Recombinant Human BCL2L1 protein(Met1-Arg212), His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | BCL2L1-6872H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human BCL2L1 (NP_612815.1) (Met1-Arg212) was expressed in E. coli, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Availability | April 17, 2025 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 1-212 a.a. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile 5mM Tris, 1% Glycerol, pH 8. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Bio-activity : | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized human BID at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human BCL2L1, The EC50 of biotinylated human BCL2L1 is 7.1 ng/mL. 3. Immobilized mouse BID at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human BCL2L1, The EC50 of biotinylated human BCL2L1 is 7.01 ng/mL. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human BCL2L1 consists of 222 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 25.2 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 30.5 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Purity : | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | BCL2L1 BCL2-like 1 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | BCL2L1 |
| Synonyms | BCL2L1; BCL2-like 1; bcl-2-like protein 1; Bcl X; bcl xL; bcl xS; BCL2L; BCLX; PPP1R52; protein phosphatase 1; regulatory subunit 52; apoptosis regulator Bcl-X; protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 52; BCLXL; BCLXS; Bcl-X; bcl-xL; bcl-xS; BCL-XL/S; DKFZp781P2092; |
| Gene ID | 598 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001191 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001182 |
| MIM | 600039 |
| UniProt ID | Q07817 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| Bcl2l1-6871M | Active Recombinant Mouse Bcl2l1 protein(Met1-Arg212), His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| RFL8692SF | Recombinant Full Length Pig Bcl-2-Like Protein 1(Bcl2L1) Protein, His-Tagged | +Inquiry |
| BCL2L1-1349H | Recombinant Human BCL2L1, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| BCL2L1-9318Z | Recombinant Zebrafish BCL2L1 | +Inquiry |
| BCL2L1-8192H | Recombinant Human BCL2L1 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| BCL2L1-8488HCL | Recombinant Human BCL2L1 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
| BCL2L1-8489HCL | Recombinant Human BCL2L1 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Cerella C, et al. Leukemia. 2024
Certain subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) resist venetoclax treatments, making it crucial to find weak spots to tackle this issue. We've seen that mixing venetoclax with cardiac glycosides (CGs) can enhance effectiveness against AML. However, using CGs in cancer hasn't been popular due to missing markers that predict success. We've found that AML cells' response to the CG UNBS1450 links to the ATPase Na+/K+ subunit alpha 1 and BCL2L1 expression ratio. Public AML data highlights that the differentiation of specific leukemia types is a strong predictor, along with certain gene rearrangements and mutations. It appears that BCL2L1 shields cells from death caused by CGs impacting ion balance and protein synthesis. In animal models, CGs are generally well-tolerated and can range from halting tumor growth to shrinking them.
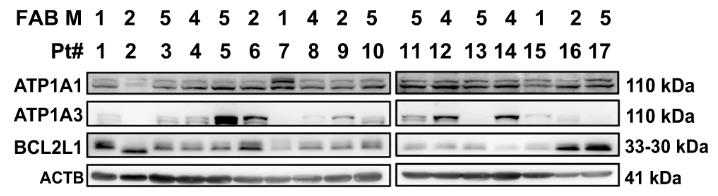
Fig1. Western blot analysis of the indicated proteins.
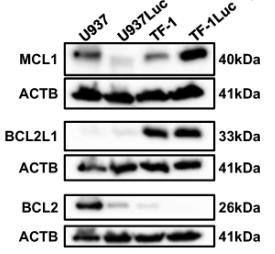
Fig2. Western blot analysis and quantification of MCL1, BCL2L1, and BCL2 proteins in U937Luc and TF-1Luc cell lines.
Case 2: Loo LSW, et al. Cell Death Dis. 2020
The process of turning human pluripotent stem cells into pancreatic cells involves both cell growth and cell death. Yet, how these changes shape cell identity isn't clear. We studied how the BCL-2 protein family is expressed during pancreatic development and found that BCL-xL goes up, while BAK and cleaved CASP3, markers of cell death, go down. Blocking BCL-xL increases cell death and reduces pancreatic markers, despite a rise in the anti-death protein BCL-2. RNA sequencing showed that stopping BCL-xL also decreased many metabolic genes. Energy tests revealed reduced glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation when BCL-xL was blocked. Early interference with BCL-xL harms the development of INS+ pancreatic beta-like cells. In summary, more mature pancreatic progenitors rely on BCL-xL to survive, while less mature ones, if they survive the treatment, appear less developed.
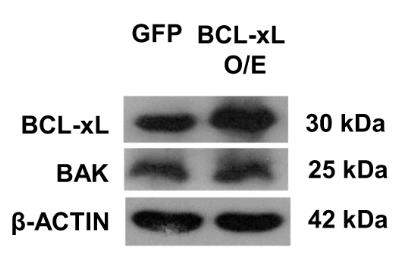
Fig1. Western blot showing the expression of BAK protein upon overexpression of BCL-xL in undifferentiated hPSCs.
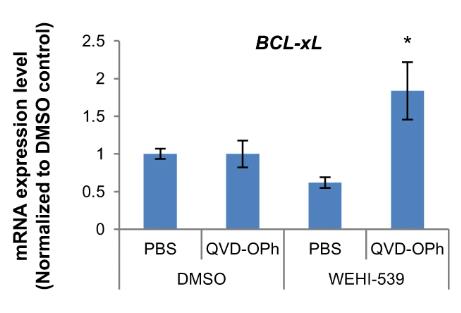
Fig2. Expression of BCL-xL gene transcripts upon treatment with WEHI-539 and QVD-OPh on D7 cells.
Recombinant Human BCL2L1, or Bcl-XL, is a key protein involved in controlling cell death, making it an important focus for both scientific research and industrial production.
In research, rhBCL2L1 is used to explore how programmed cell death works. Part of the Bcl-2 family, this protein is located in mitochondrial membranes and is key in managing cell death, impacting development and tissue health. It's essential for calcium uptake, which plays a role in apoptosis. In cancer, too much of it can help tumors dodge the immune system and resist chemotherapy. Scientists are exploring how pathways like p53 and MAPK keep BCL2L1 in check to grasp how cells decide between survival and death.
On the industrial side, rhBCL2L1 is manufactured for drug development, especially in cancer therapy, because of its role in preventing cell death. Producing this protein helps create high-quality reagents for research, aiding in the discovery of new treatments. Additionally, this process supports the development of diagnostic tools, such as antibodies, which are essential for measuring BCL2L1 levels in biological samples, aiding in research and therapeutic advancements.
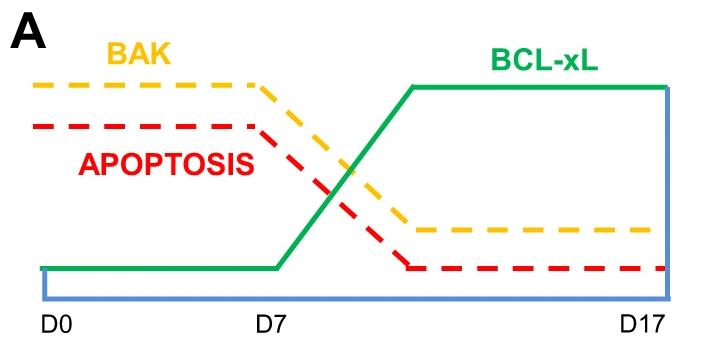
Fig1. Inverse relationship between BCL-xL and BAK proteins contributing to pancreatic specification. (Kengo Adachi, 2007)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All BCL2L1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All BCL2L1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


