Active Recombinant Human AMPX Protein, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | JAK2-1420H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human JAK2 (a.a. 808-end) with N-terminal His-tag was expressed in a baculovirus expression system. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Case Study
- Application
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Insect Cells |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 808-end a.a. |
| Description : | This gene encodes a non-receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a central role in cytokine and growth factor signalling. The primary isoform of this protein has an N-terminal FERM domain that is required for erythropoietin receptor association, an SH2 domain that binds STAT transcription factors, a pseudokinase domain and a C-terminal tyrosine kinase domain. Cytokine binding induces autophosphorylation and activation of this kinase. This kinase then recruits and phosphorylates signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins. Growth factors like TGF-beta 1 also induce phosphorylation and activation of this kinase and translocation of downstream STAT proteins to the nucleus where they influence gene transcription. Mutations in this gene are associated with numerous inflammatory diseases and malignancies. This gene is a downstream target of the pleiotropic cytokine IL6 that is produced by B cells, T cells, dendritic cells and macrophages to produce an immune response or inflammation. Disregulation of the IL6/JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathways produces increased cellular proliferation and myeloproliferative neoplasms of hematopoietic stem cells. A nonsynonymous mutation in the pseudokinase domain of this gene disrupts the domains inhibitory effect and results in constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation activity and hypersensitivity to cytokine signalling. This gene and the IL6/JAK2/STAT3 signalling pathway is a therapeutic target for the treatment of excessive inflammatory responses to viral infections. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. |
| Form : | Aqueous buffer solution |
| Bio-activity : | 124 pmol/min/μg |
| Molecular Mass : | 42.5 kDa |
| Applications : | Useful for the study of enzyme kinetics, screening inhibitors, and selectivity profiling. |
| Storage : | At least 6 months at –80 centigrade. |
| Concentration : | 0.25 mg/mL |
| Storage Buffer : | 40 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 110 mM NaCl, 2.2 mM KCl, 3 mM DTT, 0.04% Tween-20 and 20% Glycerol |
| Shipping : | -80 centigrade |
| Gene Name | JAK2 Janus kinase 2 [ Homo sapiens (human) ] |
| Official Symbol | JAK2 |
| Synonyms | JAK2; Janus kinase 2; JTK10; tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2; JAK-2; Janus kinase 2 (a protein tyrosine kinase); EC 2.7.10.2 |
| Gene ID | 3717 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_004972 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_004963 |
| MIM | 147796 |
| UniProt ID | O60674 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| JAK2-157H | Recombinant Human JAK2 protein, His/MBP-tagged | +Inquiry |
| JAK2-3184H | Recombinant Human JAK2 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| JAK2-532H | Recombinant Human Janus Kinase 2, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| JAK2-3372H | Recombinant Human JAK2 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | +Inquiry |
| JAK2-28H | Recombinant Human JAK2 Protein, FLAG/Avi-tagged, Biotin-labeled | +Inquiry |
Case 1: Washington C, et al. PLoS Genet. 2020
Researchers report here that Rabex-5-mediated Ras ubiquitination requires Ras Tyrosine 4 (Y4), a site of known phosphorylation. Y4 phosphomimic substitution in oncogenic Ras blocked the morphological phenotypes associated with oncogenic Ras in vivo dependent on the presence of Rabex-5. They developed polyclonal antibodies raised against an N-terminal Ras peptide phosphorylated at Y4. These anti-phospho-Y4 antibodies showed dramatic recognition of recombinant wild-type Ras and RasG12V proteins when incubated with JAK2 or SRC kinases but not of RasY4F or RasY4F,G12V recombinant proteins suggesting that JAK2 and SRC could promote phosphorylation of Ras proteins at Y4 in vitro. A role for JAK2, SRC, and EGFR (kinases with well-known roles to activate signaling through Ras), to promote Ras Y4 phosphorylation could represent a feedback mechanism to limit Ras activation and thus establish Ras homeostasis.
