Recombinant Canine ACVR1 protein(Met1-Glu123), hFc-tagged
| Cat.No. : | ACVR1-160C |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Canine ACVR1 (XP_549615.2) (Met1-Glu123) was expressed in HEK293 with the Fc region of Human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Canine |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | Fc |
| Protein Length : | Met1-Glu123 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant canine ACVR1/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 344 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 38.6 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 68 and 44 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method |
| Purity : | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| MIM-Weblink : |
| Gene Name | ACVR1 activin A receptor, type I [ Canis lupus familiaris (dog) ] |
| Official Symbol | ACVR1 |
| Synonyms | ACVR1; activin A receptor, type I; activin receptor type-1 |
| Gene ID | 478757 |
| mRNA Refseq | XM_549615 |
| Protein Refseq | XP_549615 |
| UniProt ID |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| ACVR1-9172H | Recombinant Human ACVR1 | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-1022H | Recombinant Human ACVR1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-1408H | Recombinant Human Activin A Receptor, Type I | +Inquiry |
| Acvr1-8719R | Recombinant Rat Acvr1 protein, hFc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-3442H | Recombinant Human ACVR1 protein, hFc-tagged, For Organoid Culture | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| ACVR1-2686MCL | Recombinant Mouse ACVR1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-478HCL | Recombinant Human ACVR1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-967CCL | Recombinant Canine ACVR1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-1232CCL | Recombinant Cynomolgus ACVR1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-1305RCL | Recombinant Rat ACVR1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Cao H, et al. Sci Rep. 2020
Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is a fatal childhood brain tumor with a median survival of less than a year. Researchers reassessed the roles of the two prevalent ACVR1 kinase domain mutants, G328V and R206H, associated with DIPG, in light of new data on their ATPase activities. At 37°C, the G328V variant exhibits a 1.8-fold increase in kinase activity compared to the wild-type, while R206H shows similar activity. This elevated activity in G328V aligns with the longer survival times observed in DIPG patients with this mutation. Considering the interaction between ACVR1 and TβRI pathways and the off-targets of ACVR1 inhibitors, we confirmed the efficacy of several TβRI inhibitors on DIPG cell lines derived from patient tumors with ACVR1 wild-type and G328V mutations at doses of 20-50 μM. SU-DIPG-IV cells with H3.1K27M and ACVR1 G328V mutations were less responsive to TβRI inhibition than SF8628 cells with H3.3K27M and wild-type ACVR1.
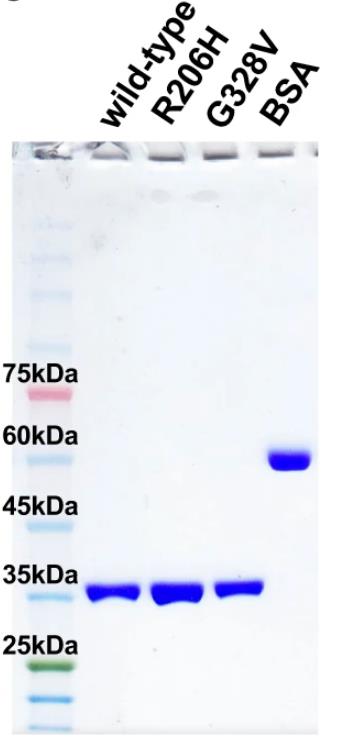
Fig1. Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel of purified ACVR1 kinase domain stocks used for kinase assays.
