Recombinant Human ADM protein(Tyr95-Tyr146), hFc-tagged
| Cat.No. : | ADM-7324H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human ADM (P35318) (Tyr95-Tyr146) was expressed in HEK293, with the fused Fc region of Human IgG1 at the N-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | Fc |
| Protein Length : | 95-146 a.a. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human ADM/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 340 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 38 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 39 in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 93 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | ADM adrenomedullin [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | ADM |
| Synonyms | ADM; adrenomedullin; AM; preproadrenomedullin; |
| Gene ID | 133 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001124 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001115 |
| MIM | 103275 |
| UniProt ID | P35318 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| Adm-235R | Recombinant Rat Adm Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ADM-186R | Recombinant Rat ADM Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ADM-856H | Recombinant Human ADM Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | +Inquiry |
| ADM-85H | Recombinant Human ADM Protein, His&SUMO-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ADM-351M | Recombinant Mouse ADM Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| ADM-1530HCL | Recombinant Human ADM cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Chen L, et al. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012
When there's not much oxygen, adrenomedullin (ADM) and hypoxia-inducing factor-1α (HIF-1α) are key in helping cells grow. We used to think ADM only got triggered by HIF-1, but new studies show ADM can impact HIF-1, too. Researchers created two types of human endothelial cells where HIF-1α activity was reduced using specific siRNAs (hy926-siHIF-1α and HMEC-siHIF-1α). They looked at how ADM and HIF-1α were expressed at the mRNA and protein levels in EA.hy926 and HMEC1 cells under low-oxygen situations. After treating the cells with ADM, they checked cell growth and how HIF-1α and its related genes (like VEGF, PFKP, PGK1, and AK1) behaved. They also measured proline hydroxylase (PHD) mRNA levels and activity. It turns out that under low oxygen, ADM kicks in before HIF-1α in these cells. ADM boosted cell growth in a way that depends on HIF-1α. Plus, ADM increased the mRNA and protein levels of HIF-1α and its target genes by lowering PHD mRNA expression and activity.
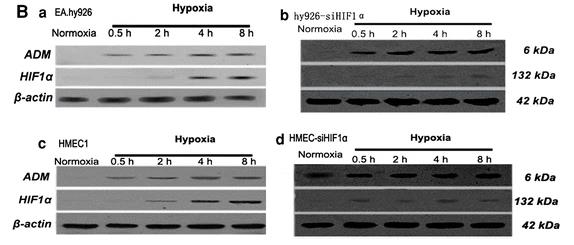
Fig1. Crude proteins extracted from the cells were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by western immunoblot.
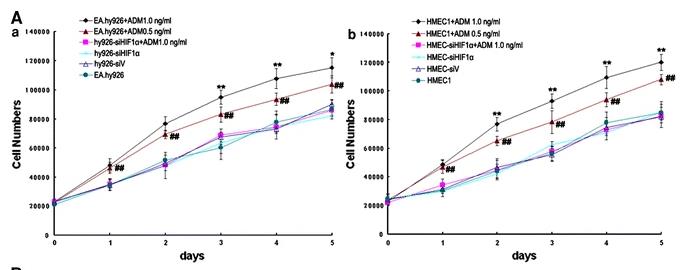
Fig2. The promoted proliferation of endothelial cells under ADM treatment is HIF-1α dependent.
Case 2: Dai X, et al. Med Oncol. 2013
Osteosarcoma is tough to treat, and current therapies fall short, highlighting the need for new targets. This study looked into adrenomedullin (ADM) levels in osteosarcoma tissues and its impact on cell growth. Researchers gathered samples from patients and controls to measure ADM with various techniques. Analyzing clinical data helped us see how ADM relates to cancer severity and outcomes. By using RNA interference to lower ADM levels in the MG-63 cell line and animal models, we found that reducing ADM significantly curbed tumor cell growth. Thus, targeting ADM could slow down osteosarcoma progression.