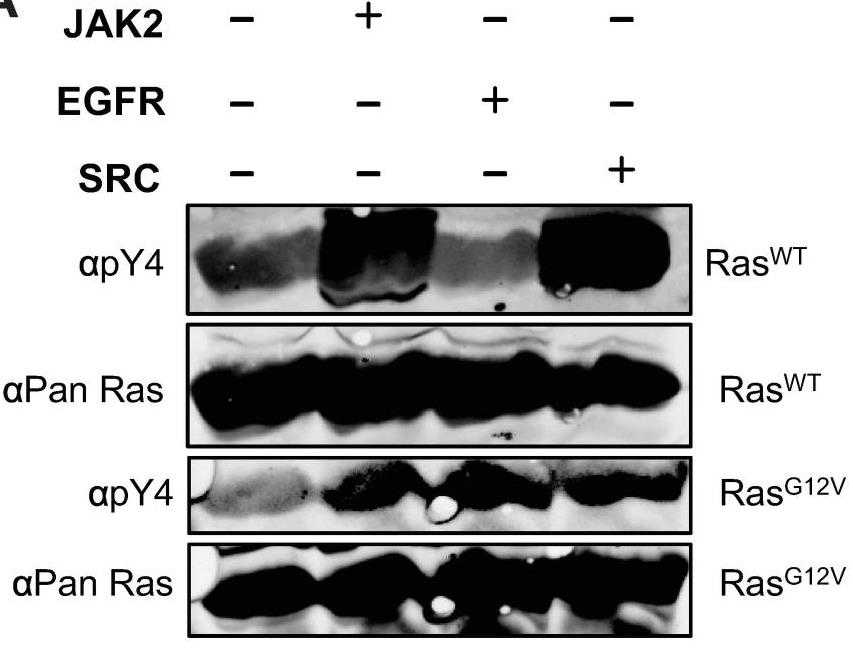
Fig1. RasWT and RasG12V proteins incubated in the presence or absence of JAK2, EGFR, or SRC proteins.
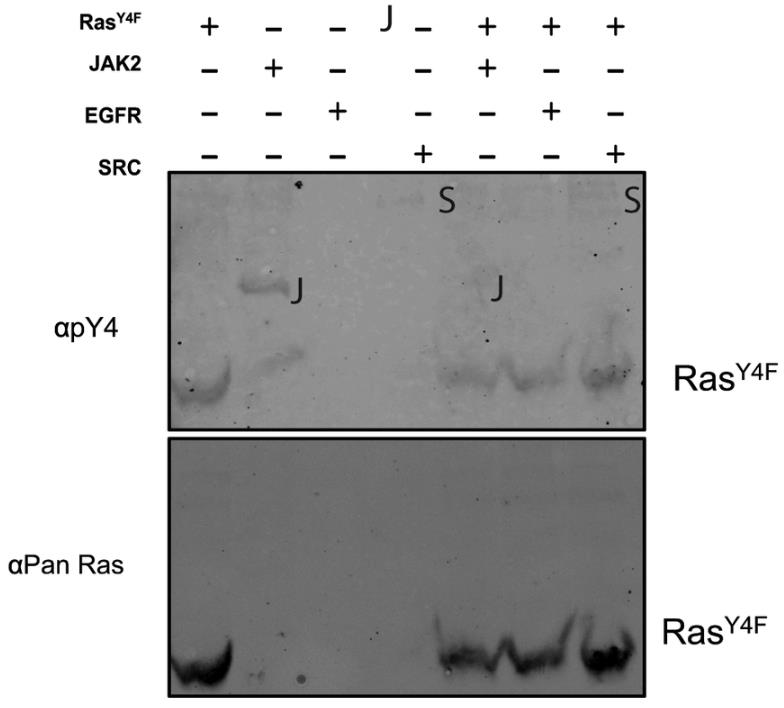
Fig2. RasY4F protein incubated in the presence or absence of JAK2, EGFR, or SRC proteins.