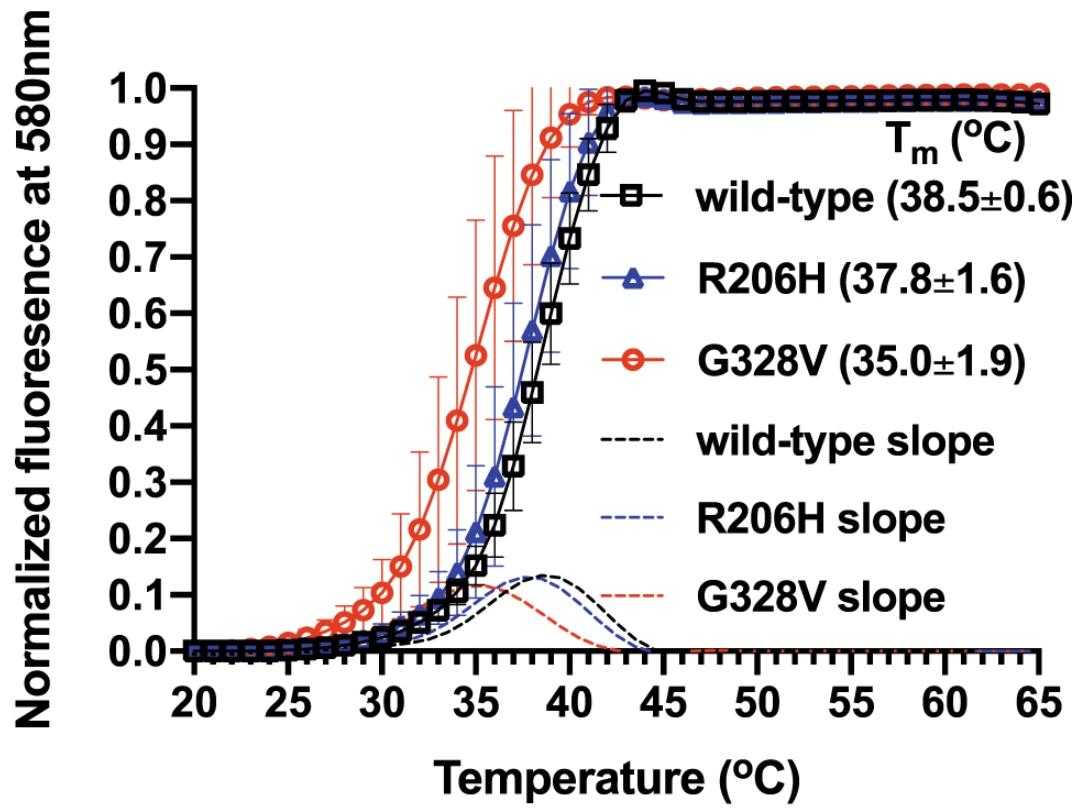
Fig2. Melting curves of wild-type, R206H and G328V ACVR1 kinase domains.
Case 2: Tyagi A, et al. Leukemia. 2024
Here activin A receptor type I (ACVR1), part of the TGF-β superfamily, promotes acute myeloid leukemia (AML) growth and is a potential therapeutic target. Overexpressed in FLT3-mutated AML, ACVR1 inhibition enhances sensitivity to FLT3 inhibitors. This new ACVR1 inhibitor, TP-0184, selectively halts growth in these AML cell lines. TP-0184 binds to ACVR1 and FLT3 with high affinity, blocking downstream signaling, and significantly suppresses leukemia growth in FLT3-mutated AML cell lines and xenograft models when used alone or with venetoclax. This indicates ACVR1 as a new biomarker in AML resistance to FLT3 inhibitors and positions TP-0184 as a promising therapeutic agent for FLT3-mutated AML.
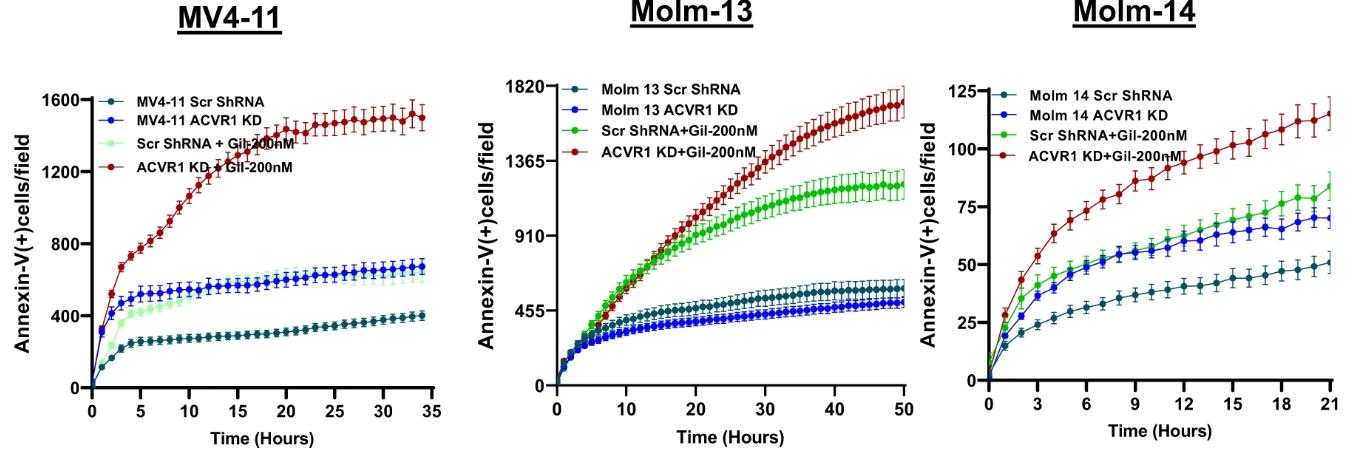
Fig1. Time kinetics of ACVR1 KD and scrambled shRNA control FLT3-mutated MV4-11, MOLM-13, and MOLM-14 AML cell lines.
