TREM1
-
Official Full Name
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 -
Overview
TREM-1 stimulates neutrophil and monocyte-mediated inflammatory responses. It triggers release of pro- inflammatory chemokines and cytokines, as well as increased surface expression of cell activation markers. TREM-1 is an amplifier of inflammatory responses that are triggered by bacterial and fungal infections and is a crucial mediator of septic shock. It interacts with TYROBP/DAP12. TREM-1 is highly expressed in adult liver, lung and spleen than in corresponding fetal tissue. It is also expressed in the lymph node, placenta, spinal cord and heart tissues. Expression is more elevated in peripheral blood leukocytes than in the bone marrow and in normal cells than malignant cells. TREM-1 is expressed at low levels in the early development of the hematopoietic system and in the promonocytic stage and at high levels in mature monocytes. It is strongly expressed in acute inflammatory lesions caused by bacteria and fungi. Isoform 2 was detected in the lung, liver and mature monocytes. TREM-1 is up-regulated by bacteria, fungi and bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS). -
Synonyms
CD354;TREM-1;triggering receptor expressed on monocytes 1;triggering-receptor TREM1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Cattle
- Pig
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Mouse
- CHO
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- Fc
- T7
- Non
- hIgG4
- APC
- Flag
Background
What is TREM1 Protein?
TREM1 gene (triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 6 at locus 6p21. This gene encodes a receptor belonging to the Ig superfamily that is expressed on myeloid cells. This protein amplifies neutrophil and monocyte-mediated inflammatory responses triggered by bacterial and fungal infections by stimulating release of pro-inflammatory chemokines and cytokines, as well as increased surface expression of cell activation markers. The TREM1 protein is consisted of 234 amino acids and TREM1 molecular weight is approximately 26.4 kDa.
What is the Function of TREM1 Protein?
The TREM1 protein is a receptor that is mainly expressed on the surface of myeloid cells, such as neutrophils and monocytes. It plays an important role in probiotic and adaptive immunity, particularly in amplifying inflammatory responses. The TREM1 protein is activated with multiple ligands (such as PGLYRP1, HMGB1, or HSP70) to form a complex with the transmembrane adapter TYROBP/DAP12, which initiates a SYK-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation cascade and activates multiple downstream mediators including BTK, MAPK1, MAPK3, or phospholipase C-γ. This cascade promotes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and/or chemokines by neutrophils and macrophages and promotes their migration, thereby amplifying the inflammatory response triggered by bacterial and fungal infections.
TREM1 Related Signaling Pathway
When TREM1 is activated, it rapidly activates the spleen tyrosine kinase SYK, followed by downstream signaling pathways such as PI3K, PLC-Gamma, and ERK, which induce Ca2+ mobilization and rearrangement of the actin cytoskeleton. It also activates transcription factors such as Elk1, NFA, AP1, c-Fos, c-Jun, and Nf-κB, which are involved in encoding the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and cell surface molecules. In addition, TREM1-induced activation of PI3K and ERK pathways may promote mitochondrial integrity and cell survival by inactivating pro-apoptotic factors. Ligands of TREM1 include platelets, peptidoglycan recognition protein 1 (PGLYRP1), high mobility protein 1 (HMGB1), heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70), and actin. When these ligands bind to TREM1, they enhance the immune response of myeloid cells and promote the production of inflammatory mediators such as IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-18, IL-1B, and TNF-α. The signaling pathway of TREM1 interacts with other pattern recognition receptors, such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and NOD-like receptors (NLRs), and can work synergistically to amplify the immunoinflammatory response.
TREM1 Related Diseases
TREM1 has been linked to a variety of inflammatory and infectious diseases, including but not limited to sepsis caused by bacteria and fungi, acute lung injury, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, and Alzheimer's disease. TREM1 affects the progression and severity of the disease by enhancing the immune response of myeloid cells and the production of inflammatory mediators. In addition, the expression level of TREM1 also serves as a biomarker for the severity and prognosis of certain diseases, for example in sepsis and certain cancers.
