SOCS3
-
Official Full Name
suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the STAT-induced STAT inhibitor (SSI), also known as suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS), family. SSI family members are cytokine-inducible negative regulators of cytokine signaling. The expression of this gene is induced by various cytokines, including IL6, IL10, and interferon (IFN)-gamma. The protein encoded by this gene can bind to JAK2 kinase, and inhibit the activity of JAK2 kinase. Studies of the mouse counterpart of this gene suggested the roles of this gene in the negative regulation of fetal liver hematopoiesis, and placental development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
SOCS3;suppressor of cytokine signaling 3;CIS3;SSI3;ATOD4;Cish3;SSI-3;SOCS-3;STAT-induced STAT inhibitor 3;cytokine-inducible SH2 protein 3
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- His
- Trx
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
Background
What is SOCS3 protein?
SOCS3 gene (suppressor of cytokine signaling 3) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q25. This gene encodes a member of the STAT-induced STAT inhibitor (SSI), also known as suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS), family. SSI family members are cytokine-inducible negative regulators of cytokine signaling. The expression of this gene is induced by various cytokines, including IL6, IL10, and interferon (IFN)-gamma. The protein encoded by this gene can bind to JAK2 kinase, and inhibit the activity of JAK2 kinase. Studies of the mouse counterpart of this gene suggested the roles of this gene in the negative regulation of fetal liver hematopoiesis, and placental development. The SOCS3 protein is consisted of 225 amino acids and SOCS3 molecular weight is approximately 24.8 kDa.
What is the function of SOCS3 protein?
SOCS3 is able to interact with a variety of cytokine signaling pathways, particularly through the JAK/STAT pathway, by directly binding to JAK kinase and cytokine receptors, thereby inhibiting STAT3 activation. SOCS3 plays a role in controlling the proliferation, differentiation and function of immune cells, and plays an important role in regulating inflammatory response and host immune response to infection. SOCS3 can affect leptin signaling and regulate the feedback inhibition of leptin signaling by interacting with the binding site of leptin receptors. SOCS3 plays a role in regulating fetal liver hematopoietic and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) signaling.
SOCS3 Related Signaling Pathway
SOCS3 is able to interact with Janus kinase (JAK) and signal transducers and transcriptional activators (STAT), in particular by recruiting E3 ubiquitin ligases through its SOCS box domain, promoting ubiquitination of JAKs or STATs and subsequent proteasomal degradation, thereby inhibiting the activation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. SOCS3 inhibits cytokine signaling through interactions with cytokine receptors, such as binding to the IL-6 receptor subunit gp130. SOCS3 is able to inhibit insulin signaling by affecting insulin receptor substrate (IRS) proteins through ubiquitin-mediated degradation. SOCS3 controls inflammation by regulating the signaling of inflammatory cytokines, such as inhibiting IL-6 and IL-11.
