Recombinant Human CD69 protein, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CD69-2225H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CD69 protein(Q07108)(62-199aa), fused with C-terminal His tag, was expressed in HEK293. |
| Availability | April 20, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 62-199aa |
| Tag : | C-His |
| Form : | Lyophilized from a 0.2 um filtered 20 mM Tris-HCl, 0.5 M NaCl, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0 |
| Bio-activity : | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized Human CD69 at 2 μg/mL can bind Anti-CD69 recombinant antibody, the EC50 is 23.17-26.04 ng/mL. |
| Molecular Mass : | 18.7 kDa |
| Endotoxin : | Less than 1.0 EU/ug as determined by LAL method. |
| Purity : | Greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Storage : | Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20°C/-80°C. |
| AA Sequence : | SVGQYNCPGQYTFSMPSDSHVSSCSEDWVGYQRKCYFISTVKRSWTSAQNACSEHGATLAVIDSEKDMNFLKRYAGREEHWVGLKKEPGHPWKWSNGKEFNNWFNVTGSDKCVFLKNTEVSSMECEKNLYWICNKPYK |
| Gene Name | CD69 CD69 molecule [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CD69 |
| Synonyms | CD69; CD69 molecule; CD69 antigen (p60, early T cell activation antigen); early activation antigen CD69; CLEC2C; leukocyte surface antigen Leu-23; early T-cell activation antigen p60; early lymphocyte activation antigen; activation inducer molecule (AIM/CD69); C-type lectin domain family 2, member C; CD69 antigen (p60, early T-cell activation antigen); AIM; EA1; MLR-3; GP32/28; BL-AC/P26; |
| Gene ID | 969 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001781 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001772 |
| MIM | 107273 |
| UniProt ID | Q07108 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CD69-3028HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CD69 Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CD69-5844H | Recombinant Human CD69 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CD69-3101H | Recombinant Human CD69 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CD69-0844H | Recombinant Human CD69 Protein, GST-Tagged | +Inquiry |
| CD69-694H | Recombinant Human CD69 Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CD69-2573HCL | Recombinant Human CD69 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Koizume S, et al. Cancer Sci. 2023
Cancer tissues often lack oxygen and nutrients due to poor blood supply. We've found that in ovarian clear cell carcinoma (CCC) cells, ICAM1 is highly active during fatty acid and oxygen starvation, helping the cells resist death. Similarly, CD69, a protein known for activating immune cells, is also produced in CCC cells. Our research shows that CD69 boosts CCC cells' ability to stick to fibronectin, enhancing survival by promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Tests on tumor samples showed CD69 is mostly found in CCC tumors compared to other ovarian cancer types. This indicates that CD69 may aid CCC progression through its interaction with fibronectin.
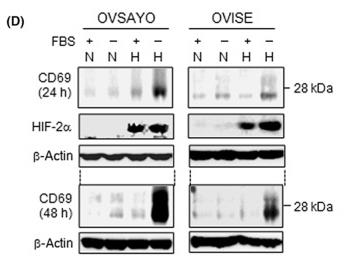
Fig1. Western blot analysis of CD69 expression.

Fig2. Western blot analysis of CD69 expression in shRNA transfected OVSAYO cells.
Case 2: Ishikawa C, et al. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013
HTLV-1 infection is linked to adult T-cell leukemia (ATL) and other inflammatory diseases. CD69, a marker for lymphocyte activation, is influenced by HTLV-1. Our study showed that CD69 expression increases in most HTLV-1-transformed T-cell lines and ATL patient cells due to the viral protein Tax, unlike in MT-2 cells and normal blood cells where it's absent. Tax boosts CD69 through specific signaling pathways. In MT-2 cells, CD69 isn't expressed due to an epigenetic change. Overall, CD69 is regulated by Tax, potentially impacting cell activation and HTLV-1-related diseases.
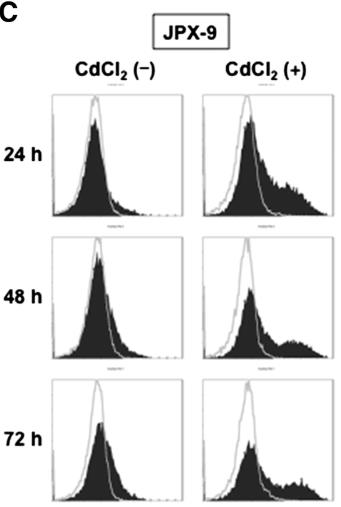
Fig1. Flow cytometric analysis of Tax-mediated cell surface expression of CD69.
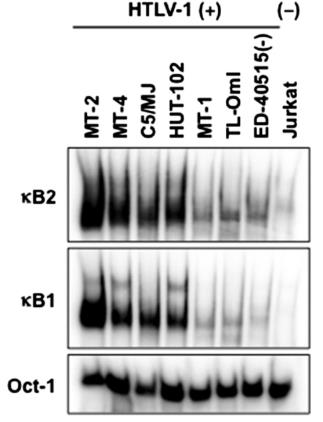
Fig2. HTLV-1 infection is associated with binding of NF-κB to the NF-κB sites in CD69 promoter.
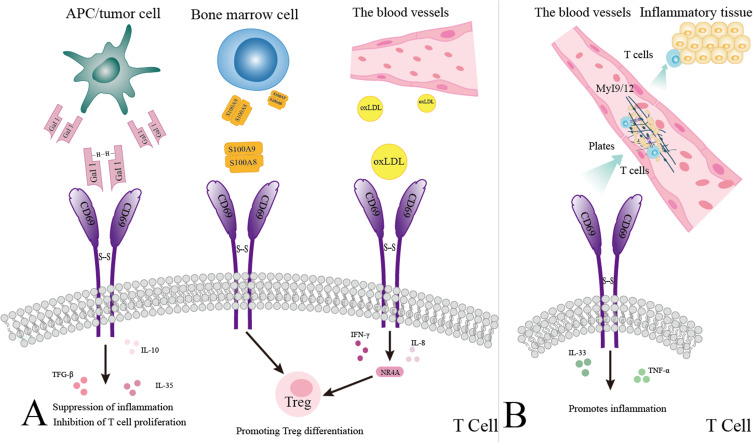
Fig1. T cell immune responses mediated by CD69 binding to ligands. (Yuchen Li, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CD69 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CD69 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