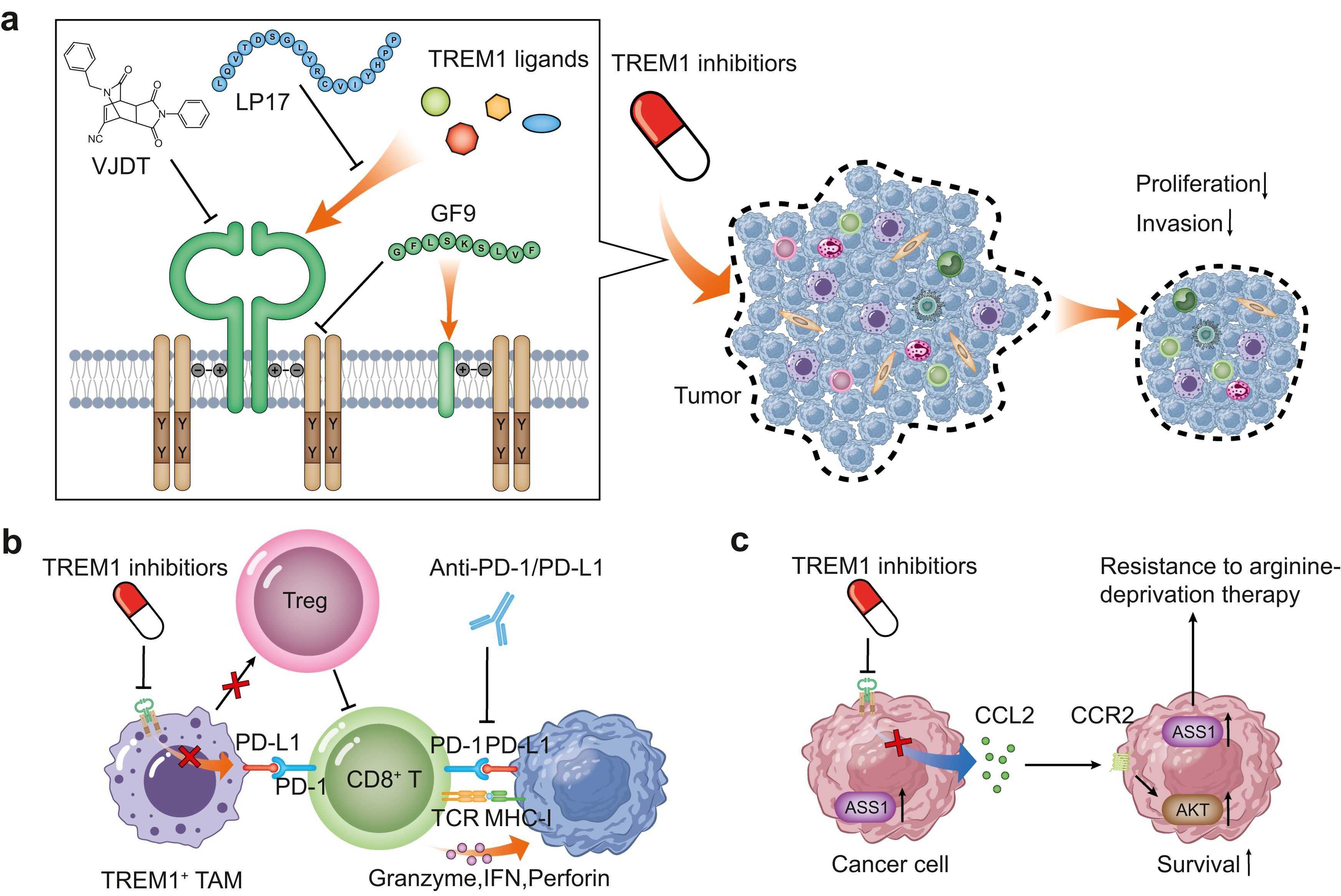
Fig1. Therapeutic effects of TREM1 inhibition in cancer. (Chenyang Li, 2024)
Bioapplications of TREM1
The applications of TREM1 have focused on its use as a biomarker to assess the severity and prognosis of certain inflammatory diseases, particularly in sepsis and acute lung injury. In addition, the soluble form of TREM1 (sTREM1) has been studied as an indicator of disease activity and response to treatment. Clinical trials are also exploring the potential of TREM1 inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory diseases, for example by inhibiting TREM1 with drugs such as nangibotide, thereby reducing the inflammatory response and improving clinical outcomes.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Lin Zhang, 2024
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 (TREM1), which belongs to the Ig-like superfamily expressed on myeloid cells, is reportedly involved in various diseases but has rarely been studied in glioma. In this study, the prognostic value and functional roles of TREM2 in glioma were analyzed. TERM1 was observed to be significantly upregulated in GBM compared to in other grade gliomas and was associated with poor prognosis. Increased TREM1 accompanied distinct mutation and amplification of driver oncogenes. Moreover, gene ontology and KEGG analyses showed that TREM1 might play a role in immunologic biological processes in glioma. TREM1 was also found to be tightly correlated with immune checkpoint molecules. xCell research revealed a link between TREM1 expression and multiple immune cell types, especially monocytes and macrophages. Single-cell analysis and immunofluorescence results showed that macrophages expressed TREM1. In vitro, inhibition of TREM1 signaling could result in a decrease in tumor-promoting effects of monocytes/TAMs.
