Recombinant Human CAMKV protein(Met1-Ser501), His&GST-tagged
| Cat.No. : | CAMKV-7337H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human CAMKV (NP_076951.2) (Met 1-Ser 501) was expressed in Insect Cells, fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Insect Cells |
| Tag : | GST&His |
| Protein Length : | Met1-Ser501 |
| Form : | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4, 10% glycerol Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Molecular Mass : | The recombinant human CAMKV/GST chimera consists of 738 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 82.2 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 80 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| Endotoxin : | < 1.0 EU per μg of the protein as determined by the LAL method. |
| Purity : | > 80 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Samples are stable for up to twelve months from date of receipt at -20°C to -80°C. Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | It is recommended that sterile water be added to the vial to prepare a stock solution of 0.2 ug/ul. Centrifuge the vial at 4°C before opening to recover the entire contents. |
| Gene Name | CAMKV CaM kinase-like vesicle-associated [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | CAMKV |
| Synonyms | CAMKV; CaM kinase-like vesicle-associated; caM kinase-like vesicle-associated protein; MGC8407; VACAMKL; vesicle-associated calmodulin-binding protein; 1G5; |
| Gene ID | 79012 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_024046 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_076951 |
| UniProt ID | Q8NCB2 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| CAMKV-10689H | Recombinant Human CAMKV, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CAMKV-2675M | Recombinant Mouse CAMKV Protein | +Inquiry |
| Camkv-1948M | Recombinant Mouse Camkv Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CAMKV-7337H | Recombinant Human CAMKV protein(Met1-Ser501), His&GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| CAMKV-2793HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CAMKV Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| CAMKV-605HCL | Recombinant Human CAMKV cell lysate | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Liang Z, et al. Nat Commun. 2016
Dendritic spine stability relies on synaptic input and changes in the actin cytoskeleton and protein synthesis, but the details are not fully understood. Researchers identified CaMKv, a pseudokinase from the CaMK family, as vital for maintaining dendritic spines. Found in dendrites, CaMKv's production is controlled by neuronal activity and is inhibited when phosphorylated by Cdk5. Knocking down CaMKv in mice affects synaptic transmission and memory, causing hyperactivity. This shows that regulating CaMKv through synthesis and phosphorylation is key to maintaining dendritic spines, highlighting a unique pathway in brain function and signaling.
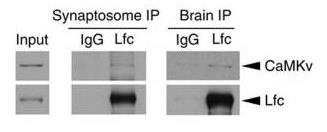
Fig1. CaMKv was co-immunoprecipitated with Lfc in brain homogenate and synaptosome fractions.
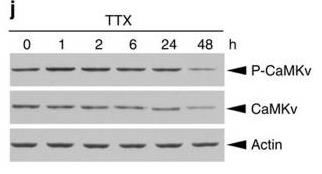
Fig2. CaMKv phosphorylation increased on activity blockade.
Case 2: Gilligan M, et al. Ann Neurol. 2024
This report describes autoimmune paraneoplastic encephalitis linked to IgG antibodies against CAMKV. CAMKV was pinpointed as a significant antigen using human protein microarray in patients with similar brain staining. Confirmed by various assays, the condition appeared in mostly women aged 53-74, with symptoms like mental changes, seizures, and memory loss. MRI revealed distinct abnormalities. Associated cancers included uterine adenocarcinoma showing CAMKV activity, bladder carcinoma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Two cases followed cancer treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Initial treatments like corticosteroids helped, but three patients died from cancer.
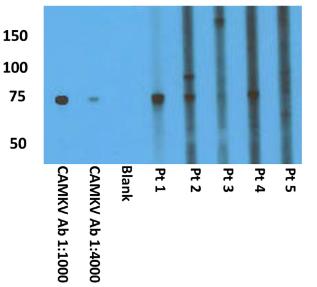
Fig1. Mouse whole brain lysate, denatured and separated by electrophoresis, when probed with rabbit polyclonal CAMKV antibody or candidate patient (pt) serums.
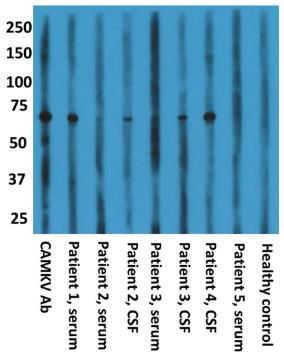
Fig2. Western blot using recombinant CAMKV protein produced a ~ 70-kDa band when probed with commercial CAMKV antibody.
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All CAMKV Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All CAMKV Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


