GTP binding protein CDC42; dJ224A6.1.1 (cell division cycle 42 (GTP-binding protein, 25kD)); dJ224A6.1.2 (cell division cycle 42 (GTP-binding protein, 25kD)); |
| Gene ID | 998 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001039802 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001034891 |
| MIM | 116952 |
| UniProt ID | P60953 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CDC42-0934H | Recombinant Human CDC42 Protein, GST-Tagged | +Inquiry |
| CDC42-3101HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CDC42 Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CDC42-1712H | Recombinant Human CDC42 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | +Inquiry |
| CDC42-1394H | Recombinant Human Cell Division Cycle 42, T7-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CDC42-3139M | Recombinant Mouse CDC42 Protein | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CDC42-7655HCL | Recombinant Human CDC42 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Daimon E, et al. Sci Rep. 2021
Macrothrombocytopenia, often linked to actin-related mutations, is a key feature in Takenouchi-Kosaki syndrome (TKS) with the Y64C Cdc42 variant. In this study, we found that Y64C localizes more to the cell membrane, increasing its activity but reducing interactions with proteins like Pak1/2. This results in abnormal cell structures and decreased platelet-like particle production. These defects were improved by inhibiting Cdc42 or through chemical prenylation, suggesting possible treatment paths for TKS.

Fig1. Total cell lysates from HEK293 cells transiently expressing EYFP-tagged WT or Cdc42 variants were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting.
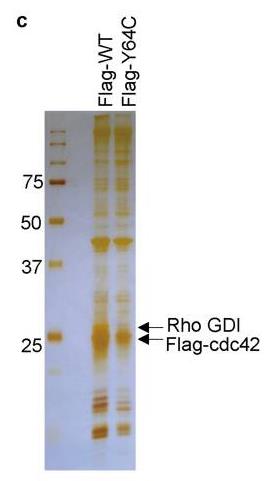
Fig2. Flag-tagged WT or Y64C was introduced into HEK293 cells by lentivirus and immunopurified using anti-Flag agarose.
Case 2: Chernichenko N, et al. Mol Cancer Res. 2020
Perineural invasion (PNI) involves cancer spreading along nerves, linked to bad outcomes. GDNF interacts with RET receptors on cancer cells to trigger PNI, with Cdc42's early activation playing a crucial role. Suppressing Cdc42 disrupts pancreatic cancer cells' direction towards nerves. ARHGEF7 (β-Pix) is vital for activating Cdc42, guiding cells towards nerves. In nerve models, Cdc42 controls movement direction without affecting speed, while Rac1 affects speed but not direction. In mice, reducing Cdc42 decreases PNI's severity and related paralysis. This highlights the GDNF-RET-β-Pix-Cdc42 pathway as crucial for cancer cell direction towards nerves, suggesting new treatment targets.
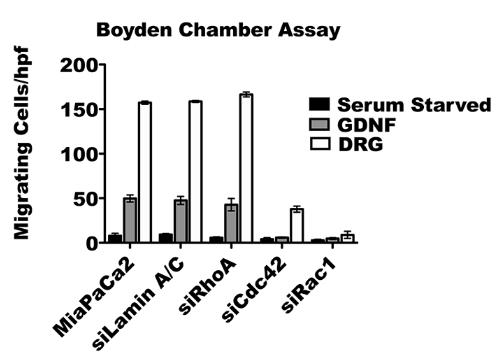
Fig1. Serum-starved siRNA transfected Cdc42, Rac1, RhoA, or LaminA/C.
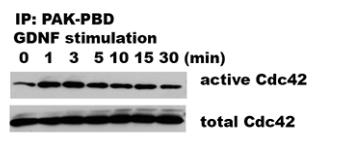
Fig2. Western blots of GST pull-down assays assess for changes in the active, GTP-bound forms.
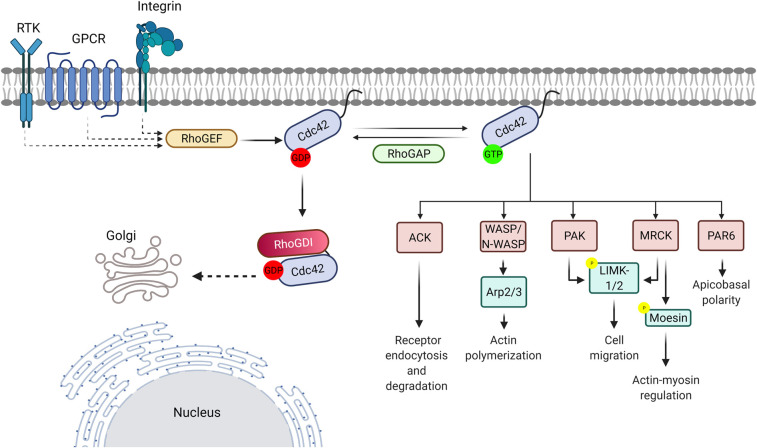
Fig1. The regulation of Cdc42. (Natasha P Murphy, 2021)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CDC42 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CDC42 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