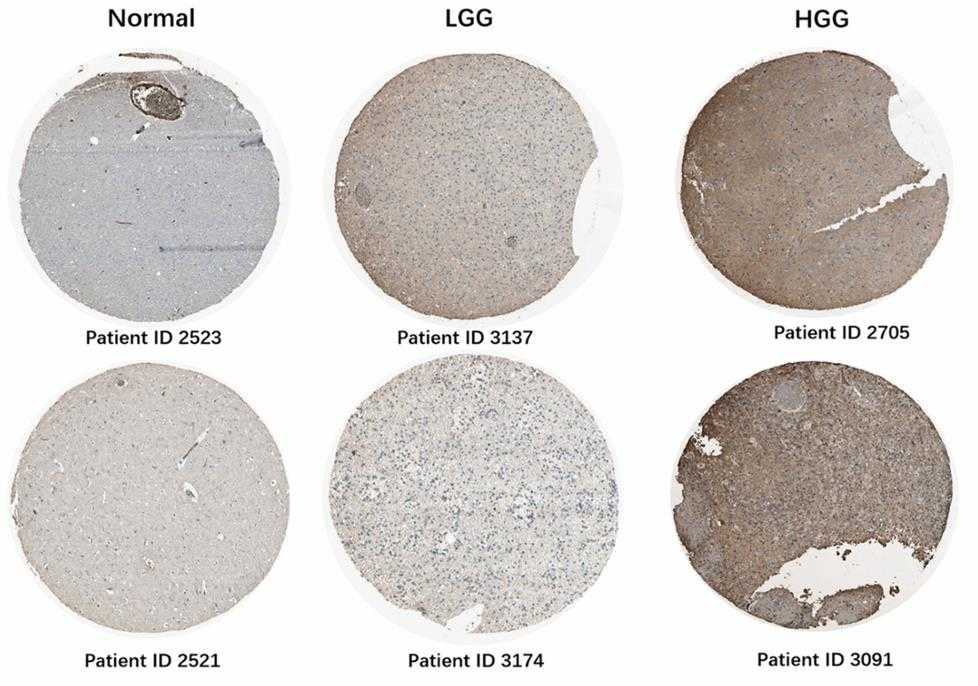
Fig1. Analysis of TREM1 protein levels in glioma tissues of different grades from the Human Protein Atlas.
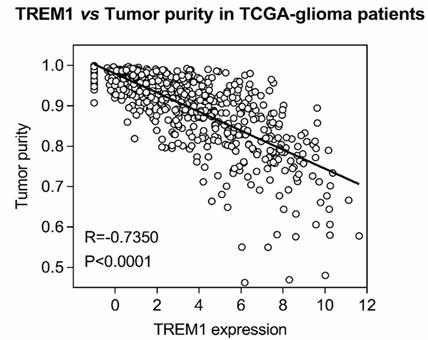
Fig2. CorrelationanalysisbetweenTREM1expression levels and tumor purity in the TCGA database.
Case Study 2: Pan Pan, 2021
Soluble TREM-1 (sTREM-1) expression was found to be upregulated in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (SA-AKI) and predicted to be a potential biomarker. However, the mechanism remains unclear. The human kidney-2 (HK-2) cell line was treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and used to examine the potential roles of TREM-1 in apoptosis and autophagy. A cell viability assay was employed to assess the number of viable cells and as a measure of the proliferative index. The concentrations of sTREM-1, interleukin (IL)-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) and IL-6 in cell-free culture supernatants were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Western blot analysis was performed to analyze apoptosis, autophagy and the relevant signaling pathways. The results suggested that TREM-1 overexpression after LPS treatment decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis. The concentrations of sTREM-1, IL-1β, TNFα and IL-6 in cell-free culture supernatants were increased in the TREM-1 overexpression group after LPS treatment. Expression of the antiapoptotic gene Bcl-2 was downregulated in the TREM-1 overexpression group, while that of the proapoptotic genes Bax, cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-9 was upregulated. Overexpression of TREM-1 downregulated expression of the autophagy genes Beclin-1, Atg-5 and LC3b and increased the gene expression of p62, which inhibits autophagy. Conversely, treatment with TREM-1-specific shRNA had the opposite effects. The nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway (P-p65/p65 and P-IκBα/IκBα) in LPS-induced HK-2 cells was regulated by TREM-1.
