TJP1
-
Official Full Name
tight junction protein 1 (zona occludens 1) -
Overview
Tight junctions, or zona occludens, form a continuous barrier to fluids across the epithelium and endothelium. They function in regulation of paracellular permeability and in the maintenance of cell polarity, blocking the movement of transmembrane protein -
Synonyms
TJP1;tight junction protein 1 (zona occludens 1);tight junction protein ZO-1;DKFZp686M05161;MGC133289;tight junction protein ZO 1;ZO 1;zona occludens 1;zona occludens protein 1;zonula occludens 1 protein;zonula occludens protein 1;ZO-1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Dog
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Non
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- His
- Flag
Background
What is TJP1 protein?
TJP1 gene (tight junction protein 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 15 at locus 15q13. TJP1, also known as ZO-1, is a protein that is very important in cell biology. It is a compact junction protein that is mainly found in the tight junctions of epithelial and endothelial cells, a form of intercellular junction that is essential for maintaining the selective permeability of the cell layer and forming an intercellular barrier. The TJP1 protein is consisted of 1748 amino acids and TJP1 molecular weight is approximately 195.5 kDa.
What is the function of TJP1 protein?
TJP1, also known as ZO-1, is a tight-linking protein that plays a key role in maintaining cellular connections, regulating the permeability of cellular bypases, and maintaining the polarity of epithelial and endothelial cells. TJP1 is involved in many biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, metastasis of tumor cells, and gene transcription regulation. In the liver, TJP1 regulates the liver's circadian clock by interacting with mTOR (mechanistic target of rapamycin), which influences the metabolic activity and behavior of cells. TJP1 also interacts with PER1 (period circadian regulator 1) to prevent its intracellular metastasis, and during feeding, the activation of mTOR leads to the phosphorylation of TJP1, weakening its binding to PER1, thereby promoting nuclear transfer of PER1 and regulating circadian oscillation.
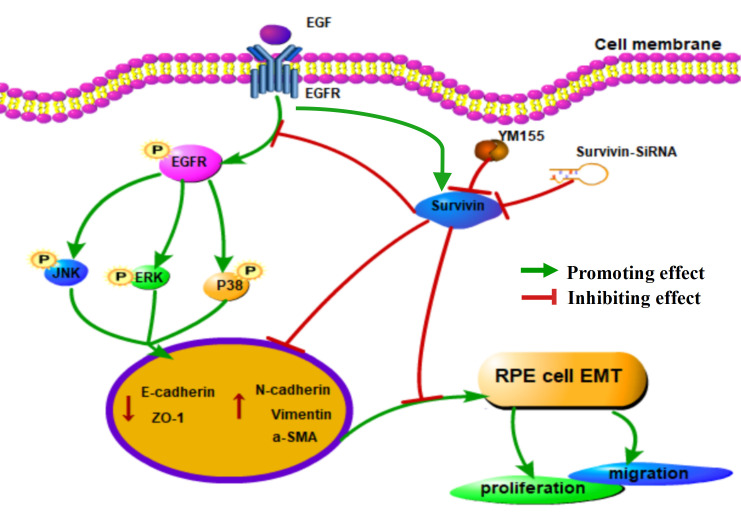
Fig1. Schematic diagram of survivin inhibition affecting EGF-induced EMT in RPE cells via the EGFR/MAPK signaling pathway. (Yusheng Zhu, 2024)
TJP1 related signaling pathway
The TJP1-associated signaling pathway is a complex network of molecular interactions involving multiple intracellular signaling pathways and molecular regulatory mechanisms. TJP1 plays a role at cell junctions, where it not only helps form a physical barrier between cells, but is also involved in regulating cell polarity and permeability. The structure and function of TJP1 are affected by various signal transduction pathways, which may involve MAPK/ERK pathway, PI3K/AKT pathway, Rho GTPase signaling, Wnt/β-catenin pathway, etc. These signaling pathways can respond to different stimuli, such as growth factors, cellular interactions, stress factors, etc., which in turn affect the expression, localization, and function of TJP1. In addition, TJP1 also interacts with a variety of intracellular proteins, which are involved in cytoskeleton organization, cell division, gene transcription regulation and other processes.
TJP1 related diseases
TJP1 is a tight-linking protein that plays a role in a variety of diseases. TJP1 is associated with tight intercellular connectivity, which affects intercellular communication and the permeability of cell bypasses. In cancer, TJP1 expression levels are associated with tumor aggressiveness and prognosis. For example, in leiomyosarcoma, increased expression of TJP1 is associated with tumor cell aggregation and sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs such as doxorubicin. In addition, the expression of TJP1 in lung cancer is also associated with tumor aggressiveness, migration, and proliferation, suggesting that it may serve as a therapeutic target. In bladder cancer, TJP1 promotes vascular remodeling by regulating USP2/TWIST1. TJP1 is also associated with arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy, in which mutations in the TJP1 gene can lead to the development of the disease.