Case 2: Yang J, et al. J Cancer. 2024
OTUB1, an essential deubiquitinating enzyme, is upregulated in various types of cancer. Previous studies have shown that OTUB1 may be an oncogene in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), but its specific regulatory mechanism remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the mechanism by which OTUB1 and the JAK2/STAT1 signaling pathway co-regulate the growth of GBM. Using bioinformatics, GBM tissues, and cells, researchers evaluated the expression and clinical significance of OTUB1 in GBM. Subsequently, they explored the regulatory mechanisms of OTUB1 on malignant behaviors in GBM in vitro and in vivo. In addition, they added the JAK2 inhibitor AZD1480 to explore the regulation of OTUB1 for JAK2/STAT1 pathway in GBM.
The results showed OTUB1 expression was upregulated in GBM. Silencing OTUB1 promotes apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at G1 phase, inhibiting cell proliferation. In vivo experiments revealed that OTUB1 knockdown inhibited tumor growth, further emphasizing its crucial role in GBM progression. Mechanistically, OTUB1 was negatively correlated with the JAK2/STAT1 pathway in GBM. The addition of the JAK2 inhibitor AZD1480 significantly reversed the effects of silencing OTUB1 on GBM.
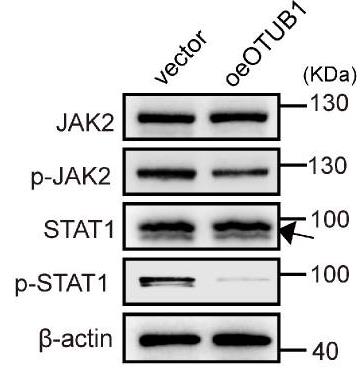
Fig1. Expression of JAK, p-JAK2, STAT1, p-STAT1, and p-STAT1 in U87 cells with OTUB1 overexpression using Western blot.
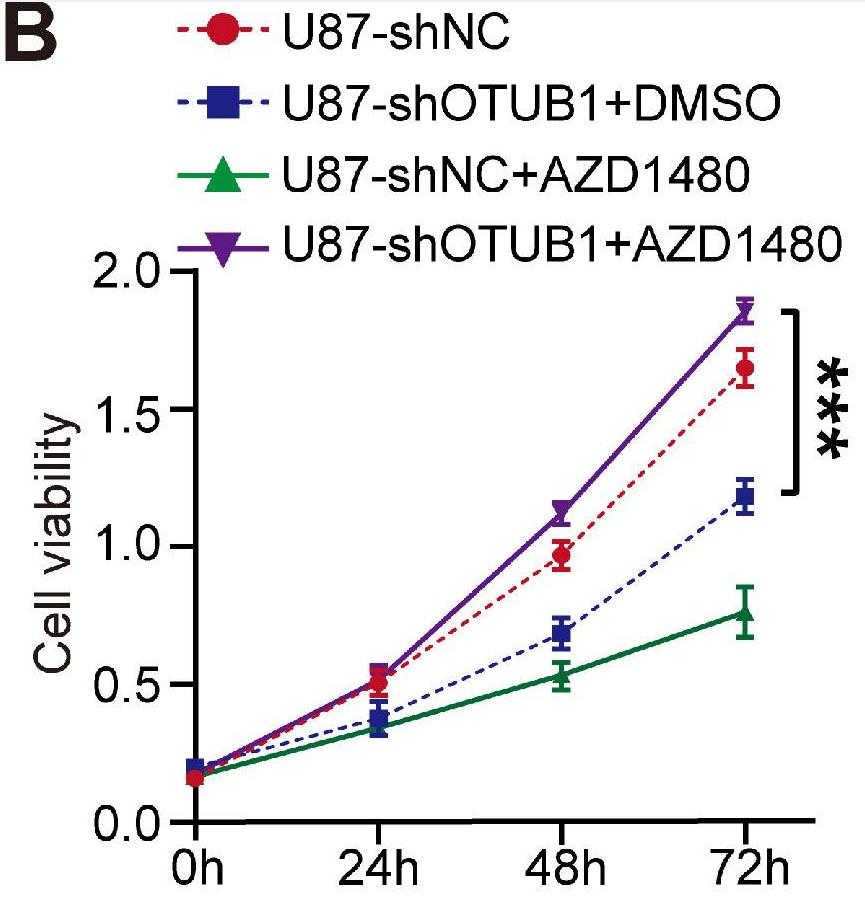
Fig2. The effect of the JAK2/STAT1 pathway on the viability of OTUB1-silenced GBM cells assessed using the CCK-8 assay.