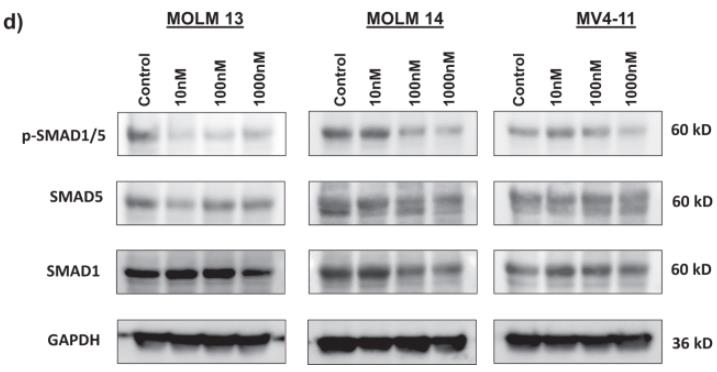
Fig2. Downstream signaling proteins of ACVR1, p-SMAD1/5, SMAD5, and SMAD1 were measured by western blot.
ACVR1 protein, also known as activin A type I receptor, is a protein that plays an important role in many biological processes and belongs to the transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily. This receptor is mainly involved in biological processes such as cell growth, differentiation, apoptosis and morphogenesis. Abnormal function of ACVR1 protein is associated with a variety of diseases, including fibrous dysplasia and certain cancers.
Recombinant Canine ACVR1 protein, as a genetically engineered protein with similar structure and function to the natural protein, has a wide range of applications, especially in scientific research, clinical medicine, veterinary science and biotechnology.
In the field of scientific research, recombinant ACVR1 protein is an important tool for studying signal transduction, disease model construction and drug development. It helps scientists to deeply understand the function and mechanism of ACVR1 in cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis. By constructing disease models related to ACVR1, such as fibrous dysplasia, researchers can introduce specific gene mutations in experimental animals to simulate human diseases, and then study disease mechanisms and potential treatment strategies. In addition, by studying the interaction between recombinant ACVR1 and its ligands and inhibitors, scientists can look for potential therapeutic drugs, which is crucial for developing treatments for diseases with abnormal ACVR1 function.
In clinical medicine, the application of recombinant ACVR1 protein includes the development of diagnostic reagents and the study of treatment methods. It can be used to develop diagnostic reagents for ACVR1-related diseases to help detect and evaluate diseases at an early stage. At the same time, as a potential therapeutic target, researchers are studying treatments for diseases with abnormal ACVR1 function, such as progressive myositis ossificans progressiva (FOP).
In veterinary science, recombinant ACVR1 protein helps to study genetic diseases caused by abnormal ACVR1 in specific dog breeds, which is of great significance for canine breeding and health management.
In the field of biotechnology, the application of recombinant ACVR1 protein extends to protein engineering and modification, and it can be used to develop biological agents with specific functions or characteristics. For example, by studying the role of ACVR1 in the maintenance of nerve branches, new possibilities can be provided for the treatment of neurological diseases. In addition, ACVR1 protein also plays an important role in regulating stem cell pluripotency, which provides new research directions for stem cell therapy and regenerative medicine.
