UBE2T
-
Official Full Name
ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T (putative) -
Overview
The covalent conjugation of ubiquitin to proteins regulates diverse cellular pathways and proteins. Ubiquitin is;transferred to a target protein through a concerted action of a ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1), a;ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2), such as UBE2T, and a ubiquitin ligase (E3) (Machida et al., 2006 (PubMed;16916645)). -
Synonyms
UBE2T;ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2T (putative);ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 T;HSPC150;ubiquitin-protein ligase T;ubiquitin carrier protein T;ubiquitin conjugating enzyme;cell proliferation-inducing gene 50 protein;HSPC150 protein similar to ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme;PIG50
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- GST
- Non
- His
- SUMO
- Strep
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is UBE2T Protein?
UBE2T is a protein that helps cells stay healthy by marking other proteins for recycling or changing how they work. It’s part of a system that keeps cells in balance and is super important for fixing DNA damage. When it doesn’t work right, it can lead to cancer and make treatments less effective. UBE2T is found in many parts of the body and helps with things like cell growth, stress responses, and programmed cell death. Because it’s so important for these processes, it could be a good target for treating cancer and other diseases.What is the Function of UBE2T Protein?
UBE2T is a key enzyme that helps cells tag proteins for recycling or changing their function. It's super important for fixing DNA damage, especially in a pathway called Fanconi anemia, where it keeps our genetic material stable. UBE2T also helps control the cell cycle, handle stress, and manage cell death. When it goes wrong, it can lead to cancer and make treatments less effective. Because it does so many important jobs, UBE2T could be a great target for treating cancer and other genetic issues.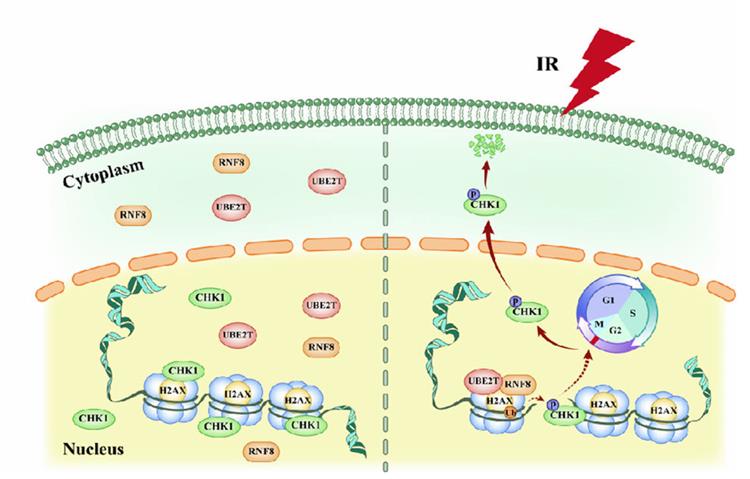
Fig1. UBE2T confers resistance to RT in HCC patients. (Jingyuan Sun, 2020)
UBE2T Related Signaling Pathway
UBE2T is a major player in the ubiquitin-proteasome system, which is crucial for DNA repair and regulating the cell cycle. It’s a key part of the Fanconi anemia pathway, helping to fix DNA damage and keep our genes stable. UBE2T also works with other important pathways, like p53 and NF-κB, which control cell death and how cells respond to stress. When UBE2T doesn’t work right, it can lead to cancer by messing up DNA repair. Because of its many important jobs, UBE2T is a big focus in cancer research and could be a good target for treating cancer and genetic diseases.UBE2T Related Diseases
UBE2T is linked to a few diseases, especially ones that involve problems with DNA repair and genetic stability. It’s a big deal in the Fanconi anemia pathway—if it doesn’t work right, it can cause a genetic disorder that leads to bone marrow failure, developmental issues, and a higher risk of cancer. UBE2T also shows up in cancer, where having too much of it can make tumors grow and resist chemotherapy, especially in breast and ovarian cancer. It might also play a role in neurodegenerative diseases because it helps with protein breakdown. All these links mean UBE2T could be a good target for treating genetic disorders and cancers.Bioapplications of UBE2T