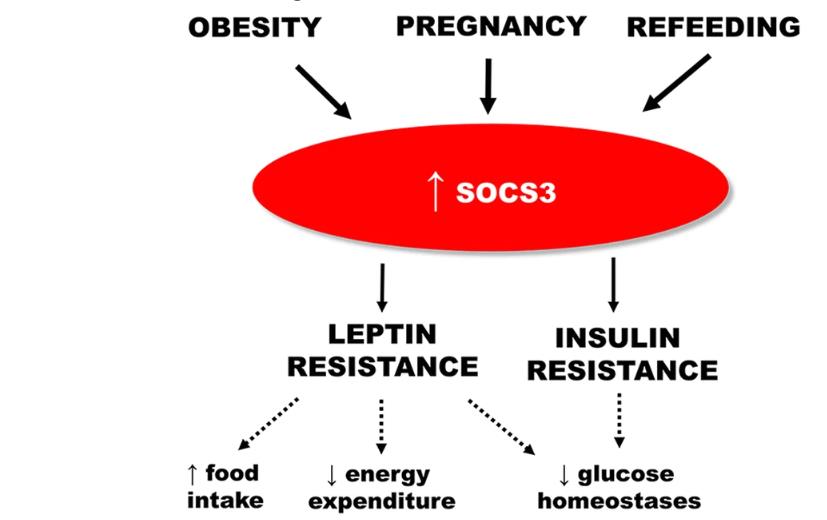
Fig1. Scheme showing the involvement of SOCS3 in leptin and insulin resistance and its main effects on energetic metabolism. (João A B Pedroso, 2019)
SOCS3 Related Diseases
Abnormal expression or dysfunction of SOCS3 protein has been associated with a variety of diseases, especially in abnormal immune regulation and tumor development. In the field of cancer, SOCS3 expression levels may vary in some cases depending on tumor type, either as a tumor suppressor or as a factor that promotes tumor development. For example, low expression of SOCS3 may be associated with increased ability of tumor cells to proliferate, survive, and metastasize, while its high expression may help inhibit tumor growth in some cases. In addition, SOCS3 also plays a role in inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain autoimmune diseases, and is involved in the pathogenesis of the disease by affecting cytokine signaling. In infectious diseases, SOCS3 can be involved in regulating the host's immune response to pathogens, influencing the outcome of infection.
Bioapplications of SOCS3
As an important regulator of tumor development, the regulatory mechanism of SOCS3 could serve as a novel strategy for the development of targeted therapies, especially in cancer types where SOCS3 expression is strongly associated with tumor growth and patient prognosis. The regulatory properties of SOCS3 offer the possibility of developing novel drugs that mimic the function of SOCS3 to inhibit excessive cytokine signaling, or to treat related diseases by enhancing the action of SOCS3. The expression level of SOCS3 can be used as a biomarker of disease status, especially in cancer and other immune-related diseases, to aid in disease diagnosis, prognosis assessment and treatment response monitoring.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yufeng Liu, 2024
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a life-threatening renal disease and needs urgent therapies. Wogonin is renoprotective in DN. This study aimed to explore the mechanism of how wogonin regulated high glucose (HG)-induced renal cell injury. Diabetic mice (db/db), control db/m mice, and normal glucose (NG)- or HG-treated human tubule epithelial cells (HK-2) were used to evaluate the levels of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3), Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), inflammation and fibrosis. Lentivirus was used to regulate SOCS3 and TLR4 expressions. The results showed HG downregulated SOCS3 but upregulated TLR4 and JAK/STAT, fibrosis, and inflammasome-related proteins. Meanwhile, wogonin upregulated SOCS3 and downregulated TLR4 under HG conditions. Wogonin-induced SOCS3 overexpression directly decreased TLR4 levels and attenuated JAK/STAT signaling pathway-related inflammation and fibrosis, but SOCS3 knockdown significantly antagonized the protective effects of wogonin.
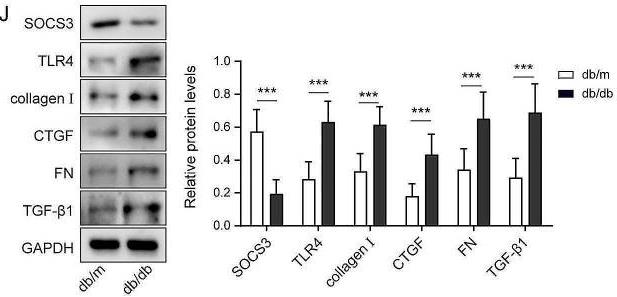
Fig1. Western blot measured the protein levels of SOCS3 and other proteins.