JAK2 is a key member of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, which plays an important role in cytokine signaling. By binding to cytokine receptors, JAK2 mediates signal transduction of various cytokines such as interferon and growth factors. The activation and regulation mechanisms of JAK2 are important in a variety of diseases. JAK2 is involved in the transduction of cytokine signals, and studying JAK2 helps to understand how cytokines regulate immune responses and other biological processes. The applications of the protein JAK2 (Janus kinase 2) are mainly in the field of medical research and therapy, especially in the treatment of blood diseases and tumors.
Jak2-mutated hematopoietic stem cells exhibit different phenotypic and functional characteristics during the treatment of myroproliferative tumors (MPN). Studies on acute T-lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) have shown that JAK2-mutated leukemia cells affect downstream signaling through positive and negative regulatory mechanisms, thus promoting the proliferation of leukemia cells.
JAK2 has potential as a therapeutic target in drug development. JAK2 inhibitors can be used to treat blood diseases and tumors associated with JAK2 mutations. For example, interferon-alpha reduces the mutation load by promoting apoptosis or proliferation of JAK2-mutated hematopoietic stem cells.
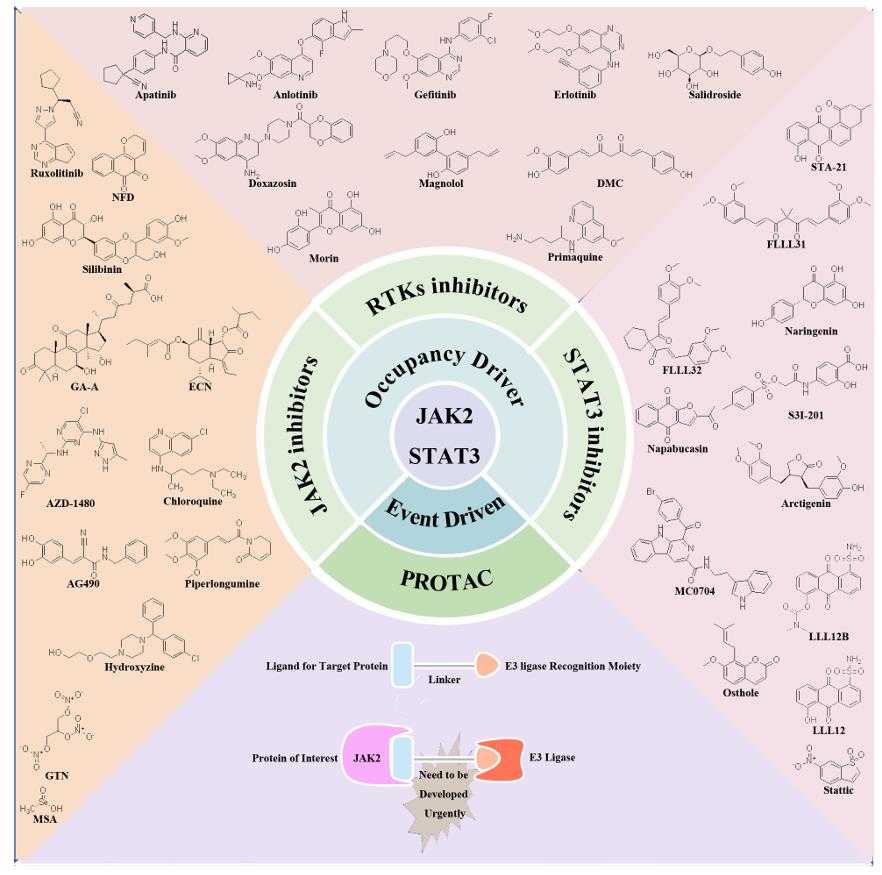
Fig1. Potential therapeutic targets and inhibitors targeting JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway for TNBC treatment. (Lin Long, 2024)
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews
- Q&As
Ask a Question for All JAK2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All JAK2 Products
Required fields are marked with *
Inquiry Basket