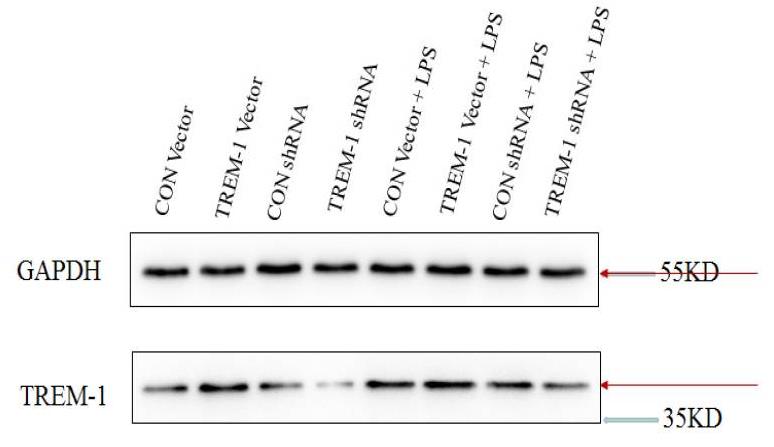
Fig3. Representative immunoblotting results indicating suppression of TREM-1 by siRNA or overexpression of TREM-1.
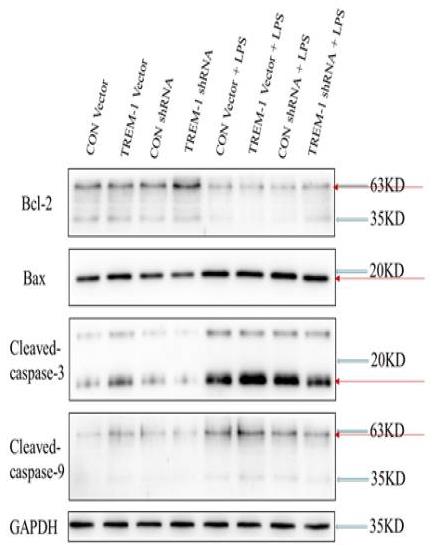
Fig4. LPS-induced HK-2 cell apoptosis was mediated by TREM-1.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TREM1-212H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TREM1-116H)
Involved Pathway
TREM1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TREM1 participated on our site, such as Adaptive Immune System,Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall,DAP12 interactions, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TREM1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hemostasis | GATA5,KCNMB1,CLU,BA1,DGKQ,PIK3R6,KIF4A,ANXA2,MAFGA,SERPINF2B |
| Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell | NCR3LG1,CD200,CD300E,CD96,SIGLEC7,CLEC2D,CLEC2H,TREML1,LAIR2,CD300LF |
| Adaptive Immune System | WWP1,DNM1,CD300LH,GAN,HLA-DQB2,WSB1,DZIP3,GRAP2A,TRIM9,FRS2A |
| Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall | SLC7A10,PPIA,NADL1.1,DOK2,SLC16A8,GRB14,GRB7,SLC3A2A,CEACAM6,SLC3A2B |
| Immune System | LRRFIP1,ACTR2B,HERC5,IFIT3,GBP6,TRIM38,RIPK3,CTSB,SPSB2,HECTD3 |
| Innate Immune System | CTSK,ABI1,NLRP4,TAX1BP1,CFHL1,BTR16,DEFB103A,DEFB4B,NOD1,RNF216 |
| DAP12 interactions | SPTBN1,KLB,PEA15A,SIRPB1,FGFR1B,SPTB,IL17RD,LAMTOR2,JAK1,PRKAR1AA |
Protein Function
TREM1 has several biochemical functions, for example, receptor activity,scaffold protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TREM1 itself. We selected most functions TREM1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TREM1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| receptor activity | CD200R4,NLGN4A,VMN1R46,STRA6,GRIA4B,LDLR,VMN1R52,NR2C2,ADIPOR1A,ATP6AP2 |
| scaffold protein binding | KCNQ1,NOS3,CHRNA7,GRID2,SRC,GRIN2A,NOS1,MDM2,NLGN4X,KRT15 |
Interacting Protein
TREM1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TREM1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TREM1.
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References