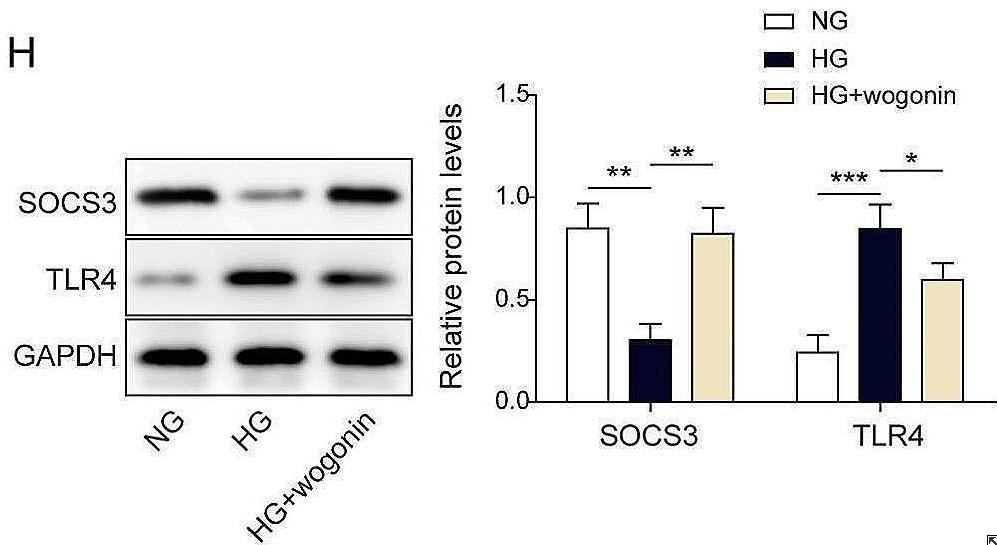
Fig2. The protein levels of SOCS3 and TLR4 were detected by western blot.
Case Study 2: Tianxi Wang, 2024
Pathological ocular angiogenesis has long been associated with myeloid cell activation. However, the precise cellular and molecular mechanisms governing the intricate crosstalk between the immune system and vascular changes during ocular neovascularization formation remain elusive. In this study, researchers demonstrated that the absence of the suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) in myeloid cells led to a substantial accumulation of microglia and macrophage subsets during the neovascularization process. The single-cell RNA sequencing data analysis revealed a remarkable increase in the expression of the secreted phosphoprotein 1 (Spp1) gene within these microglia and macrophages, identifying subsets of Spp1-expressing microglia and macrophages during neovascularization formation in angiogenesis mouse models. Notably, the number of Spp1-expressing microglia and macrophages exhibited further elevation during neovascularization in mice lacking myeloid SOCS3. Importantly, pharmaceutical activation of SOCS3 or blocking of SPP1 resulted in a significant reduction in pathological neovascularization.
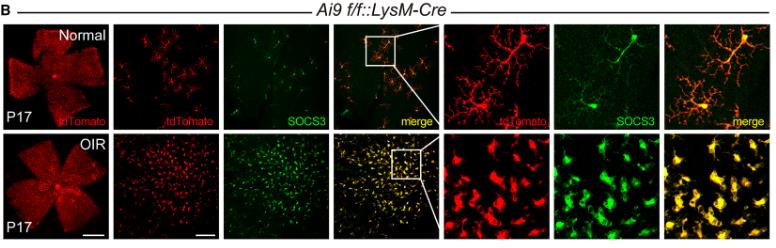
Fig3. Representative flat mounts of SOCS3 (green)-stained normal and OIR retinas from myeloid-specific LysM-Cre driven-Ai9 tdTomato (red) reporter mice.