UBE2T is a big deal in cancer research and genetic disorders. It’s a key enzyme that helps fix DNA and keeps our genes stable. In cancers like breast and ovarian, having too much UBE2T can make tumors grow and resist treatment. It’s also important in Fanconi anemia, a genetic disorder that affects bone marrow and increases cancer risk. UBE2T’s role in breaking down proteins also gives us clues about neurodegenerative diseases. All these roles make UBE2T a valuable target for developing new treatments and diagnostics.Case Study
Case Study 1: Zhu Z. et al. Cell Death Dis. 2022
Researchers discovered that UBE2T, a protein linked to cancer, fuels liver cancer by ramping up pyrimidine metabolism. When UBE2T is overactive, it increases enzymes like CAD, DHODH, and UMPS, which help cancer cells grow and spread. By using a drug that blocks DHODH, they were able to stop UBE2T from promoting cancer. The study also showed that UBE2T activates a key signaling pathway called Akt/β-catenin. This research offers fresh clues on how liver cancer develops and suggests new ways to treat it.-
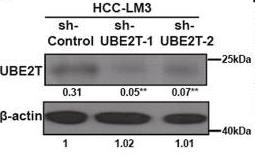 Fig1. WB for UBE2T expression in HCC-LM3 cells transduced with a control shRNA lentiviral vector or two independent shRNA lentiviral vectors targeting UBE2T.
Fig1. WB for UBE2T expression in HCC-LM3 cells transduced with a control shRNA lentiviral vector or two independent shRNA lentiviral vectors targeting UBE2T. -
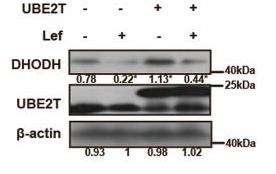 Fig2. Total cells lysate from UBE2T-overexpressing and control HCC-LM3 cells treated with or without Lef (50 μM, 48 h) were analyzed by WB.
Fig2. Total cells lysate from UBE2T-overexpressing and control HCC-LM3 cells treated with or without Lef (50 μM, 48 h) were analyzed by WB.
Case Study 2: Sun J. et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020
Radioresistance is a big problem in treating liver cancer with radiation. It happens because the cancer cells don't respond well to DNA damage, making radiation less effective. We looked at liver cancer tissues and found that a gene called UBE2T was way more active in cancer cells. In experiments, UBE2T made cancer cells more resistant to radiation by changing how DNA damage is handled. Specifically, UBE2T works with another protein to modify a key part of the DNA repair process, which then affects a checkpoint protein called CHK1. Blocking this process made the cancer cells less resistant to radiation. Our findings suggest that targeting UBE2T could improve radiation therapy for liver cancer patients.-
 Fig3. FLAG-UBE2T complexes were purified from 293 T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids and then treated with or without IR.
Fig3. FLAG-UBE2T complexes were purified from 293 T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids and then treated with or without IR. -
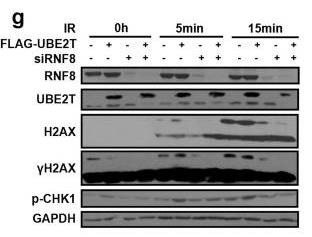 Fig4. UBE2T overexpressing cells or control cells were transfected with siRNA-RNF8 or siRNA-control.
Fig4. UBE2T overexpressing cells or control cells were transfected with siRNA-RNF8 or siRNA-control.
