Recombinant Canine CCL5 Protein
| Cat.No. : | CCL5-424C |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Canine CCL5 Protein was expressed in E. coli. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Canine |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Protein Length : | Ser24-Ser91 |
| Description : | CCL5, also known as RANTES (Regulated upon Activation, Normal T cell Expressed and presumably Secreted), is an 8 kDa beta -chemokine that plays a primary role in the inflammatory immune response by means of its ability to attract and activate leukocytes. Human and mouse RANTES exhibit cross-species activity on human and mouse cells. Mature canine CCL5 shares 74% - 84% amino acid seqeuence identity with cotton rat, feline, human, mouse, and rat CCL5. CCL5 is secreted by many cell types at inflammatory sites, and it exerts a wide range of activities through the receptors CCR1, CCR3, CCR4, and CCR5. Inflammatory responses can be impaired by the sequestration of CCL5 by the cytomegalovirus protein US28. In humans, CCR5 binding to CCL5 inhibits the infectivity of R5 (M-tropic) but not X4 (T-tropic) strains of HIV-1. The two N-terminal residues of CCL5 can be removed by CD26/DPPIV, generating a protein that functions as a chemotaxis inhibitor and more effectively blocks M-tropic HIV-1 infection of monocytes. Oligomerization of CCL5 on glycosaminoglycans is required for CCR1-mediated leukocyte adhesion and activation as well as CCL5's interaction with the chemokine CXCL4/PF4. The deposition of CCL5 on activated vascular endothelial cells is crucial for monocyte adhesion to damaged vasculature, but CCL5 oligomerization is not required for the extravasation of adherent leukocytes. CCL5 is upregulated in breast cancer and promotes tumor progression through the attraction of proinflammatory macrophages in addition to its actions on tumor cells, stromal cells, and the vasculature. |
| Form : | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Acetonitrile and TFA with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Bio-activity : | Measured by its ability to chemoattract BaF3 mouse pro‑B cells transfected with human CCR5. The ED50 for this effect is 2‑10 ng/mL. |
| Molecular Mass : | Predicted Molecular Mass: 7.9 kDa SDS-PAGE: 7.9 kDa, reducing conditions |
| Endotoxin : | <0.01 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method. |
| Purity : | >95%, by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and visualized by silver stain. |
| Storage : | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 centigrade as supplied. 1 month, 2 to 8 centigrade under sterile conditions after reconstitution. 3 months, -20 to -70 centigrade under sterile conditions after reconstitution. |
| Shipping : | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Reconstitution : | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Publications : |
Recruitment of classical monocytes can be inhibited by disturbing heteromers of neutrophil HNP1 and platelet CCL5 (2015)
|
| Gene Name | CCL5 C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 [ Canis lupus familiaris (dog) ] |
| Official Symbol | CCL5 |
| Synonyms | CCL5; C-C motif chemokine ligand 5; chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5; D17S136Enormally T-expressed, and presumably secreted; EoCP; Eosinophil chemotactic cytokine; RANTES; SISd; SIS-delta; small inducible cytokine A5 (RANTES); small inducible cytokine subfamily A (Cys-Cys), member 5; Small-inducible cytokine A5; T cell-specific protein P228; T-cell specific protein p288; TCP228T-cell-specific protein RANTES |
| Gene ID | 403522 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001003010.2 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001003010.1 |
| UniProt ID | Q8HYS0 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| Ccl5-259M | Active Recombinant Mouse Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand 5 | +Inquiry |
| CCL5-776R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey CCL5 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CCL5-521H | Recombinant Human CCL5 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CCL5-147S | Recombinant Swine Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand 5 | +Inquiry |
| Ccl5-616M | Recombinant Mouse Ccl5 protein | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CCL5-2706HCL | Recombinant Human CCL5 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Liu C, et al. Cell Death Differ. 2020
Macrophages in the tumor microenvironment contribute to colorectal cancer (CRC) progression and immune evasion, but the specific mechanisms are not well understood. This study showed that macrophage infiltration, triggered by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or a high-cholesterol diet (HCD), significantly enhanced CRC growth, and LPS along with poly (I:C) increased CT26 cell allograft tumor volume. We found that CCL5, released by macrophages, inhibits T-cell killing of HT29 cells and promotes immune evasion by stabilizing PD-L1. This process involves the formation of nuclear factor kappa-B p65/STAT3 complexes that bind to the CSN5 promoter, upregulating its expression, which in turn affects PD-L1 deubiquitination and stability. High CSN5 expression in CRC correlates with poorer survival.
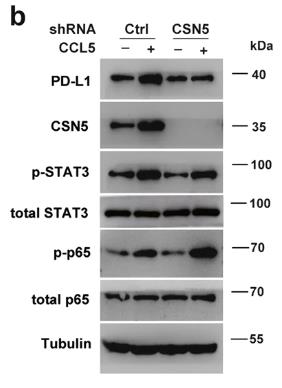
Fig1. Western blot analysis of PD-L1, p65, and STAT3 expressions in CSN5-deleted HT29 cells after CCL5 stimulation.
