Recombinant Human ATXN2 Protein, GST-tagged
| Cat.No. : | ATXN2-156H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human ATXN2 Protein(NP_001297050.1)(251-600 aa), fuesd with N-terminal GST tag, was expressed in E. coli. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | GST |
| Protein Length : | 251-600 aa |
| Description : | This gene belongs to a group of genes that is associated with microsatellite-expansion diseases, a class of neurological and neuromuscular disorders caused by expansion of short stretches of repetitive DNA. The protein encoded by this gene has two globular domains near the N-terminus, one of which contains a clathrin-mediated trans-Golgi signal and an endoplasmic reticulum exit signal. The encoded cytoplasmic protein localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane, is involved in endocytosis, and modulates mTOR signals, modifying ribosomal translation and mitochondrial function. The N-terminal region of the protein contains a polyglutamine tract of 14-31 residues that can be expanded in the pathogenic state to 32-200 residues. Intermediate length expansions of this tract increase susceptibility to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, while long expansions of this tract result in spinocerebellar ataxia-2, an autosomal-dominantly inherited, neurodegenerative disorder. Genome-wide association studies indicate that loss-of-function mutations in this gene may be associated with susceptibility to type I diabetes, obesity and hypertension. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| Form : | The purified protein was Lyophilized from sterile PBS (58mM Na2HPO4,17mM NaH2PO4, 68mM NaCl, pH8.). 5 % trehalose and 5 % mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Bio-activity : | Not tested. |
| AA Sequence : | GSDQRVVNGGVPWPSPCPSPSSRPPSRYQSGPNSLPPRAATPTRPPSRPPSRPSRPPSHPSAHGSPAPVSTMPKRMSSEGPPRMSPKAQRHPRNHRVSAGRGSISSGLEFVSHNPPSEAATPPVARTSPSGGTWSSVVSGVPRLSPKTHRPRSPRQNSIGNTPSGPVLASPQAGIIPTEAVAMPIPAASPTPASPASNRAVTPSSEAKDSRLQDQRQNSPAGNKENIKPNETSPSFSKAENKGISPVVSEHRKQIDDLKKFKNDFRLQPSSTSESMDQLLNKNREGEKSRDLIKDKIEPSAKDSFIENSSSNCTSGSSKPNSPSISPSILSNTEHKRGPEVTSQGVQTSS |
| Purity : | 75%, by SDS-PAGE with Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. |
| Applications : | Blocking peptide |
| Stability : | Store for up to 12 months at -20°C to -80°C as lyophilized powder. |
| Storage : | Short-term storage: Store at 2-8°C for (1-2 weeks). Long-term storage: Aliquot and store at -20°C to -80°C for up to 3 months, buffer containing 50% glycerol is recommended for reconstitution. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | Reconstitute at 0.25 µg/μl in 200 μl sterile water for short-term storage. Reconstitution with 200 μl 50% glycerol solution is recommended for longer term storage (see Stability and Storage for more details). If a different concentration is needed for your purposes please adjust the reconstitution volume as required (please note: the ion concentration of the final solution will vary according to the volume used). Note: Centrifuge vial before opening. When reconstituting, gently pipet and wash down the sides of the vial to ensure full recovery of the protein into solution. |
| Shipping : | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature (see below). |
| Gene Name | ATXN2 ataxin 2 [ Homo sapiens (human) ] |
| Official Symbol | ATXN2 |
| Synonyms | ATX2; SCA2; TNRC13 |
| Gene ID | 6311 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001310121.1 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001297050.1 |
| MIM | 601517 |
| UniProt ID | Q99700 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| ATXN2-10068H | Recombinant Human ATXN2, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Atxn2-3688M | Recombinant Mouse Atxn2, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ATXN2-6860Z | Recombinant Zebrafish ATXN2 | +Inquiry |
| ATXN2-1031H | Recombinant Human ATXN2 protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ATXN2-10069H | Recombinant Human ATXN2 Protein, Non tagged | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Wang Q, et al. J Immunol Res. 2022
As one of the primary therapeutic choices, chemotherapy is widely adopted for progressive gastric cancer (GC), but the development of chemoresistance has limited chemotherapy efficacy and partly contributes to poor prognosis. Immunotherapy is increasingly being applied in the clinical treatment of GC and is also benefitting patients. To ascertain whether ATXN2 affects chemotherapy efficacy in GC cells and its role in GC immune escape, researchers performed high-throughput sequencing to clarify genes differentially expressed between 5-FU-resistant and 5-FU-sensitive GC cells and then conducted qRT-PCR to assess ATXN2 expression in GC tissues. Furthermore, the influence of ATXN2 on resistance was studied in vitro and in vivo, ATXN2 and other protein expression levels were detected using Western blotting and immunohistochemistry (IHC), and the direct association of SP1 and ATXN2 was confirmed through luciferase reporter gene analysis. The elevated ATXN2 in GC tumors and a negative correlation between ATXN2 levels and the prognosis of GC. Furthermore, by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway, ATXN2 was found to promote chemoresistance in GC, facilitating BCL2L1 expression.

Fig1. ATXN2 upregulation in SGC7901 cells and ATXN2 downregulation in SGC7901/5-FU cells.