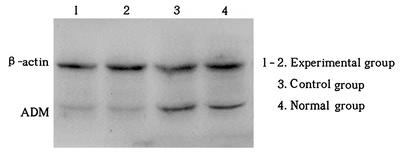
Fig1. Demonstration of less ADM protein in the experimental group than in controls.

Fig2. Western blotting detects the expression of ADM protein in vivo following siRNA against ADM in vivo.
Adrenomedullin (ADM) is a hormone made up of 52 amino acids, crucial for managing activities in the cardiovascular and lymphatic systems. As a member of the calcitonin/CGRP family, it has some shared structural features and a complex receptor setup. ADM works through the calcitonin receptor-like receptor mixed with proteins that modify its activity, which is vital for its function. Present in several human tissues, ADM is involved in numerous biological activities, serving as both a handy diagnostic marker and a promising therapeutic target. It also plays a role in keeping the balance of cellular methylation, impacting the modifications of DNA, RNA, and proteins that affect gene activity and cell functions. In research and industrial settings, recombinant Human ADM protein is valuable for probing cardiovascular health, controlling blood pressure, and aiding tissue repair. It's also a key player in creating new therapies and drugs, providing a deeper look into its role in health and disease.
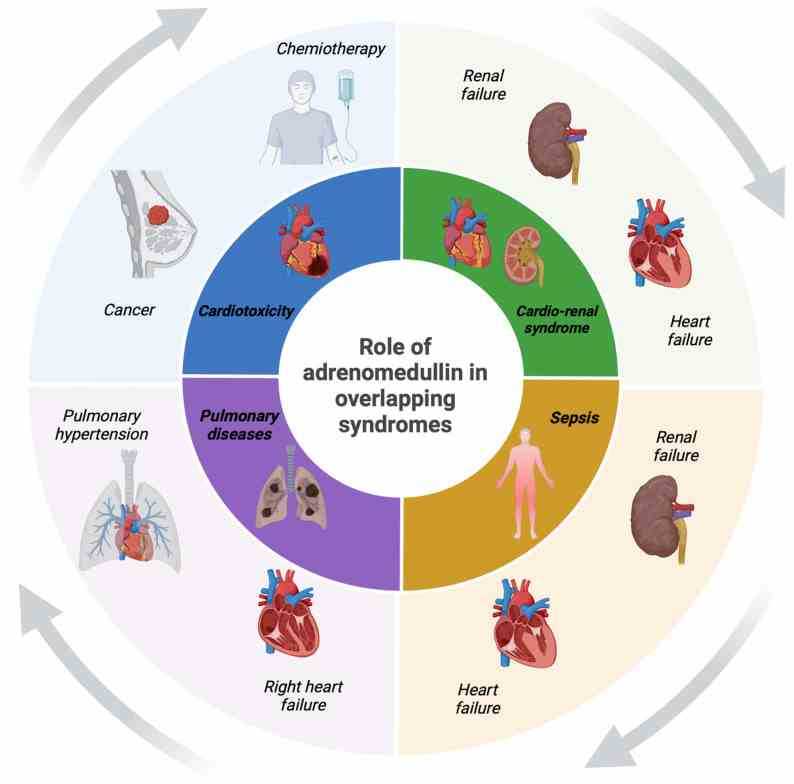
Fig1. The role of ADM in overlapping diseases. (Matteo Antonio Sacco, 2024)
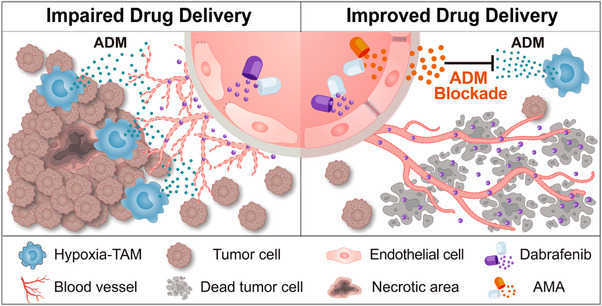
Fig2. Targeting hypoxia-TAM-secreted ADM for tumour vessel normalization. (Zhen Qin, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All ADM Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All ADM Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