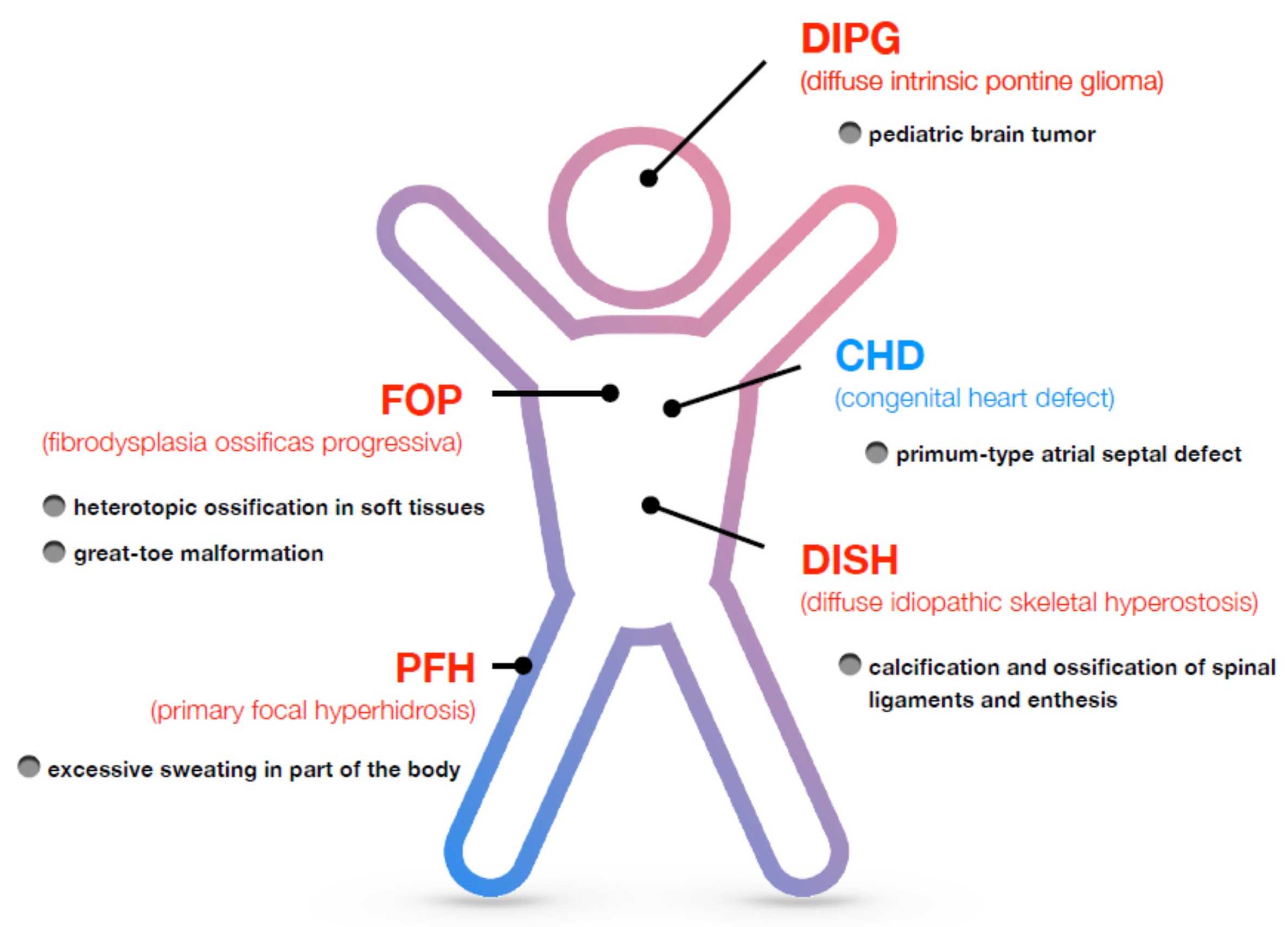
Fig1. Disorders associated with ALK2/ACVR1. (Takenobu Katagiri, 2021)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All ACVR1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All ACVR1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