Involved Pathway
UBE2T involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways UBE2T participated on our site, such as Fanconi anemia pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with UBE2T were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Fanconi Anemia Pathway | FANCF,MUS81,CDK5R2,DCLRE1A,WDR48,RPA3,SLX4,FANCA,TELO2,EME2 |
-
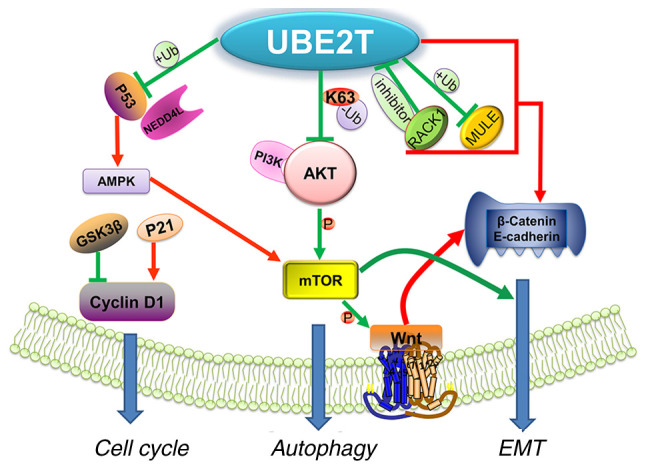 Fig1. The major proteins, their ubiquitination, and the biological processes that UBE2T regulates. (Nengqian Ma, 2023)
Fig1. The major proteins, their ubiquitination, and the biological processes that UBE2T regulates. (Nengqian Ma, 2023) -
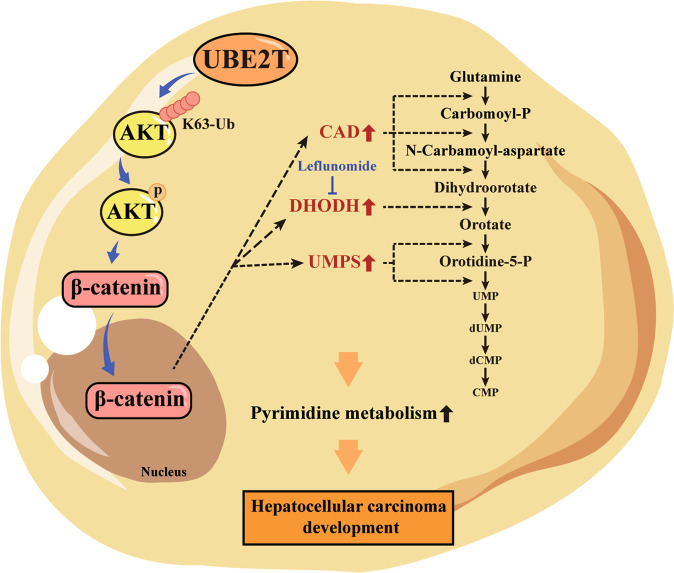 Fig2. The schematic of UBE2T-mediated regulation of pyrimidine metabolism and HCC development. (Zhenru Zhu, 2022)
Fig2. The schematic of UBE2T-mediated regulation of pyrimidine metabolism and HCC development. (Zhenru Zhu, 2022)
Protein Function
UBE2T has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,chromatin binding,ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by UBE2T itself. We selected most functions UBE2T had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with UBE2T. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity | UBE2A,UBE2H,UBE2G1,UBE2L3,UBE2Q2,UBE2D2,UBE2D2A,UBE2V2,UBE2S,UBE2E1 |
| ATP binding | EPRS,ABCC12,RAD50,ACTR3B,SUCLG1,STK17A,PC,HSC70,DGKAA,CDK10 |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | TRAF4B,MGRN1,UBE2E1,RNF5,SIAH1,CDC23,SHPRH,MARCH5,UBE2L3,MUL1B |
| chromatin binding | ATRX,TMPOA,TRP63,HMGB2B,TDRD3,WAC,ORC1L,HMG20B,TAL1,RBPJ |
| ubiquitin protein ligase activity | RNF4,TRIM3,PARK2,HECTD2,SMURF2,UBE2Z,UBE2J1,HERC5,NEURL3,UBE2W |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | UQCRC1,CUL5,FAF1,SKI,TUBB,GRIK2,HSPA5,TUBA1B,TSG101,GABARAP |
Interacting Protein
UBE2T has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with UBE2T here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of UBE2T.
ARIH2;UBE2V1;MGRN1;TRIM27;PCGF2;RNF144B;LNX2;RNF128;MARCH5;AMFR;SNURF
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Hodson, C; Purkiss, A; et al. Structure of the Human FANCL RING-Ube2T Complex Reveals Determinants of Cognate E3-E2 Selection. STRUCTURE 22:337-344(2014).
- Renaudin, X; Guervilly, JH; et al. Proteomic analysis reveals a FANCA-modulated neddylation pathway involved in CXCR5 membrane targeting and cell mobility. JOURNAL OF CELL SCIENCE 127:3546-3554(2014).