Bioapplications of TJP1
TJP1 protein has a wide range of applications in medicine and biology. First of all, TJP1 is an important part of the tight junction, and its expression and function changes are closely related to the occurrence and development of many diseases, including tumor, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and so on. Therefore, TJP1 is often used as a diagnostic marker for these diseases, helping doctors with early diagnosis and disease monitoring. Second, TJP1 also plays a key role in embryonic development and cell differentiation, so it is also an important indicator in developmental biology research. In addition, TJP1 has been used to study cellular communication and signaling mechanisms, as well as the screening and development of novel drugs.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Matthew A Odenwald, 2017
TJP1 (ZO-1) is essential for the formation and expansion of epithelial cells within tubular organs. Epithelial cells lacking TJP1 form cysts with multiple chambers and defects in the early polarization stage. It was found that the actin-binding domain and U5-GuK domain of TJP1 are essential for single cavity development. Although mutations in the actin-binding region can be overcome by strong polarization signals from the extracellular matrix, mutations in the U5-GuK domain cannot. The U5-GuK domain of TJP1 interacts with the OCEL domain of occludin, which is equally necessary for single-cavity formation and proper positioning of mitotic spindles.
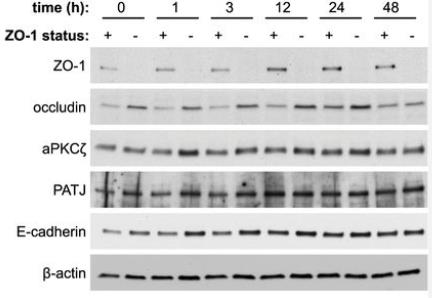
Fig1. Immunoblotting analysis at the indicated times after Ca2+ repletion showing ZO-1, occludin, aPKCζ, PATJ, E-cadherin and β-actin.
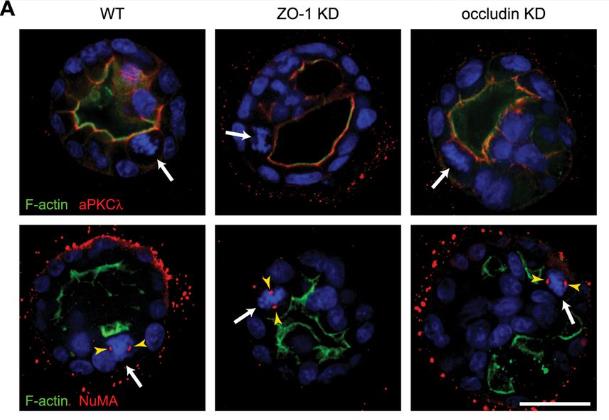
Fig2. WT, ZO-1 KD and occludin KD cysts were grown in Matrigel for 4–6 days and stained.
Case Study 2: Andrea K Watters, 2015
Studies have shown that neural stem cells (NSCs) often exist in clusters near brain microvessels, and this structure is also seen in neurospheres formed in in vitro NSC culture. The formation of neurospheres is essential for the maintenance of stem cell characteristics and proliferative state, but the mechanism of their formation is not well understood. Our study found that human NSCs express multiple tight junction proteins (TJPs), including ZO-1, occludin, claudin-1, -3, -5, and -12. Their relative mRNA expression was measured by quantitative PCR, and protein expression was confirmed by flow cytometry and immunofluorescence microscopy. The results showed that the expression of TJPs was down-regulated when neural differentiation was induced, suggesting that the regulation of TJPs may be related to neural differentiation procedures. Importantly, when the helper TJP ZO-1 was knocked down, levels of key stem cell markers in undifferentiated NSCs were reduced.
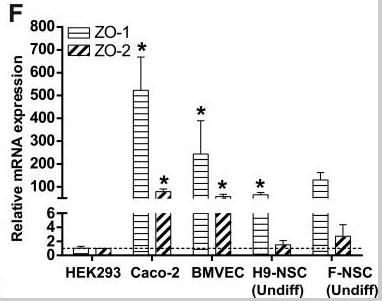
Fig3. Relative mRNA expression of ZO-1 and ZO-2 in HEK293 cells, Caco-2 cells, BVMECs, and NSCs.