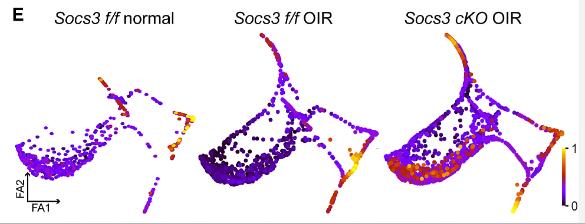
Fig4. Pseudotime analysis of significantly enriched clusters in the three groups, with latent time calculated using scVelo's latent time function.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SOCS3-1315H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SOCS3-6682H)
Involved Pathway
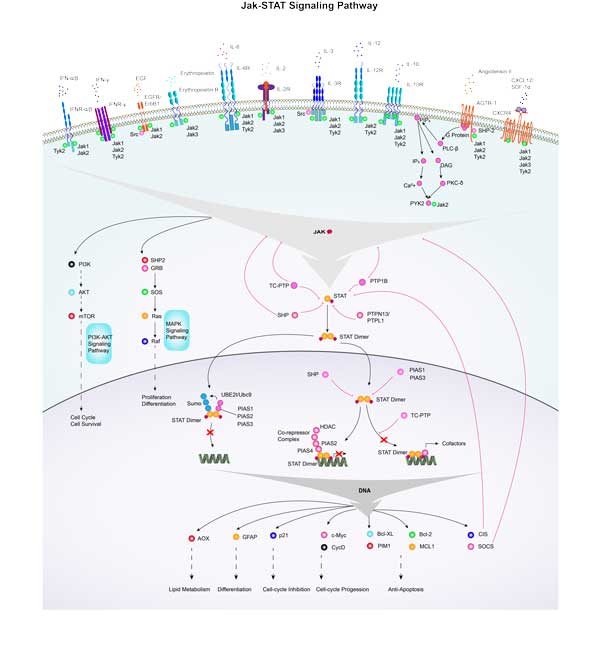
SOCS3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SOCS3 participated on our site, such as Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis,Osteoclast differentiation,Jak-STAT signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SOCS3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis C | PIAS1,RAF1,PPP2R2A,PPP2CA,MAPK9,PIK3CD,PIK3R2,IFNA7,IL-8,IFNAR2 |
| TNF signaling pathway | BCL3,TRADD,TAB2,MMP14,CASP8,Ccl12,IL6,LTA,IL1B,TRAF2 |
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | CUL4A,SIAH1,PIAS4A,RHOBTB1,UBE2N,PRP19,UBE2G2,CUL4B,FBXW11,UBE2H |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | SDHB,NDUFA5,IKBKB,IRS1,PIK3CD,INS,SDHC,PIK3R2,ADIPOR1,UQCR10 |
| Herpes simplex infection | IRF9,IFNA3,Ccl12,HCFC1,CUL1B,HLA-DPB1,IL12A,TTC6,ARNTL1A,UBE2R2 |
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | G6PC,PPARAB,CD36,ACSL1A,CAMKK1A,NFKBIE,PRKAB1,NFKBIAA,AKT2,SOCS3B |
| Type II diabetes mellitus | PRKCZ,PKM2,INS-IGF2,MAPK8,CACNA1G,HK3,PIK3CD,IRS4,HKDC1,ADIPOQ |
| Insulin signaling pathway | PIK3CG,PHKA1,PIK3R3A,PRKAG3,RPS6KB1B,CALM3B,PRKAA2,IRS1,HK1,PHKA2 |
| Influenza A | FURIN,IL12B,MX1,IL6,BLB2,LOC780933,PIK3CG,IRF7,BLB1,XPO1 |
Protein Function
SOCS3 has several biochemical functions, for example, protein binding,protein kinase inhibitor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SOCS3 itself. We selected most functions SOCS3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SOCS3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | MR1,CTSH,MAPKBP1,MRPL23,CHCHD2,RMND1,STX10,C6orf226,CHGB,CRY1 |
| protein kinase inhibitor activity | SOCS6B,CISHB,TESC,SOCS1B,SOCS3A,JIP1,CHP,NCK1,GMFB,GMFG |
Interacting Protein
SOCS3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SOCS3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SOCS3.
PTK2;YES1;KIAA1958;MAP1S;TRDN;SH2D2A;RASA1
SOCS3 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Kim, G; Ouzounova, M; et al. SOCS3-mediated regulation of inflammatory cytokines in PTEN and p53 inactivated triple negative breast cancer model. ONCOGENE 34:671-680(2015).
- Cianciulli, A; Dragone, T; et al. IL-10 plays a pivotal role in anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol in activated microglia cells. INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY 24:369-376(2015).