Recombinant Human C7 protein(Met1-Gln843), hFc-tagged
| Cat.No. : | C7-7368H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human C7 (P10643) (Met1-Gln843) was expressed in HEK293, fused with the Fc region of Human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | Fc |
| Protein Length : | 1-843 a.a. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human C7 /Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 1062 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 118 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 118 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | C7 complement component 7 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | C7 |
| Synonyms | C7; complement component 7; complement component C7; |
| Gene ID | 730 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000587 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000578 |
| MIM | 217070 |
| UniProt ID | P10643 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| C7-823P | Recombinant Pig C7 protein, His & GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| C7-0585H | Recombinant Human C7 Protein (Ser122-His456), His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| C7-821H | Recombinant Human C7 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| C7-2439H | Recombinant Human C7 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| C7-7369H | Recombinant Human C7 protein(Met1-Gln843), His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| C7-56H | Native Human Complement C7 | +Inquiry |
| C7-102H | Active Native Human C7 Protein | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| C7-1425HCL | Recombinant Human C7 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| C7-1500HCL | Recombinant Human C7 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Thai CT, et al. J Immunol. 2004
More than 30 years ago, researchers found that latent C5 can bind reversibly to C6 and C7. This reversible binding differs from the stable associations seen with activated C5b during the membrane attack complex formation, though they likely share common molecular interactions. Recent discoveries show that these reversible bindings are driven by the C345C domain of the C5 alpha-chain. Previously, the binding sites were identified on a C6 fragment containing two factor I modules (FIMs) and a larger C7 fragment with similar FIMs and short consensus repeat modules. In the recent study, scientists expressed C7's tandem FIMs in bacteria, finding that these recombinant FIMs bind to both C5 and the C5-C345C domain with high affinity, as verified through experiments like surface plasmon resonance.

Fig1. 13% SDS-polyacrylamide gel stained with Brilliant Blue showing the electrophoretic migration of the reduced (+2ME) and nonreduced (−2ME) forms of rC7-FIMs.
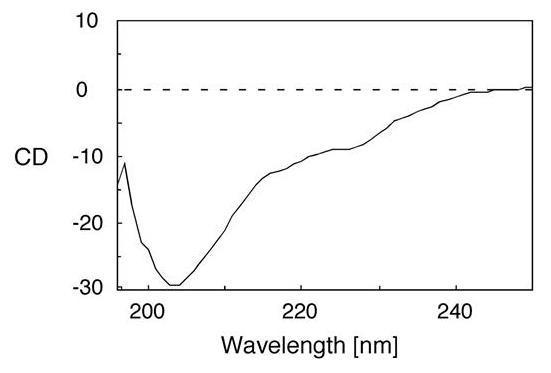
Fig2. CD spectrum of rC7-FIMs.
Case 2: Thai CT, et al. J Immunol. 2005
Complement component C5 interacts with C6 and C7 through reversible reactions, unlike the more permanent associations involved in forming the membrane attack complex (MAC). Earlier, we showed that the C345C domain (or NTR) of C5 is key in these reversible interactions, directly binding to the FIMs segment of C7 but not C6. It suggests that this interaction is also vital for the MAC's assembly. Recently, we developed a new technique to simulate MAC assembly using a surface plasmon resonance setup, enabling us to observe how C7, C8, and C9 join the complex. Our findings revealed a very strong binding affinity of C7 to C5b,6 and showed that specific concentrations of recombinant C5 and C7 modules could effectively block early MAC formation and subsequent erythrocyte lysis through the complement pathways.
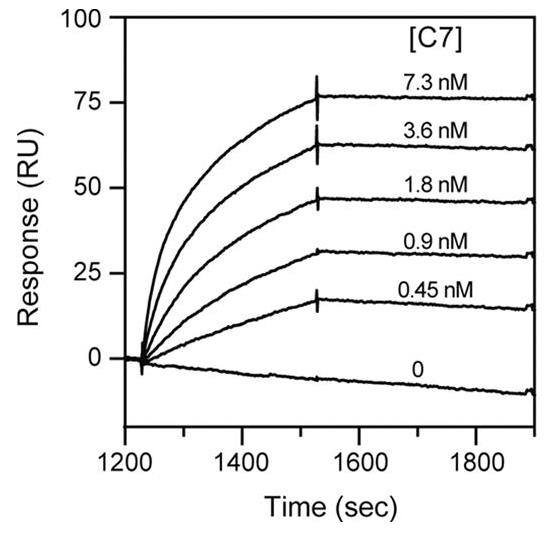
Fig1. Binding of C7 to immobilized C5b,6.
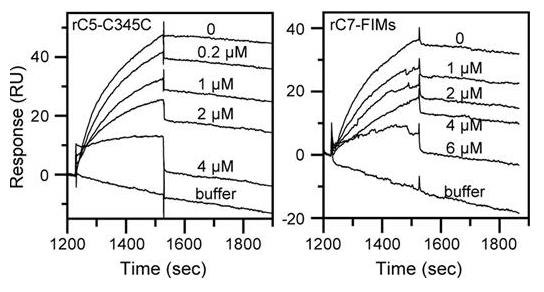
Fig2. Recombinant C5-C345C and rC7-FIMs inhibit binding of C7 to immobilized C5b,6.
Human C7, a part of the membrane attack complex (MAC), plays a key role in immune defenses. Its recombinant form, rhC7, is widely used in research to explore how it helps form pores in cell membranes, leading to cell breakdown. This understanding is crucial for studying the activation of the complement system and its role in immune responses. Researchers utilize rhC7 in immunoassays like ELISA and immunohistochemistry to study its levels and distribution in various tissues. Interestingly, studies have also indicated that related compounds like recombinant type VII collagen might have therapeutic potentials, such as promoting wound healing in certain skin disorders.
In the industrial arena, rhC7 is utilized for drug discovery and developing treatments for complement-mediated diseases. It's produced in systems like HEK293 cells, often tagged for easy purification, and serves as a tool and target for creating new therapies. Its production ensures the availability of standardized research materials, underpinning the accuracy of scientific experiments. rhC7 is also vital for making diagnostic tools and antibodies that can measure C7 in biological samples, enhancing research into its functions and related medical conditions.
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All C7 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All C7 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