Fig2. Flow cytometric analysis of PD-L1 expression in SGC7901 cells overexpressing ATXN2 or treated with an AKT inhibitor.
Case 2: Inagaki H, et al. J Biol Chem. 2020
The RNA-binding protein Ataxin-2 binds to and stabilizes a number of mRNA sequences, including that of the transactive response DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43). However, it has yet to be unambiguously demonstrated that Ataxin-2 is actually involved in activating the translation of its target mRNAs. Here researchers provide direct evidence from a polysome profile analysis showing that Ataxin-2 enhances translation of target mRNAs. They established method for transcriptional pulse-chase analysis under conditions of suppressing deadenylation revealed that Ataxin-2 promotes post-transcriptional polyadenylation of the target mRNAs. Furthermore, Ataxin-2 binds to a poly(A)-binding protein PABPC1 and a noncanonical poly(A) polymerase PAPD4 via its intrinsically disordered region (amino acids 906-1095) to recruit PAPD4 to the targets. Post-transcriptional polyadenylation by Ataxin-2 explains not only how it activates translation but also how it stabilizes target mRNAs, including TDP-43 mRNA. These findings suggest that Ataxin-2-induced cytoplasmic polyadenylation and activation of translation might impact neurodegeneration (i.e. TDP-43 proteinopathies), and this process could be a therapeutic target for Ataxin-2-related neurodegenerative disorders.

Fig1. Total RNA was isolated from each sample and mRNA were detected by Northern blotting analysis.
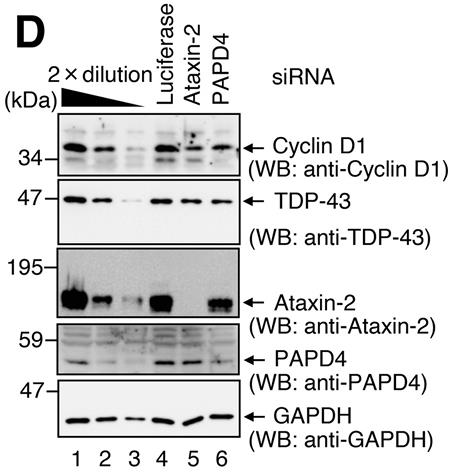
Fig2. Western blotting (WB) to analyze the indicated protein expression.
ATXN2 (Ataxin-2) is a highly expressed protein in the nervous system that is involved in a variety of cellular functions, including RNA metabolism, translation, stress response, and calcium ion regulation. The ATXN2 gene has been implicated in a variety of neurological diseases, especially spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson's disease (PD), and Machado-Joseph disease (MJD/SCA3). In terms of application, ATXN2 research mainly focuses on the following areas:
1. Disease research. To investigate the role of ATXN2 in nerve cell protection and cell death and explore its influence in neurodegenerative diseases. As ATXN2 is associated with a variety of neurodegenerative diseases, therapies targeting ATXN2 are being investigated, such as animal models using antisense oligonucleotides to treat SCA2, showing potential therapeutic feasibility.
2. Drug screening and development. Through gene knockout or overexpression of ATXN2, animal models or cellular models are established to simulate human disease for disease mechanism research and drug testing. As a drug target, ATXN2 is being used to develop drugs to treat related diseases.
3. Discovery of biomarkers. The expression level of ATXN2 or its variant form may serve as a biomarker for certain diseases and help in the diagnosis and prognosis assessment of the disease.
4. Studies on metabolism and energy balance. The role of ATXN2 in regulating overall body metabolism and circadian rhythms is being investigated and may be linked to diseases such as obesity and diabetes.
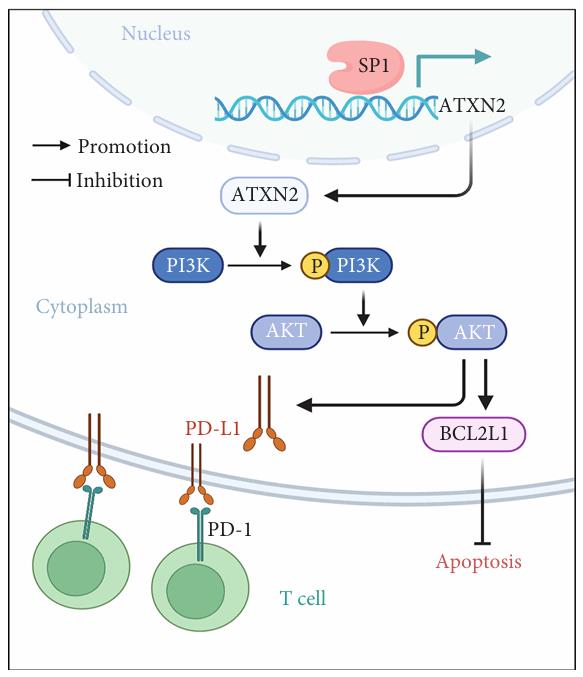
Fig1. Schematic of the model for the SP1/ATXN2/PI3K-Akt/BCL2L1 and SP1/ATXN2/PI3K-Akt/PD-L1 pathways. (Qi Wang, 2022)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All ATXN2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All ATXN2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