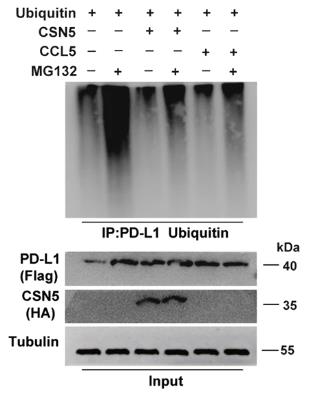
Fig2. Ubiquitination assay of PD-L1 in HEK293 cells in response to treatment with 10 μM MG-132 for 3 h or CCL5.
Case 2: Ma Z, et al. Protein J. 2022
CCL5 plays a significant role in the tumor microenvironment, particularly in tumor invasion and metastasis, but its specific impact on ovarian cancer remains unclear. This study aimed to express and purify recombinant CCL5 protein to explore its effects on ovarian cancer cell proliferation. The human CCL5 gene was cloned into the pET-30a vector for expression in E. coli BL21, and the soluble His-CCL5 protein was expressed and purified using affinity chromatography. MTT assays revealed that CCL5 stimulates ovarian cancer cell growth by activating the MEK/ERK pathway, increasing the phosphorylation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase, and upregulating the mRNA levels of Jun, NF-κB2, Nras, Relb, and Traf2. The use of a MEK inhibitor reduced the mRNA levels of Jun, NF-κB2, and Traf2, confirming that exogenous CCL5 enhances ovarian cancer cell proliferation via MEK/ERK signaling and the expression of these genes.
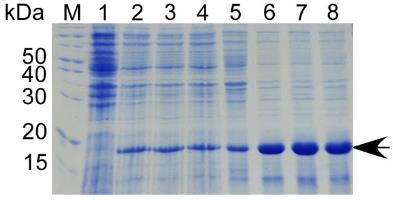
Fig1. Coomassie bright blue staining analysis the expression of His-CCL5 at 28 °C.

Fig2. The protein levels were analyzed using western blot on A2780 cells and CCL5-treated A2780 cells.
CCL5 (also known as RANTES, Regulated on Activation, Normal T cell Expressed and Secreted) is a CC chemokine that plays a key role in the immune system, especially in the regulation of inflammatory responses and tumor microenvironment. Under non-inflammatory conditions, CCL5 is also constitutively expressed by memory T cells and NK cells and is essential for the maintenance of tissue-resident memory T cells. In addition, the role of CCL5 in tumor development is multifaceted, which can promote tumor cell invasion and metastasis, and recruit anti-inflammatory immune cells such as regulatory T cells (Tregs), thereby inhibiting anti-tumor immunity. Recombinant Canine CCL5 protein, i.e., canine chemokine (CCL5), is often used as a standard in cytokine research or as an important molecule for studying canine immune responses.
Recombinant Canine CCL5 protein has a wide range of applications in scientific research and biotechnology, especially in immunology, drug screening and disease model research. CCL5 is an important chemokine that plays a central role in regulating the migration and activation of immune cells. In immune research, CCL5 is a key factor in studying the migration mechanisms of T cells and other immune cells, which helps to understand how the immune system responds to various stimuli. In addition, CCL5 also plays an important role in drug screening, which promotes the screening of anti-inflammatory drugs or other immunomodulatory drugs to inhibit the activity of CCL5, providing a new strategy for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and autoimmune diseases. In disease model research, recombinant Canine CCL5 protein is used to study canine disease models involving the immune system and inflammatory response, such as autoimmune diseases or allergic reactions, which helps to reveal the pathogenesis of these diseases and develop new treatments.
In the biotechnology and pharmaceutical fields, the application of recombinant Canine CCL5 protein is also expanding. It is used as a template to develop new biologics or immunomodulators that may have potential effects on regulating immune responses and treating related diseases. In addition, CCL5 protein is also used to develop diagnostic reagents for detecting canine diseases or specific immune responses, which helps to identify potential biomarkers to monitor the health and disease status of dogs. These applications not only promote further understanding of the function and mechanism of CCL5, but also provide valuable tools for new targets for the future treatment of a variety of diseases.
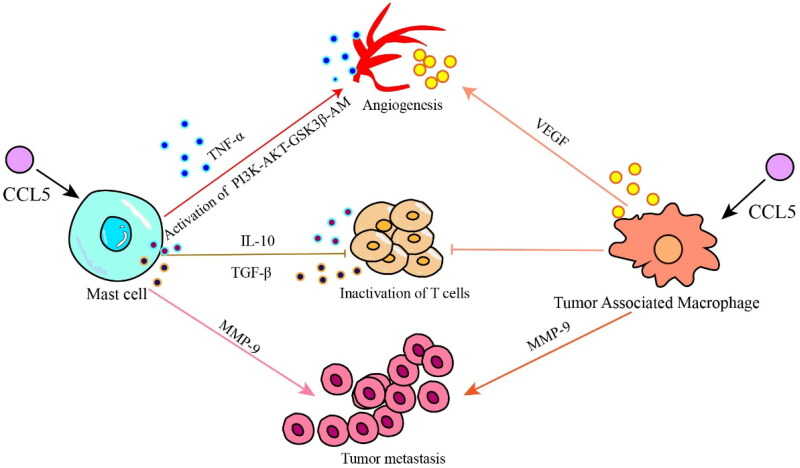
Fig1. CCL5 promotes tumor progression by recruiting immunosuppressive cells. (Xin-Feng Zhang, 2023)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CCL5 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CCL5 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