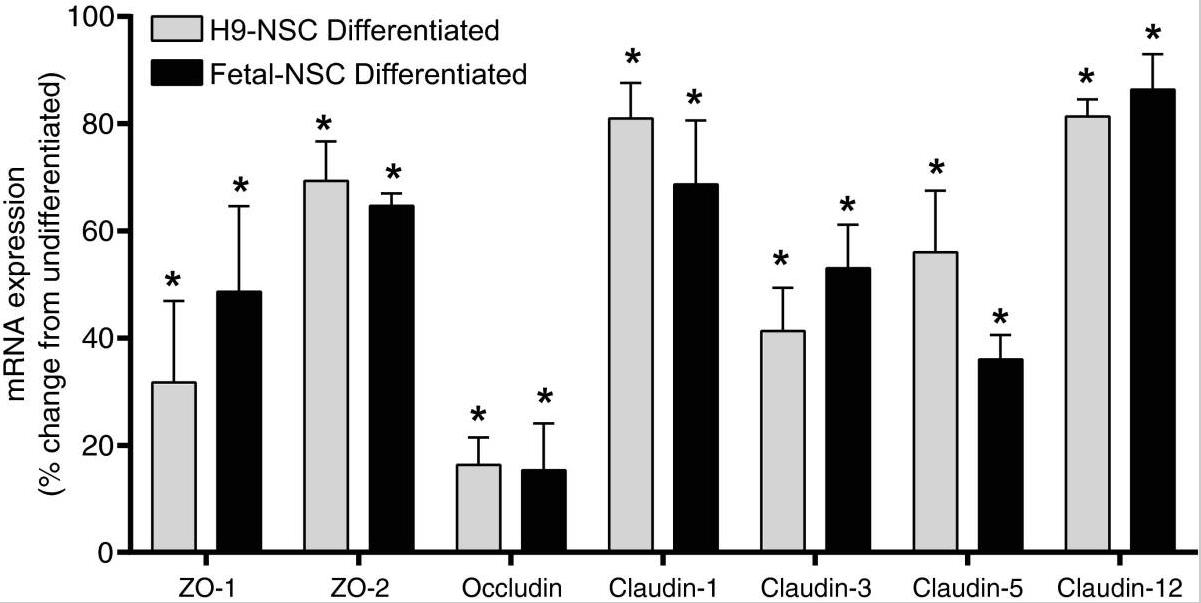
Fig4. Decreased expression of TJPs in differentiated H9-NSCs and F-NSC.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TJP1-464H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TJP1-6723H)
Involved Pathway
TJP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TJP1 participated on our site, such as Adherens junction,Tight junction,Gap junction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TJP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Vibrio cholerae infection | ATP6V1A,ATP6V0E1,PRKACG,ATP6AP1,KDELR1,GNAS,ATP6V0C,ATP6V1E2,ATP6V0A1,ATP6V0B |
| Gap junction | GRM1,TUBA8L2,PRKACAA,GNA11,HRASA,PRKACBA,HTR2B,ADRB3A,RAF1A,TUBB2B |
| Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection | CXCL1,ATP6V0A2,CCL5,ATP6V1C1,ATP6V1F,ATP6V0A4,ATP6V0C,ATP6V0E1,ATP6V1E1,MAPK12 |
| Adherens junction | CTNNA3,WASLA,PVRL3B,SSX2IPA,INSR,SSX2IP,PVRL1,RAC3B,ACTB2,TGFBR1 |
| Tight junction | CLDN14,MYH1A,SYMPK,YBX3,MYH6,CLDN10,CLDN7,PPP2CA,SHROOM3,PARD6GA |
| Salmonella infection | LBP,ARPC5LA,WASLB,NFKB1,DYNC1LI1,PYCARD,CXCL1,CCL4L1,MAPK14A,MAPK11 |
Protein Function
TJP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, calmodulin binding,protein binding,protein domain specific binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TJP1 itself. We selected most functions TJP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TJP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| calmodulin binding | MYH13,OBSCN,PLA2G6,TTN,KCNH1,ORAI1,KCNN1B,CAMK2B1,KCNQ3,RGS16 |
| protein domain specific binding | OSBP,IKBKG,NFE2L2,IL1B,Ar,TACC2,TH,TFDP1,PLXND1,UNC13A |
| protein binding | SDHA,ZNF165,HIST1H4F,IL-8,RND2,ARHGAP33,CYB5R2,DEDD2,SGIP1,PLUNC |
Interacting Protein
TJP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TJP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TJP1.
GJA1;ACTN4;Gjc1;Wwtr1;GJD3;VMP1;Gja1
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



